
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
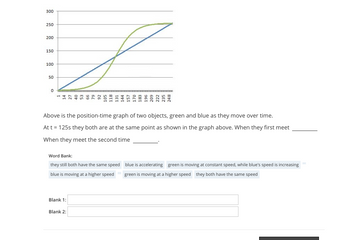
Transcribed Image Text:300
250
200
150
S
100
50
0
Above is the
position-time graph of two objects, green and blue as they move over time.
At t = 125s they both are at the same point as shown in the graph above. When they first meet
When they meet the second time
Word Bank:
blue is accelerating green is moving at constant speed, while blue's speed is increasing
they still both have the same speed
blue is moving at a higher speed
green is moving at a higher speed they both have the same speed
Blank 1:
Blank 2:
92
105
118
131
144
157
170
183
196
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Car X Car Y At time t = 0, car X traveling with speed vo passes car Y which is just starting to move. Both cars then travel on two parallel lanes of the same straight road. The graphs of speed v versus time t for both cars are shown above. Which of the following is true at time t = 20 seconds? a. Car X is accelerating faster than car Y O b. Car Y is in front of car X O c. Car Y is passing car X O d. Car Y is behind car Xarrow_forwardI can't figure this one out!arrow_forwardDuring which of the following time intervals is the object moving in the negative direction? A. 0-4 seconds B. 4 to 7 seconds C. 7 to 10 seconds D. All of the intervals listed above E. None of the intervals listedarrow_forward
- On the Apollo 14 mission to the moon, astronaut Buzz Aldrin hit a golf ball with a golf club improvised from a tool. The free-fall acceleration on the moon is 1/6 of its value on earth. Suppose he hit the ball with a speed of 29 m/sm/s at an angle 22 ∘∘ above the horizontal. a. how long was the ball in flight in seconds? b. how far did it travel in meters? c. If there was no air resistance, how much farther would it travel in meters on the moon than on earth?arrow_forward2.) A buggy car starts at 10 m and travels in the +x direction with a constant velocity of 1.5 m/s for 4 s. The car immediately stops for 3 s and turns around and travels in the opposite direction with a constant velocity of 2 m/s for 10 s. a. Draw a position -vs- time graph and velocity -vs- time graph.arrow_forward1.) Let sA = 15t^2 + 10t + 20 and sB= 5t^2 + 40t, where t ≥ 0, be the position functions of cars A and B, respectively, that are moving along parallel straight lanes of a highway (here, t is in minutes and s in feet). a.) At what instant of time do they have the same velocity? b.) Which car is ahead when the two cars have the same velocity? Please show your complete solution thanks.arrow_forward
- A ball is dropped from rest from the top of a building. Two motion detectors which are positioned outside of two different windows, one above the other, record the velocities of -15.5 m/s and -17.2 m/s as the ball goes past them. (no air resistance) a. How far apart are the motion sensors mounted? b. How far from the top motion sensor is the top of the building where the ball was released? c. If the second motion sensor can also measure the time it takes for the ball to hit the ground after passing it as 3.50 seconds, how tall is the building?arrow_forwardA car traveling at a speed of 25 m/s suddenly sees the red light 40 m ahead of him. The driver takes 0.75 s to react and slows the car down at a constant rate of 10 m/s2. 1. How long does it take the car to come to a complete stop from the moment the break was applied? 2. Find the total time the car takes to come to a complete stop from the moment the driver first saw the red light. 3. Determine whether the car ran the red light.arrow_forwardA car gains speed at a constant rate as it moves to the right. It covers the distance between two points 60.0 meters apart in 6.00 seconds. Its speed as it passes the second point is 15.0 m/s. a) What was the velocity of the car at the first point? b) What was the acceleration of the car? c) Assuming the car began from rest and continued with this same acceleration, at what distance before the first point did the car begin?arrow_forward
- The position of an object moving in one dimension is given by the equation: x = 18t - 2t + 4 %3D 1. Are there any points in time when the object will be not in motion? (i.e. when its velocity is zero) 2. What are the position, speed and acceleration of this object at t=5s.arrow_forward16. Below is a graph showing the motion of a car. Which of the following is true? velocity/m s 12 A B C D The acceleration is constant all the time. The velocity is constant all the time. The car is moving all the time. The car moves after 7 seconds. B acceleration 17. An object is thrown vertically upwards into the air. Taking velocity upwards as positive, which of the following graphs best represents the variation of acceleration with time? A acceleration D 0 C acceleration 0 acceleration 0 time time time/s time time ( 18. The graph below shows the speed of a cyclist who is moving along a hilly road without peddling. He is depending on moving down the slopes to gather the speed. ) ) All About Physics: Multiple-Choice Questions Workout 'O' Level speed A C At which point was the bottom of the first hill reached? velocity/km h-¹ 19. A rocket is launched vertically and the velocity-time graph is obtained as shown below, The maximum height reached by the rocket is 2000----- 4000 km 8000…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON