
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
If the 2-in.-diameter shaft is made from cast iron having tensile and compressive ultimate stress of 1sult2t = 50 ksi and 1sult2c = 75 ksi, respectively, determine if the shaft fails according to Mohr’s failure criterion.
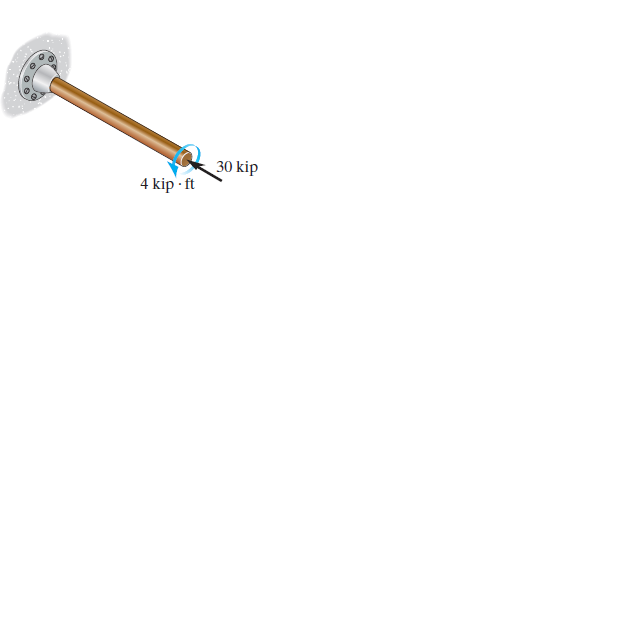
Transcribed Image Text:30 kip
4 kip' · ft
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Explain What factors determine the requirements for traffic control and safety hardware management data collection survey frequencies?arrow_forwardA small aluminum alloy [E = 71 GPa] tee shape is used as a simply supported beam as shown. For this beam, a = 120 mm. The cross- sectional dimensions of the tee shape are b = 17 mm, d = 26 mm, andt = 6 mm. After loads are applied to the beam at B, C, and D, a compressive normal strain of 460 µɛ is measured from a strain gage located at c = 10 mm below the topmost edge of the tee stem at section 1-1. What is the applied load P? P P ЗР Strain gage C |D H Answer: P = Narrow_forwardQuestion 4 : Please answer part A and B!arrow_forward
- The point loads are placed at the fixed positions shown in the figure and they are live loads. A k a b a b dn = 1₂ Icr= M B 7 Ast Stress profile (concrete) Cross section before cracking Aso Cross section Asc Ast N.A. Q2) Now, the live load increases gradually and the moment at the critical section just exceeds the cracking moment (Mcr), but the compressive section of the concrete is still under the linear elastic region. Please be reminded that in the flexural design, the crack of the concrete section starts where the tensile stress reaches the tensile strength. It is assumed that the cracks then propagate rapidly up to the entire tension section (up to the neutral axis) and this cracked concrete section cannot resist the tension. It should be noted that in reality, concrete sections between the primary cracks can still resist some tensile stresses as shown in the figure, which should be considered in the displacement design. However, in flexure design, we design the critical section…arrow_forwardThe aluminum bar ACDB is rigidly connected to a steel tube in CD. The data is presented in the table. If the load P is equal to 125 kN, determine: The stress of aluminum in segment AC. Answ: 63.66 MPa The stress of aluminum in segment CD. Answ: 13.93 MPa The stress in steel in segment CD. Answ: 39.79 MPa The total deformation of the bar. Answ: 0.29273 mmarrow_forwardConsider the compound system consisting of three sections with cross-sectional areas 3A, 2A, and A and loaded as shown. Which of the following gives the maximum average normal stress in the system shown? 6P 4P A5.5 P/A B.4.5 P/A 3A 2A A 3P C.4 P/A D.3 P/A 4P 6P Which of the following is the highest value of stress within the strain hardening region of a typical elasto-plastic material subjected to tensile test? A. Elastic Limit B.Yield Stress C.Ultimate Stress D.Proportional Limit What is the lateral strain of a uniaxially loaded member if its longitudinal strain is 0.02 and its Poisson's ratio is equal to 0.3? A.+0.006 B.-0.006 C.+0.667 D.-0.667 Which of the following is the highest value of stress within the elastic region of a typical elasto-plastic material subjected to tensile test? A.Yield Stress B.Elastic Limit C.Ultimate Stress D.Proportional Limitarrow_forward
- In the following beam system, the beam is subjected to uniform distributed load W = 25 lb /in. Assume a = 90-inch, b = 130-inch, C = 40 inch and d = 50 inch a) Determine the resultant force produced at the pin C for the distributed load, W b) What is the factor of safety that exists for pin C with respect to its fracture strength? assume that the pin at C fractures when the resultant force reaches a value 35000 lb.arrow_forwardA 42 meter solid shaft is under torsional loading 53 Nm. If in this application, the allowable shear stress for the material is 369 MPa. Calculate the required minimum diameter of the shaft: _____ mm ( input the value directly from your calculation before rounding it up to an engineering accepted diameter) Pay attention to units, and calculate your answer to one decimal place.arrow_forwardN = 7arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning