
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
For the beam below, use the Force Method and FE deflection tables to determine all the reaction forces of the beam. Select the moment at A as the redundant. Draw the shear, moment and approximate deflected shape of the beam. Label the values of shear and moment at the dashed lines.
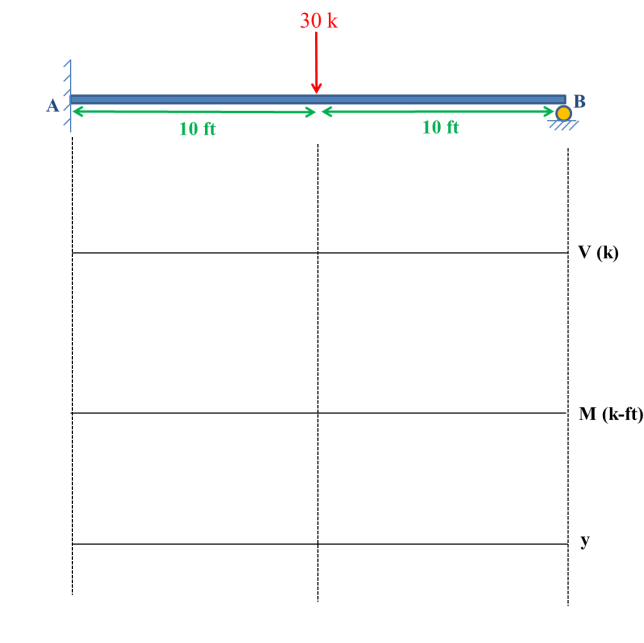
Transcribed Image Text:30 k
10 ft
10 ft
V (k)
M (k-ft)
У
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 10 steps with 10 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For the given statically indeterminate beam find: Deflection diagram Moment equation of the beam Using integration, find the equations for slope and deflection Find the support reactions for the beamarrow_forward2. Determine the equations of the elastic curve for the beam using the x coordinate. (Please use thesecond-order or fourth-order integration method)(a) Specify the slope at A and maximum deflection. EI is constant.(b) Determine the deflection at the center of the beam and the slope at B. EI is constant.arrow_forwardSOLVE STEP BY STEP, DONT USE AIarrow_forward
- Determine/derive the Shear and Moment Equations of each segment of the beam (kindly include the FBD). Compute the Reactions and Draw the detailed Shear and Moment Diagram indicating values.arrow_forwardFor the beam and loading shown use the double-integration method the equation of the elastic curve for segment AB of the beam, (b) the deflection midway between A and B, and (c) the slope at B. Assume that El is constant for the beam. to determine (a) L.arrow_forwardStart with the shear diagram. To use a segment of the left end of the beam to develop the expression for the shear, the vertical reaction at A must be known. Calculate the vertical reaction at A. Let a positive force act up. Write an expression for the internal shear for an arbitrary point between A and B. Write an expression for the internal shear for an arbitrary point between B and C. Draw the shear diagram for the beam. Write an expression for the bending moment at an arbitrary point between A and B. Use the standard sign convention for the internal moment for a beam. Write an expression for the bending moment at an arbitrary point between B and C. Draw the moment diagram for the beam.arrow_forward
- For the beam below, determine the displacement at x = 2L/3 from the fixed support using the deflection tables provided in the FE equation packet. Take EI as a constant. Indicate the direction of the displacement also.arrow_forwardA simply supported beam carries a moment applied to one end as shown. El is constant. a) Calculate the support reaction forces for the beam b) Write out the M(x) equation using discontinuity functions. c) Determine the slope and deflection equations by integrating the M(x) equation as needed and using two B.C. to solve for the integration constants, C1 and C2. d) Calculate the deflection at the mid-span of the beam. e) Check: Calculate the deflection at point B (right support). A 12Aarrow_forwardUsing the virtual work method determine slope of the beam at "A". Beam is subjected to a uniformly Distributed Load “W" and a concentrated moment "WL^2" at “A" (Express the results in terms of W, L, and EI) w ikIft=constant)arrow_forward
- Solve the problem by the moment-area method. The beam has constant flexural rigidity EI. A simple beam AB supports two concentrated loads P at the positions shown in the figure. B C 4. 4 A support C at the midpoint of the beam is positioned at distance d below the beam before the loads are applied. Assuming that d = 12 mm, L = 5.4 m, E = 200 GPa, and I = 193 x 10° mm, calculate the magnitude of the loads P (in kN) so that the beam just touches the support at C. 163.87 x kNarrow_forwardPROBLEM # 3: Use the conjugate beam method and determine the slope at B and the displacement at C of the beam. "EI" is constant. 2 A В a a a aarrow_forwardProblem 2: For the beam given below: (a) Calculate all support reactions. (b) Draw the shear diagram. Show all important values of shear. Show the sign convention within each region. (c) Draw the moment diagram. Show all important values of moment. Show the sign conventions within each region (concavity: smiley face, sad face, etc.) (d) Sketch the deflected shape. Show supports in your sketch. For your solution, let w = 2 kips/ft and L = 20 ft. A L 22 B L W Carrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning