
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
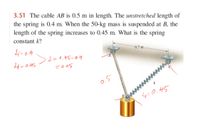
Transcribed Image Text:3.51 The cable AB is 0.5 m in length. The unstretched length of
the spring is 0.4 m. When the 50-kg mass is suspended at B, the
length of the spring increases to 0.45 m. What is the spring
constant k?
4=0.4
- 0.7 m
4=0.45
S = 0.45-04
-0.05
O.5
そ
タ=0.45
B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Statics an 2.18 A 200# stone is being lifted off the ground by a lev- ering bar. Determine the push P required to keep the stone in the position shown. Varignon's Theorem The French mathematician Pierre Varignon developed a very important theorem of statics. It states that the mo- ment of a force about a point (axis) is equal to the algebraic 1W=200* 3011 36" 47arrow_forwardA 4.2‑kg brown hare walks on a horizontal beam (the beam's mass m = 2.8 kg and length a = 2.4 m). The beam is suspended with two ropes attached to the ends of the beam. What should be the distance between the hare and the left end of the beam so that the tension in the left rope is three times as big as the tension in the right rope? 1. The distance from the left end, b = If the hare is at the distance found in the previous question, calculate the tension in each rope. 2. The tension in the left rope, T1 = 3. The tension in the right rope, T2 = ------------------------------------------------------------------ A bike wheel has a radius of R = 0.62 m and a mass of m = 2.6 kg spins at 270 rpm. What is the angular momentum of the wheel? Assume that the wheel has a shape of a ring. The angular momentum of the wheel, L ? A typical bowling ball might have a mass of 7 kg and a radius of 12 cm. How fast the ball should spin to have the same angular momentum as the wheel from the…arrow_forwardTwo massless springs with different spring constants k₁= 100 N/m and k₂ = 10 N/m are aligned vertically, as shown in figure 1. A block of mass m = 0.12 kg is placed on the bottom spring. The distance between the top of the box and the top spring is h = 0.35 m. You compress the bottom spring Ay = 0.3 m from its equilibrium position (figure 2). When you let go, the box flies up (figure 3) and compresses the top spring (figure 4). Treat the upward direction (↑) as positive, such that the compression of the top spring is a positive displacement. What is the maximum compression of the top spring due to the flying box? Give your answer in units of meters to 2 decimal places. Use g = 9.8 m/s^2. Assume air resistance is negligible. T h EW Ay (2) www Backup link to image (opens in new tab). fumand M риту 4 ² ↑ M ? wwwarrow_forward
- 7. The arrangement in the drawing shows a block (mass = 14.0 kg) that is held in position on a frictionless incline by a cord (length = 0.582 m). The mass per unit length of the cord is 1.30 x 10-2 kg/m, so the mass of the cord is negligible compared to the mass of the block. The cord is being vibrated at a frequency of 166 Hz (vibration source not shown in the drawing). What is the smallest angle 0 between 15.0° and 90.0° at which a standing wave exists on the cord?arrow_forwardTh lamp , mass = 10 Kg, is suspended in the position shown. The undeformed length of spring AB is 0.84 m and the spring has a stiffness of K = 784 N/m. For L= 2.8 m find Tension in cable AC , Internal force in spring AB, length of ACarrow_forwardProblem. Consider the following problem. Find the displacement of node 4. Assume F2=200 N, F3=300 N, F4=400 N and Kı= 100, K2= 200, and K3= 300 N/mm. F. 3 2 3 4 Note: The stiffness matrix of individual springs should be first written, then the equilibrium equations at each node should be written, expanded in terms of nodal displacement, and used to perform the assembly of the global stiffness matrix of the problem. Then, the appropriate boundary conditions should be applied and the nodal displacement vector should be found. Every step should be shown; missing any step would result in point deduction even if the final answer is correct.arrow_forward
- A board sits in equilibrium. On the left end, there is a wire that supports the board from the ceiling, and to the right, there is a sawhorse that supports the board from the ground. The sawhorse is a distance d= 1/5l from the right edge of the board. There is a block with mass ms= 4.5kg that is a distance 3/4l from the right edge of the board. Finally the board has a mass mb= 11kg. c) Write down Newton's 2nd law. Put the equation in terms of mb, ms, g, T, and Fn. Where T is the tension in the wire, and Fn is the normal force of the sawhorse on the board. d) Write down Newton's 2nd Law for rotations. Put the equation in terms of l, mb, ms, g, T, and Fn.arrow_forwardThe linkage shown is used in a vehicle suspension system. Find the forces indicated below when a static force of F = 1000 lb is applied to the tire at point C at an angle of 0 = 17° as shown. Assume the connection of the wheel to member AB is rigid. 1 h₁ K: LOFF 0 W₁ h₂ h3 h4 h5 B W₁₂ AXHIMAL W4 hs: h₂ cc i❀O BY NC SA 2013 Michael Swanbom W3 - W₁ Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value Variable Value h₁ 6.6 in W1 7.5 in 16.6 in W2 4.6 in 14.6 in W3 8.3 in 10.2 in W4 6.2 in 5.2 in W5 9.7 inarrow_forwardCivil engineeringarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY