
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Calculate the theoretical flame temperature of a gas mixture consisting of 20% CO and 80% N2
when burned with 100% excess air, both air and gas initially being at 298 K. The standard heat
of reaction at 298 K is –283.178 J/mol CO. The heat capacity in
J/mol K are given by CP = a + bT + gT2, where
a b g
CO2 26.54 42.45 ? 10–3 – 14.298 ? 10–6
O2 25.61 13.26 ? 10–3 – 4.208 ? 10–6
N2 27.03 5.815 ? 10–3 – 0.289 ? 10–6
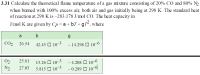
Transcribed Image Text:3.31 Calculate the theoretical flame temperature of a gas mixture consisting of 20% CO and 80% N2
when burned with 100% excess air, both air and gas initially being at 298 K. The standard heat
of reaction at 298 K is –283.178 J/mol CO. The heat capacity in
J/mol K are given by Cp= a + bT+gT², where
a
b
CO2
26.54
42.45 O 10-3
- 14.298 O 10–6
02
25.61
13.26 O 10-3
5.815 O 10-3
- 4.208 O 10–6
- 0.289 O 10-6
N2
27.03
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 8 steps with 14 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please help with homework as soon as you can. Box in answer.arrow_forward5arrow_forwardA food product containing 80% moisture content is being frozen. Predict the specific heat of the product at -8 ° C when 82% of the air is frozen. The specific heat of the dry product is 2.5 kJ / (kg ° C). it is assumed that the specific heat of water at -10 ° C is the same as that of water at 0 ° C, and the specific heat of ice follows the function Cp ice = 0.0062 T frozen + 2.0649. Cp of frozen product = Answer kJ / kg ° C.arrow_forward
- 4.) Steam undergoes an Isentropic process where it is initially at 1.30 MPa and 200 C then it expands to a pressure of 0.75 MPa, thus becoming wet steam. What is the dryness of the steam and the change in enthalpy for the process? • 100%, -2766.4 kJ/kg • 98.75, -68.94 kJ/kg • 200%, -2809.7 kJ/kg • 96.95%, -105.94 kJ/kgarrow_forwardA Stirling cycle is a thermodynamic cycle similar to the Carnot cycle and is defined by the following processes. -> 2: Isothermal expansion -> 3: isochoric cooling -> 4: isothermal heating -> 1: isochoric heating Draw a PV diagram for a Stirling cycle in which 50g of Ar (treated as an ideal gas) is isothermally expanded from 4L to 16L at a temperature of 700K. The sample is then undergoes isochoric cooling to 298K. The sample is then isothermally compressed to 3L and finally undergoes isochoric heating back to 700K. Label the states 1 – 4 on the graph.arrow_forwardThe lower heating value for gaseous n-octane is 44,791 kJ/kg, and its latent heat of vaporization is 300 kJ/kg. Using this information, determine the enthalpy of formation at 298 K for liquid n-octane in kJ/kmol. (Here you are to compute the enthalpy of formation from the given information, not look it up in a property table.)arrow_forward
- Pure CO is mixed with 100 percent excess air and completely burned at constant pressure. The reactants are originally at 400 K. Determine the heat added or removed if the products leave at 600 K. The standard heat of reaction at 298 K is -282.99 kJ per mol CO burned. The mean specific heats applicable in the temperature range of this problem are 29.10, 29.70, 29.10, and 41.45 J/mol K respectively for CO, O₂, N₂ and CO₂.arrow_forwardOnce the methanol has reached its boiling point, it must be vaporized. Themolar enthalpy of vaporization for methanol is 38 kJ mol-1 . How much heat must be added to vaporize 1.00 kg methanol?arrow_forwardAF A single-effect evaporator operated at 100 kPa is used to concentrate 5 wt.% NaOH solution at 110°C and 200 kPa to 8 wt.%. The evaporator is heated by a saturated steam at 120 °C where the heat transfer area is 50 m². The overall heat transfer coefficient is 2000 J/m².s.K. The molar mass of NaOH is 40 kg/kg mol. a) what is the feed flow rate, the product flow rate and the generated vapor flow rate? b) what is the steam needed for this operation? c) what is the steam economy for this evaporator?arrow_forward
- The heat of fusion of water is 6.01 kJ/mol. The heat capacity of liquid water is 75.3 J/mol- K. The conversion of 20.0 g of ice at 0.0 °C to liquid water at 30.0°C requires kJ of heat. O 17.2 O 16.7 O 9.19 O Insufficient data are given. O 18.8arrow_forward05: Acetylene gas (C₂H₂) at 25 °C is burned during a steady-flow combustion process with 30 percent excess air at 27 °C. It is observed that 75x10³ kJ of heat is being lost from the combustion chamber to the surroundings per kmol of acetylene. Assuming combustion is complete, determine the exit temperature of the product gases.arrow_forwardA food product containing 80% moisture content is being frozen. Estimate the specific heat of the product at -8 ° C when 82% of the water is frozen. The specific heat of the dry product is 2.5 kJ / (kg ° C). it is assumed that the specific heat of water at -10 ° C is the same as the specific heat of water at 0 ° C, and the specific heat of ice follows the function Cp es = 0.0062 Tbeku + 2.0649. Cp frozen product = AnswerkJ / kg ° C.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The