
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The diagram shows a 7.0 meter log leaning on a rock. The wieght of the log is 780 Newton's. A 200 Newton boy walks up the log from the point where is touches the ground. He finds that he can only walk 5.0 meters up the log before it starts to tip over the rock WHrer is the center of gravity of the log located?
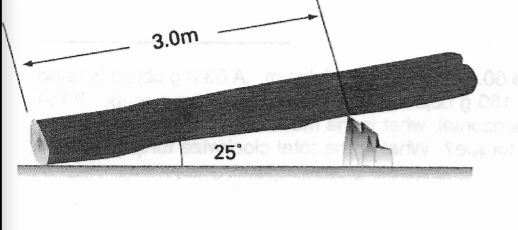
Transcribed Image Text:3.0m
25*
Expert Solution
arrow_forward![[(780)(3– x)cos(25)]=[(200)(2)cos(25)]
x= 2.487 m](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/answer/ca81707c-5dfd-48fb-85bf-a4cfe24c4000/6cd0132e-4e60-44ff-a17b-de53adc228a2/n1nezjc.png)

Step 1
The net momentum about the tip is,
![[(780)(3– x)cos(25)]=[(200)(2)cos(25)]
x= 2.487 m](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/answer/ca81707c-5dfd-48fb-85bf-a4cfe24c4000/6cd0132e-4e60-44ff-a17b-de53adc228a2/n1nezjc.png)
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Many aspects of a gymnast's motion can be modeled by representing the gymnast by four segments consisting of arms, torso (including the head), thighs, and lower legs, as in the figure below. Thigh O Arm Leg 60° 60° Torso a b In the figure, (b) shows arrows of lengths r.a locating the center of gravity of each segment. Use the data below and the coordinate system shown in figure (b) to locate the center of gravity of the gymnast shown in figure (a). Masses for the arms, thighs, and legs include both appendages. (Enter your answers in m, to at least three significant figures.) Segment Mass (kg) Length (m) rcg (m) Arms 6.81 0.548 0.236 Torso 33.6 0.613 0.337 Thighs 14.1 0.368 0.149 Legs 7.50 0.350 0.227 HINT Xcg m Ycg marrow_forwardMany aspects of a gymnast's motion can be modeled by representing the gymnast by four segments consisting of arms, torso (including the head), thighs, and lower legs, as in the figure below. Thigh O Arm Leg 60° 60° Torso In the figure, (b) shows arrows of lengths r., locating the center of gravity of each segment. Use the data below and the coordinate system shown in figure (b) to locate the center of gravity of the gymnast shown in figure (a). Masses for the arms, thighs, and legs include both appendages. (Enter your answers in m, to at least three significant figures.) Segment Mass (kg) Length (m) "cg (m) Arms 6.81 0.548 0.236 Torso 33.6 0.597 0.337 Thighs 14.1 0.368 0.149 Legs 7.58 0.350 0.227 HINT Xcg Y cgarrow_forwardIn exercise physiologystudies, it is sometimesimportant todetermine the location ofa person’s center of gravity.This can be done withthe arrangement shownin Figure P8.21. A lightplank rests on two scalesthat read Fg1 = 380. N andFg2 = 320. N. The scales are separated by a distance of 2.00 m.How far from the woman’s feet is her center of gravity?arrow_forward
- An 80 kg construction worker sits down 2.0 m from the end of a 1450 kg steel beam to eat his lunch, as shown. The cable supporting the beam is rated at 15,000 N. Should the worker be worried?arrow_forwardQ13. A 5 meter, 200N-long ladder rests against a wall. The ladders center of mass is 3.0 meters up the ladder. The coefficient of friction on the ground is 0.30. How far along the ladder can a 75-kg person climb before it slips? The angle between the ladder and ground is 56 degrees. (2.0 m)arrow_forwardThe two ends of the dumbbell shown below are made of the same material. Is the dumbbell’s center of gravity at point 1, 2, or 3? Explain.arrow_forward
- When you bend over, a series of large muscles, the erector spinae, pull on your spine to hold you up. Figure shows a simplified model of the spine as a rod of length L that pivots at its lower end. In this model, the center of gravity of the 320 N weight of the upper torso is at the center of the spine. The 160 N weight of the head and arms acts at the top of the spine. The erector spinae muscles are modeled as a single muscle that acts at an 12° angle to the spine. Suppose the person shown bends over to an angle of 30° from the horizontal. a. What is the tension in the erector muscle? Hint: Align your x-axis with the axis of the spine.b. A force from the pelvic girdle acts on the base of the spine. What is the component of this force in the direction of the spine? (This large force is the cause of many back injuries).arrow_forwardB-3 Jae, whose mass is 65.0kg is standing Im from the end of a uniform diving board 8m long. The diving board is supported at point 'A' by a pin and at point B by a frictionless wedge as shown on the figure. The diving board has a mass of 100kg. Jaer A Find the magnitude and direction of the force of the supports on the board at points 'A' and B. Imk 2m 5m Apply the static equilibrium conditions to the Jae+beam system. 99+ 團 oparrow_forwardAs a part of his daily workout routine, he lifts 10-kg dumbbells on each hand. His hands, and forearms weigh 4 kg each. If the length of each of his forearms and hands are 0.5 m, determine the force exerted by his muscles? Assume that the center of gravity of the, forearms are in the middle. Complete solution with explanation pleasearrow_forward
- 11. Find the x- and y-coordinates of the center of gravity of a 4.00-ft by 8.00-ft uniform sheet of plywood with the upper right quadrant removed as shown in Figure P8.11. Hint: The mass of any segment of the plywood sheet is proportional to the area of that segment. y (ft) 4.00 2.00 - 0+ +x (ft) 2.00 4.00 6.00 8.00 Figure P8.11arrow_forwardA horse stands with its front leg raised off the ground, as shown in the figure. figure. The left hind and right forelegs each support 300 lb of the total weight that is 1,000 lbs. a) What force is exerted by the right hind leg? b) Calculate the position of the center of gravity of the horse.arrow_forwardIn exercise physiology studies, it is sometimes important to determine the location of a person's center of gravity. This can be done with the arrangement shown in the figure below. 2.00 m A light plank rests on two scales that read F = 380 N and F = 280 N. The scales are separated by a distance of 2.00 m. How far from the woman's feet is her center of gravity? Need Help? Read Itarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON