
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
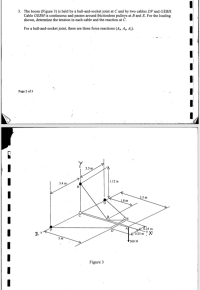
Transcribed Image Text:3. The boom (Figure 3) is held by a ball-and-socket joint at C and by two cables DF and GEBH.
Cable GEBH is continuous and passes around frictionless pulleys at B and E. For the loading
shown, determine the tension in each cable and the reaction at C.
For a ball-and-socket joint, there are three force reactions (A, An Az).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 16 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- PROBLEM 1: Consider the truss system to the right. All members are two force members. There is a pin at Point D and a roller at E. Find the forces in each member and include whether each member is in compression or tension. 3 m 12 kN 3 m 8 kN F 3 m C 3 m D 5 marrow_forwardStatics, Find the magnitude of the horizontal and vertical components of the pin reactions at A, B, and E (Ax, Ay, Bx, By, Ex, Ey)arrow_forwardi need the answer quicklyarrow_forward
- Figure b shows a truss structure in static equilibrium that is simply supported at A and C. Calculate the reaction forces RA and RC when subjected to vertical loads of 50 kN, 25 kN and 15 kN at nodes D, E & C, respectively.arrow_forward6.63 The principles of a differential chain block are indicated schematically in the figure. Determine the magnitude of force P needed to support the 800-N force. Also, find the distance x where the cable must be attached to bar AB so the bar remains horizontal. All pulleys have a radius of 60 mm.arrow_forwardStop Share The horizontal boom AO is supported by cables AB and CD, and a ball-and-socket joint at O. Calculate the tensions in the cables, and support reactions at O in terms of x. Neglect weight of the boom. L=10 kN, a= 7 m, b=3 m, c-2 m, d=4 m x A C B X b C Darrow_forward
- Helparrow_forwardTwo bars connected by a sliding block are shown in the figure. If the effect of friction is not taken into account, perform the following operations: 1.1 Draw the Free Body Diagram (F.B.D.). (1.0 point) 1.2 Determine the moment Ma necessary to keep the system in equilibrium. (1.0 point) 1.3 Determine the magnitude of the reaction at support A. (1.0 point) 1.4 Determine the magnitude of the reaction at support B. (1.0 point) 1.5 Determine the magnitude of the reaction at joint C. (1.0 point)arrow_forwardQ/1: A 10 m long vertical mast has a ball-and socket joint at A, and it is supported by two (2) cables, BD and BC as shown in Figure 1. A force 4 kN is applied at G. Draw the free body diagram (FBD) for the rigid body and determine: (a) The tensions in cables BD and BC (b) The reactions at the ball-and-socket joint at A (c) The projection of T, along the line BE (d) The angle between cable BD and line BE (e) The moment of T, along line CF T2 4 kN 5 m B 5 m T₁ 4m-F 74 m 12m xarrow_forward
- 4 kN 3 m 4 m Use the method of joints to find all reaction and member forces in the trusses.arrow_forwardQuestion 1 Member ABC of negligible weight is supported by a pin and bracket at B and by an inextensible cord attached at A and C and passing over a frictionless pulley at D. For the loading shown and neglecting the size of the pulley, calculate the tension in the cord ,the horizontal and vertical reactions at point B. (X,XX,XXX represents the last digits number of your IC). 1 257mm 75 N 167mm B 127 mmarrow_forwardA rear suspension system for a front wheel-drive vehicle is shown here. Spring EF is offset behind member CD. The normal force due to contact between 2 wheel and the road is 4200 N. Assume the weight of the wheel and suspension system components is negligible. (a) Determine the magnitude of the force in member CD. Is the member in tension or compression? (b) Determine the support reactions at A. (c) Determine the unstretched length of the spring EF given a spring constant of 150 kN/m. 60 mm 1130 mm 60 mm 245 mm D 220 mm F 260 mm E B 165 mm 90 mm F = 4200 Narrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY