
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781305635180
Author: Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
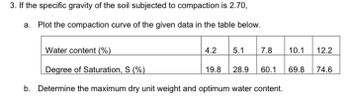
Transcribed Image Text:3. If the specific gravity of the soil subjected to compaction is 2.70,
a. Plot the compaction curve of the given data in the table below.
Water content (%)
Degree of Saturation, S (%)
b. Determine the maximum dry unit weight and optimum water content.
4.2
5.1
7.8 10.1 12.2
28.9 60.1 69.8 74.6
19.8
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For a soil, given: D10 = 0.08 mm D30 = 0.22 mm D60 = 0.41 mm Calculate the uniformity coefficient and the coefficient of gradation of the soil. 2.4 Repeat Problem 2.3 for the following: D10 = 0.24 mm D30 = 0.82 mm D60 = 1.81 mmarrow_forwardRefer to the soil in Problem 4.5. Using the Casagrande plasticity chart, graphically estimate the shrinkage limit of the soil as shown in Figure 4.22. 4.5 The following data were obtained by conducting liquid limit and plastic limit tests on a soil collected from the site. Liquid limit tests: Plastic limit test: PL = 19.3% a. Draw the flow curve and determine the liquid limit. b. Using the Casagrande plasticity chart (Figure 4.21), determine the soil type.arrow_forwardRepeat Problem 2.11 with the following data. 2.11 The grain-size characteristics of a soil are given in the following table. a. Draw the grain-size distribution curve. b. Determine the percentages of gravel, sand, silt, and clay according to the MIT system. c. Repeat Part b using the USDA system. d. Repeat Part b using the AASHTO system.arrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you
 Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305635180
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305081550
Author:Braja M. Das
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305970939
Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning