
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781305635180
Author: Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
I need detailed explanation solving this exercise from Foundation Engineering, step by step please.
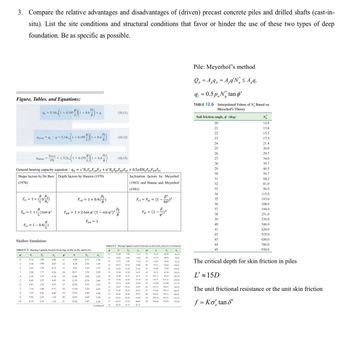
Transcribed Image Text:3. Compare the relative advantages and disadvantages of (driven) precast concrete piles and drilled shafts (cast-in-
situ). List the site conditions and structural conditions that favor or hinder the use of these two types of deep
foundation. Be as specific as possible.
Figure, Tables, and Equations:
7.5.14c (1+0.1952)(1 +0.4%) +
D
+q
(10.11)
B
Pile: Meyerhof's method
Q₁ = 4,9, = Aq'N <≤ Aq₁
q
9₁ = 0.5ptan o'
TABLE 12.6 Interpolated Values of N Based on
Meyerhof's Theory
Soil friction angle, ' (deg)
20
N₁₂
12.4
21
13.8
Qu(net) qu q = 5.14c 1 + 0.195-
= (1 + 0.1954)(1 +0.4%)
(10.12)
B
all(net)
qu(net)
FS
= 1.713c. (1 + 0.1952)(1 + 0.47%)
(10.13)
B
General bearing capacity equation qu= c'NcFcs Fca Fci+q'NqFqsFqaFqi + 0.5yBNy Fys Fya Fyi
Shape factors by De Beer Depth factors by Hansen (1970)
(1970)
Inclination factors by Meyerhof
(1963) and Hanna and Meyerhof
(1981)
BN
Fes 1+G
Fcd =1+0.4(
0.4
Во
=
Fei Fai = (1-2)²
90°)
35
222222223136
15.5
17.9
24
21.4
25
26.0
29.5
27
34.0
28
39.7
29
46.5
30
56.7
68.2
81.0
96.0
34
115.0
143.0
168.0
B
+tan
Fqs = 1 + (+) tan p'
Fqd = 1 + 2 tan q' (1 − sin ')² Dr
-
B
Fyi = (1-B
37
194.0
φ
38
231.0
Fys = 1-0.4(+)
Fyd = = 1
39
276.0
40
346.0
41
420.0
42
525.0
Shallow foundation:
TABLE 6.2 Bearing Capacity Factors From Eqs. (6.30), (6.29), and (6.31)
43
650.0
TABLE 6.2 Bearing Capacity Factors From Eqs. (6.30), (6.29), and (6.31) (Continued)
44
780.0
45
930.0
$'
N₁
N₁
Ny
$'
N₂
No
Ny
22
16.88
7.82
7.13
37
55.63
42.92
$'
No
N₁
Ny
$'
No
Na
66.19
Ny
0
5.14
1.00
0.00
11
8.80
2.71
1.44
27
23
18.05
8.66
8.20
38
61.35
48.93
78.03
24
19.32
9.60
9.44
39
67.87
55.96
92.25
1
5.38
1.09
0.07
12
9.28.
2.97
1.69
25
20.72
10.66
10.88
40
75.31
64.20
109.41
2
5.63
1.20
0.15
13
9.81
3.26
1.97
26
22.25
11.85
12.54
41
83.86
73.90
130.22
3
5.90
1.31
0.24
14
10.37
3.59
2.29
27
23.94
13.20
14.47
42
93.71
85.38
155.55
4
6.19
1.43
0.34
15
10.98
3.94
2.65
28
25.80
14.72
16.72
43
105.11
99.02
186.54
29
27.86
16.44
19.34
44
118.37
115.31
5
6.49
1.57
0.45
16
11.63
4.34
224.64
3.06
30
30.14
18.40
22.40
45
133.88
134.88
271.76
6
6.81
1.72
0.57
17
12.34
4.77
3.53
31
32.67
20.63
25.99
46
152.10
158.51
330.35
7
7.16
1.88
0.71
18
13.10
5.26
4.07
32
35.49
23.18
30.22
47
173.64
187.21
403.67
8
7.53
2.06
0.86
19
13.93
5.80
4.68
33
38.64
26.09
35.19
48
199.26
222.31
496.01
9
7.92
2.25
1.03
20
14.83
6.40
5.39
34
42.16
29.44
41.06
49
229.93
265.51
613.16
10
8.35
2.47
1.22
21
15.82
7.07
6.20
35
46.12 33.30
48.03
50
266.89
319.07
762.89
(continued)
36
50.59
37.75
56.31
The critical depth for skin friction in piles
L'≈ 15D
The unit frictional resistance or the unit skin friction
f = Kσ tan S'
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- State the method to determine the N-value of soil and the normal N-value required for supporting friction pilesarrow_forward[Geotechnical design] Please finish the answer step by step and clear to see. Thank you!arrow_forward1. We typically use load tests or pile driving formulas to test driven piles, because they are precast. List all the typical tests that are recommended on drilled shafts in order to ensure they are properly installed and ready to be integrated with the rest of the structure. 2. In case that a test drilled shaft fails, i.e. shows lower capacity than the one you have predicted in your design, what would you do?arrow_forward
- Aprecast concrete pile, 305 x 305mm in size is proposed to be installed at a site where two layers of sand exist. The upper layer is 3.7 m thick medium dense sand with y= 16 kN/m² and 6 35º The lower layer is a thick deposit of dense sand with y 19 kN/m² and 6 = 37° a) Differentiate between bored and driven piles in processes to the surrounding soil. terms of the effects of their installationarrow_forward0.45m Square prestressed concrete piles are to be installed in groups of 4 at the site shown in the figure below. The center-to-center spacing between piles is 2.55 m. - Ground Level Soft Clay Su = 15kPa - Depth =6.7m Silty Clay Su = 30kPa 3m Depth = 15.1m 3m Medium Stiff Clay S,-80kPa - Depth = 20.0m a. Calculate group capacity based on individual failure b. Calculate group capacity based on block failure c. Based on parts (a) and (b) above determine the allowable downward load capacity for the pile group. Assume factor of safety of 2.5.arrow_forwardCalculate the difference between C1 & C2 pile capacity, considering the borehole data plot.arrow_forward
- Redo Problem 9.27 with the following: center-to-center spacing of piles 5 30 in., length of piles = 45 ft, D = 12 in., cu = 860 lb/ft2, and FS = 3. Use Table 9.10.arrow_forward(i) What are the components of elastic settlement of piles? Name two parameters that affect the settlement. A 300 mm diameter pile penetrates a deep deposit of soft clay 9 m deep. Compute the skin friction and point bearing capacity. The clay has an undrained unit cohesion of 60 kN/m?. Assume a (ii) constant friction coefficient of 0.75 and use a method.arrow_forwardCompare the construction methods for driven piles versus drilled shafts and discuss the impact of these differences on their axial load capacity.arrow_forward
- Please solve quicklyarrow_forwardI need detailed help solving this exercise from Foundation Engineering. Step by step, please.arrow_forwardA rock storage pile is being designed for a mine in West Virginia. The pile is linedwith reinforced GCL overlain by a 1.5 mm thick HDPE geomembrane. A heavy nonwoven geotextile is placed on top of the geomembrane. Because the rock is porous(K = 10-2cm/s), it is used as the main LCS stone and no additional leachate collectionstone is being installed. Specify the base slope required to keep the head below 25cm if the design storm is 0.8 cm rain/day and the pipe-to-pipe lateral spacing is 60 mIs this rock a reasonable material to replace the LCS stone?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305635180
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning