
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
NMR interpretation:
Is this correct?
My reasoning is the methyl is next to the green hydrogen so following the n+1 rule, would make the methyl a doublet (d). The hydrogen to the right of the carbonyl has no neighbors, so it's a singlet (s). And the green hydrogen is a quintet (m) since it has the 1 red hydrogen and the 3 black hydrogens as neighbors.
Therefore, we should see a 3H, d 1-2.5 ppm; 1H m 4.5-6.5 ppm; 1H, d 4.5-6.5 ppm; and 1H, s 9-10ppm.
If it's not correct, can you please explain how to predict the NMR patterns and integrations for this?
Thank you!
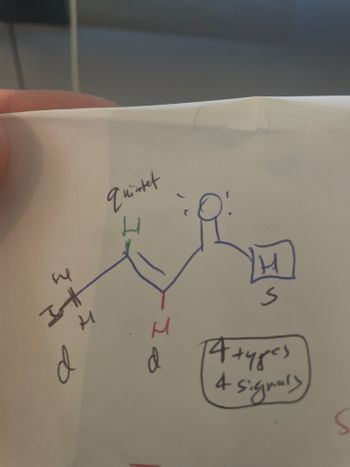
Transcribed Image Text:**Understanding NMR Spectroscopy: Signal Interpretation**
In this educational guide, we'll explore how to interpret nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra signals for a given molecular structure. The image provided illustrates a typical example of a simple organic molecule examined under NMR spectroscopy.
### Molecular Structure
The hand-drawn molecular structure in the image consists of several hydrogen atoms (H) connected to a carbon-based framework. The structure can be described as follows:
- **Main Carbon Chain:** The carbon skeleton is annotated with a set of hydrogen atoms attached directly to the carbon atoms.
- **Hydrogen Atoms (H):** Each "H" represents hydrogen atoms on the molecule, whereas the numbers and symbols around them represent their specific environments and the NMR signals they produce.
### Signal Splitting and Types
- **Signal Splitting Patterns:**
- **Quintet:** Indicated by the label "quintet" next to a hydrogen atom. This means the hydrogen atom has a splitting pattern where it signals five peaks in the NMR spectrum.
- **Doublet (d):** Doublet signals, marked as "d" beside the hydrogen atoms, indicate a splitting pattern of two peaks.
- **Singlet (S):** This signal type does not split and appears as a single peak in the spectrum.
### Interpretation
- **4 Types and 4 Signals:**
The boxed note indicates that there are "4 types" of hydrogen environments in the molecule, hence there will be "4 signals" in the NMR spectrum.
### Key Concepts:
- **Quintet (5 peaks):** Arises because the hydrogen is coupled to 4 adjacent hydrogens.
- **Doublet (2 peaks):** Arises due to the hydrogen being coupled to one adjacent hydrogen.
- **Singlet (1 peak):** No coupling; likely isolated hydrogen or a symmetrical environment.
### Diagrams
The handwritten molecular structure and annotation demonstrate the concept of NMR signal splitting based on hydrogen environments and their chemical shifts. This is a vital skill in analyzing complex molecules in organic chemistry.
Understanding these key concepts of NMR spectroscopy will allow you to interpret and predict the spectra for simple organic molecules and understand their structural implications.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2. Draw structures for compounds that have the proton nmrs described: a) C2H6O; one singlet b) CAH&Cl2O; two triplets c) CAHBO2; one singlet, one triplet and one quartetarrow_forwardShow full work. please answer this question using given information.arrow_forwardConsider the product below a) Would this product show a signal in a UV-Vis spectrum? Why? b) Would this molecule have a non-zero alpha-value in polarimetry? Why? c) What stretches would be expected in an IR spectrum of this molecule? d) Predict the 1H NMR spectrum for this molecule. For H1 to H6 e) Predict the 13C NMR spectrum and DEPT spectra for Carbon A- Carbon G. Use (+) for positive signals, (-) for negative signals, and (X) for no signal in the DEPT NMR spectra. f) If a base such as NaOH was used, it would be harder to determine the major product before running the reaction. Once the reaction was run, how would you determine the product favored using spectroscopy?arrow_forward
- We are trying to determine the substitution pattern on an aromatic ring by looking at the region from around 6 to 10 on the proton NMR spectrum. 10 We don't care what the side chain(s) is/are, we're just calling them F, and K (if needed). Which of the following compounds is represented by this proton NMR? F D OB OA A O C B C Darrow_forwardPlease do both neat and clean correctly... Provide only typed answer solution. Handwritten solution not needed thank youarrow_forwardIn the list of the following molecules, indicate whether they are aromatic, non-aromatic or anti-aromatic compounds.b) For just one aromatic compound identified in the previous list, show your analysis and the rule used to determine that it is an aromatic compound.arrow_forward
- Hello! Please help me with my Chemistry Assign. Thanks so much!arrow_forward14. Here are spectra for two of the compounds below. Draw the appropriate compound next to each. a) 13C NMR 200 b) IR 3000 ОН 150 2000 100 1500 نوع مو موج 50 Dul 1000 ولی 0 500 CI NH₂ OHarrow_forwardC&d answer pleasearrow_forward
- 2. a. Considering the five compounds shown below, which one matches the given 'H NMR spectrum? Circle your answer. 2H D 3H B 1Η m E ellle PPM 6H b. Clearly match each peak in the NMR spectrum to a specific set of H atoms in your chosen structure. Use H₁, Hb, etc. for your labels on both your structure and the spectrum. c. List all of the compounds (A, B, C, D, E) that you would expect to have an IR peak at 1710 cm¹? If none, write "NONE".arrow_forwardHighlight the most acidic of the H atoms shown in each molecule below. Note: if there are two or more H atoms with the same highest acidity, be sure you highlight them all. Also, don't worry about any additional H atoms that might exist but which aren't shown. You only need to find the most acidic H atoms of those that are shown. a H .....ΤΗ H H H Xarrow_forward7. How many non-equivalent protons are there in each of the following structures? н OCH3 хион CH3 ОН Н CH3 H3C- -OCH3 H H3C н N H H3CO OCH3 Н- Н. Н- Н- CHO -OCH3 -OCH3 -OCH3 -OCH3 CH₂OCH 3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY