
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A load is to be raised 20 ft by the hoisting system shown. Assuming gear A is initially at rest, accelerates uniformly to a speed of 120 rpm in 5 s, and then maintains a constant speed of 120 rpm, determine (a) the number of revolutions executed by gear A in raising the load, (b) the time required to raise the load.
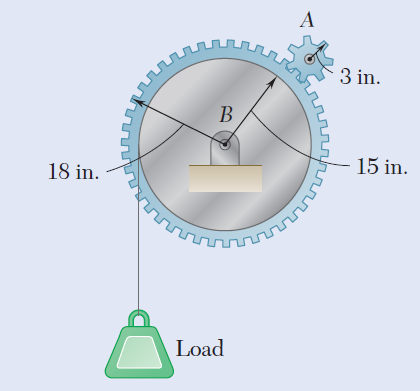
Transcribed Image Text:3 in.
15 in.
18 in.
Load
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 7. The rotor of a turbine installed in a boat with its axis along the longitudinal axis of the boat makes 1500 r.p.m. clockwise when viewed from the stern. The rotor has a mass of 750 kg and a radius of gyration of 300 mm. If at an instant, the boat pitches in the longitudinal vertical plane so that the bow rises from the horizontal plane with an angular velocity of 1 rad /s, determine the torque acting on the boat and the direction in which it tends to turn the boat at the instant. [A- kN-mlarrow_forward3 A load is to be raised 20 ft by the hoisting system shown. Assuming gear A is initially at rest, accelerates uniformly to a speed of 120 rpm in 5 s, and then maintains a constant speed of 120 pm, determine (a) the number of revolutions executed by gear A in raising the load, (b) the time required to raise the load. 3 in. B 18 in. - 15 in. Loadarrow_forward1. A gear reduction system consists of three gears A, B, and C. Knowing that gear A rotates clockwise with a constant angular velocity a- 600 rpm, determine (a) the angular velocities of gears B and C, (b) the accelerations of the points on gears B and C which are in contact. 2 in. 2 in. 4 in. 6 in. 2. In the planctary gear system shown, the radius of gears A, B, C, and D is 3 in. and the radius of the outer gear E is 9 in. Knowing that gear E has an angular vekocity of 120 rpm clockwise and that the central gear has an angular velocity of 150 rpm elockwise, determine (a) the angular velocity of cach planetary gear, (b) the angular velocity of the spider connecting the planetary gears. Earrow_forward
- A simple friction drive consists of two disks A and B. Initially, disk B has a clockwise angular velocity of 590 rpm, and disk A is at rest. Disk B is known to stop in 69 seconds, decelerating constantly. However, instead of waiting for both disks to be at rest before bringing them into contact, disk A is given a constant angular acceleration of 3.5 rad/s2 counterclockwise. a) Determine the time, in seconds, in which both disks can be brought into contact without slipping. A 2.5 in. Fuente: Beer, 11th Ed. B 3 in. b) Determine the angular velocity of disk A, in rpm, when contact is made without slipping. c) Determine the angular velocity of disk B, in rpm, when contact is made without slipping.arrow_forwardProblem (4) When the power to an electric motor is turned on the motor reaches its rated speed of 2400 rpm in 4 s, and when the power is turned off the motor coasts to rest in 40 s. Assuming uniformly accelerated motion, determine the number of revolutions that the motor executes: (a) in reaching its rated speed, (b) in coasting to rest.arrow_forwardH.W 1 A belt drive system shown, is used as a speed reducer. The input shaft rotates at 2000 rpm and has a 144-taoth sprocket with a pitch diameter of 360 mm. The output shaft has a 72-tooth sprocket with a pitch diameter of 90 mm. The center distance between the two shafts is 750 mm. Determine the following for the belt drive: a. The velocity ratio b. The angular velocity of the output shaft c. The linear belt speed d. The belt wrap on the input and output sprockets e. The belt perimeter length f. Optional: Draw the schematic of the beit drive system using CAD g. Coefficient of friction between the belt and the pulleyarrow_forward
- A uniform slender rod AB A uniform slender rod A of the rod is struck by a hammer that delivers an impulse that is perpendicular to the rod. In the subsequent motion, determine the distance b through which the rod will move each time it completes a full revolution.arrow_forward15.4 The gear A of the system shown executes 200 rev over a time interval at Delta t while its angular velocity is being increased from 300 rpm counterclockwise to 900 rpm counterclockwise at a constant rate a. Determine a and Delta t.arrow_forwardplease make sure answer matches with the provided options(it's not 6.73) and show work, thank you!!arrow_forward
- Question No. 18: (a) In an epicyclic gear train, an arm carries two gears A and B having 36 and 45 teeth respectively. If the arm rotates at 150 r.p.m in the anticlockwise direction about the centre of the gear A which is fixed, determine the speed of gear B. If the gear A instead of being fixed, makes 300 r.p.m in the clockwise direction, what will be the speed of gear B? (b) Prove that the resultant unbalanced force is minimum when half of the reciprocating masses are balanced by rotating masses.arrow_forwardNOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. A simple friction drive consists of two disks A and B. Initially, disk B has a clockwise angular velocity of 550 rpm, and disk A is at rest. It is known that disk B will coast to rest in 65 s. However, rather than waiting until both disks are at rest to bring them together, disk A is given a constant angular acceleration of 3 rad/s² counterclockwise. A 2.5 in. B 3 in. Determine at what time the disks can be brought together if they are not to slip. (You must provide an answer before moving to the next part.) The disks can be brought together at t= S.arrow_forwardplease explain the step i marked in details, SHOW YOUR WORK!!!!!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY