
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
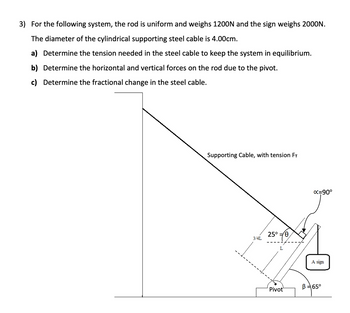
Transcribed Image Text:3) For the following system, the rod is uniform and weighs 1200N and the sign weighs 2000N.
The diameter of the cylindrical supporting steel cable is 4.00cm.
a) Determine the tension needed in the steel cable to keep the system in equilibrium.
b) Determine the horizontal and vertical forces on the rod due to the pivot.
c) Determine the fractional change in the steel cable.
Supporting Cable, with tension FT
3/4L
25°/0
L
Pivot
x=90°
A sign
B = 65°
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two masses are attached to a uniform meter stick as shown in the figure below. The masses of m1 and m2 are as given and the meter stick weighs 150 g. A force F with unknown magnitude is applied on one end of the stick at an angle of 30° to balance the system. 30 cm 40 cm 30 cm 30° m1 50 g m2 75 g slImstimee (a) What is the magnitude of F? (Ans: 6.21 N) (b) What are the reaction forces on the support? (Ans: Rx = 5.38 N; Ry = 5.80 N)arrow_forward7. A ladder of length 12 m leaning up against a wall makes a 50 degree angle with the ground. The top of the ladder has sliders so that it can slide up and down the wall. Therefore, consider the top of the ladder to be frictionless. The ladder has a weight of 189 N that acts at its center. Someone weighing Fg = 1000 N is 0.92 m vertically below B, but on the ladder. Another person is on the ground holding the ladder by pushing on it horizontally with a force F. If the coefficient of static friction is 0.32, find the horizontal force F that must be applied at a vertical height of 1.2 m to prevent the ladder from slipping. LL F 1.2 m 12 m 50⁰ Fg B .92 marrow_forwardThe diagram below shows a rigid body ABC held in equilibrium by a ball-and-socket joint at A and three cables: BD, BE and CD. A 1.80 kN force is applied at F. The mass of ABC can be neglected. a) Draw a large, clear free-body diagram for ABC. b) Determine Cartesian component force equations of equilibrium for ABCarrow_forward
- A) Determine the force in the spring with unstretched length 3 inches and a spring constant of 240 lb/ft. B) Determine the forces at A, B, C, D, and F. A 6 in. B 6 in. D 6 in. E G 8 in. 8 in.arrow_forward9arrow_forward4.8 m 2. The frame shown below is loaded with an unknown horizontal force, P. At point E, the surface exerts a force of 130 lb. on the roller. a) Draw and label all the reactions and forces acting on the frame and on the individual components, using the diagrams provided on the back of this handout. b) Determine the magnitude of the force, P, required for the frame to be in equilibrium. c) Determine the x- and y- components of the force acting at point C on member CDE, and specify the directions (→, +, t. 1). Note: For each calculation, state which diagram number (1, 2, 3, 4) you are using. Ans: P = 80 lb, C = 100 lb , C, = 75 lb 1 (by the way, FBC = 125 lb (T)) 4 in. 8 in. C 3 in. В 6 in. 1 3arrow_forward
- Please asaparrow_forward2. For the frame and loading shown to below, determine the components of the reactions at B and D if the force P = 100 lb. a) Draw the free body diagram of the entire frame and free body diagrams for all the components of the frame. Identify any two-force members and use this information in your calculations. Draw and label all forces. b) Find the x- and y- components of the reactions at B and D. Ans: Bx = 64 lb →, By = 48 lb ↑, D, = 64 lb , D, = 52 lb ↑ (By the way, FBC = 80 lb (T)) %3D %3D %3D 2 in. y А В 3 in. C 4 in. 5 in. 10 in.arrow_forwardQ2: The structure is designed to support a 40 kN load vertically and 50 kN load horizontally. The structure consists of a boom AB and rod BC joined by pins at the junctions and supports. Pin at support “c" can move in slot vertically without any friction. Ignoring the weights of the components of the structure: a) Draw Free Body Diagram of the structure, b) Determine the reaction forces at the supports. - Frictionless pin in slot 600 mm B 50 kN 800 mm 40 kNarrow_forward
- Two weights, A and C, are fixed to a bar, B. Their masses are: A = 60 kg, B = 230 kg,C = 45 kg. B is, in turn, connected to a fixed vertical post by a hinge and a support cableD. The geometry of the system is shown at right. Treat weights A and C as point masses a)What is the tension in support cable D? Be sure to include a detailed freebody diagram to accompany your analysis.b) What is the magnitude of the force provided by the hinge?c) What is the moment of inertia of the A + B + C as a rigid system, for rotationabout the hinge? For analysis, break the beam into a short piece to the left of thehinge, and a separate longer piece to the right of the hinge. If the support cable D on should break,d) what is the angular acceleration of the beam and weights at the moment the cable breaks?e) what is the magnitude of the linear acceleration experienced by each of the weights, A and C, at moment the cable breaks?arrow_forwardA uniform trapdoor shown below is 1.0 m by 1.5 m and weighs 300 N. It is supported by a single hinge (H), and by a light rope tied between the middle of the door and the floor. The door is held at the position shown, where its slab makes a 30° angle with the horizontal floor and the rope makes a 20° angle with the floor. Find the tension in the rope and the force at the hinge.arrow_forwardFast please give me all answers pleasearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY