
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

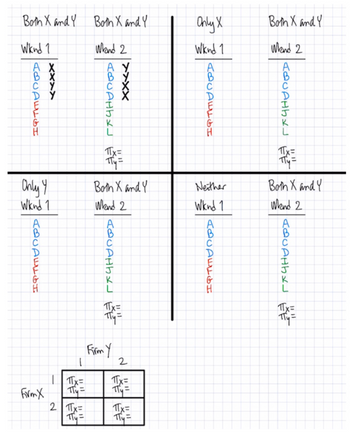
Transcribed Image Text:3) A SIMPLE MODEL OF MOVIE-LAUNCH TIMING
Consider the following model of how movie studios might think about the optimal timing of launching a movie (and thereby
entering a market). Suppose there are two studios (or movies), X and Y, and there are two holiday weekends, 1 and 2. In
weekend 1, there is a total of 8 movie fans, evenly divided into regular moviegoers {A,B,C,D} and occasional moviegoers
{E,F,G,H}. In weekend 2, there is a total of 8 movie fans, evenly divided into the same regular moviegoers from before
{A,B,C,D} and new occasional moviegoers {I,J,K,L}. All fans want to watch movies (produced at zero cost) and the price per
ticket is $1. How should we envision demand? Suppose that all moviegoers will watch a movie that they have not seen before,
but will never watch a movie for a second time. Also suppose that if two previously-unseen movies are available, the customers
will "flip a coin" and be split evenly, with alphabetically-earlier moviegoers choosing X and others choosing Y. E.g., if both
movies are available in weekend 1, then A and B will watch X while C and D watch Y, and if both movies are still available in
weekend 2, then A and B will watch Y while C and D watch X. A movie launched in weekend 1 is still available in weekend 2.
a) Determine the total box office revenue (or profit) for each firm under each combination of launch weekends: (X enters in 1,
b)
c)
Y enters in 1), (1,2), (2,1), and (2,2). TIP: Don't worry about discounting future payoffs; just add the two weekend revenues
to find the total revenue for each firm. HINT: Complete the tables below!
Find the pure strategy Nash Equilibrium for this 2x2 game of launch timing between X and Y. Intuitively explain the result.
Critique this model. What positive things can you say about this model? What negative things can you say about this model?
TIP: What seems unrealistic, overly optimistic, oversimplified, or missing from this model?
Transcribed Image Text:Both X and Y
Both X and Y
Only X
Both X and Y
Wknd 1
Wand 2
Wknd 1
Wand 2
XXXX
QUALI
120AHH
AQUALSI
Only Y
Both X and Y
Wknd 1
Whand 2
Neither
Wknd 1
Both X and Y
Wand 2
за глинопод
XXXX
AQUALSI
11 11
Firm Y
2
хилу
DI
1111
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- M7arrow_forwardYou like your job, but your boss gives lousy bonuses. You were recently offered a new job with better rewards and your friend wants to know if you intend to take it. You say, "It depends on whether the bonus this year is generous, Let's wait and see. We'll find out next week" The likely outcome of this game is your boss gives you a ousy :bonus and you ept the new job. If you want to stay at your current job and be better rewarded, you could improve your strategy if you: demand an increase in your bonus by a certain amount, but does not tel your boss about the job offer. adopt a dominant strategy to accept the other position and make this known to your boss. O tell the boss about the job offer you are prepared to take if your bonus structure does not increase by a certain amount. Cadopt a dominant strategy to stay at your current position and make this known to your boss.arrow_forwardYou and a coworker are assigned a team project on which your likelihood or a promotion will be decidedon. It is now the night before the project is due and neither has yet to start it. You both want toreceive a promotion next year, but you both also want to go to your company’s holiday party that night.Each of you wants to maximize his or her own happiness (likelihood of a promotion and mingling withyour colleagues “on the company’s dime”). If you both work, you deliver an outstanding presentation.If you both go to the party, your presentation is mediocre. If one parties and the other works, yourpresentation is above average. Partying increases happiness by 25 units. Working on the project addszero units to happiness. Happiness is also affected by your chance of a promotion, which is depends on howgood your project is. An outstanding presentation gives 40 units of happiness to each of you; an aboveaverage presentation gives 30 units of happiness; a mediocre presentation gives 10 units…arrow_forward
- QUESTION 38 What are the two routes that we use to process information, according to the Elaboration Likelihood Model (ELM)? O central & minor O central & peripheral O fundamental & peripheral O dominant & central QUESTION 39 Which statement best explains the Extended Parallel Processing Model's take-home message? O Fear appeals are most effective when they get the attention of their audience but are not so intense as to induce too high levels of fear. The more intense a fear appeal, the less successful it will be at enacting behavior change. Fear appeals are more successful if they are more intense. O Fear appeals simply do not work in changing behaviors.arrow_forwardDon't use chat gpt okkk. Solve handwriting solutions other wise I will dislike okkarrow_forwardnot use ai pleasearrow_forward
- 1) Your firm must decide whether or not to introduce a new product. If you introduce the new product, your rival will have to decide whether or not to clone it. If you don't introduce the new product, you and your rival will earn $1million each. If you introduce the new product and your rival clones it, you will lose $5million and your rival will gain $20 million (you have spent a lot on R&D and your rival will not have to spend any R&D in order to clone it). If you introduce the new product and your rival does not clone, you will make $100million and your rival will make $0. a) Draw the extensive form (the tree diagram) of this game, carefully labeling each node and outcomes associated with each action. b) Should you introduce the new product? c) How would your answer change if your rival has "promised" not to clone your product? d) What would you do if patent law prevented your rival from cloning your product?arrow_forwardE1arrow_forwardQUESTION 8 S1, S2, S3 and S4 are UIUC students who just graduated. They each have a poster of Dolly Parton that they are willing to sell. B1, 82, B3 and B4 are new students at UIUC and want to buy Dolly Parton postern for their rooms. The tables below give the minimum selling prices and maximum buying prices for each student. Minimum Selling Prices Maximum Buying Pricen X+$9 S1 $10 B1 S2 $11 B2 X+$14 S3 $20 B3 X+$16 S4 $25 B4 X+$26 If X is negative $5 (.e., Xu-$5), what is the market-clearing price? Note: Do not include the dollar sign,arrow_forward
- 1. We can use game theory to model everyday interactions. Consider a game that you're well familiar with: The choice of which side of a hallway to select if someone is coming from the other direction and has not yet made their own selection clear. How many Nash equilibria are in this game? Remember, an outcome is a Nash equilibrium if nobody has a profitable unilateral deviation; if no one has reason to be the only one to change what they're doing. 2. Consider following scenario which we can think of as a game played between two oligopoly firms, Timmer's snow removal & Jack's snow removal services. It costs Timmer $200 per customer per year. It costs Jack's $225 per customer per year. If the firms compete by strategically setting prices, what Nash equilibrium price do we expect? Explain. Remember, an outcome is a Nash equilibrium if nobody has a profitable unilateral deviation; if no one has reason to be the only one to change what they're doing.arrow_forward1. Consider the following system of equations. Y₁, Y₂ and Y3 are endogenous variables and X₁, X₂ and X3 are exogenous variables. Y₁ = a₁ + a₂Y₂ + α3Y3 + α4X₁ + α5X₂ + U₁ Y₂ B₁ + B₂Y₁+B3Y3+ B4X2+U2 Y3 = V₁ + V2X1 + Y3X2 +Y4X3 + Uz (Eq. 1) (Eq.2) (Eq.3) a) Determine if each equation is just identified, over identified or unidentified. Consider both rank and order conditions. the outem isarrow_forward4) HOTELLING LOCATIONS: MOVIE RATINGS Profit-seeking firms F1, F2, and F3 serve a market in which 300 movie fans have heterogeneous preferences about kid- friendliness. We could think of this in terms of moving ratings, such as G, PG, PG-13, R, etc. E.g., the 60 fans near the low end of the spectrum prefer something very kid-friendly, whereas the 30 fans near the high end of the spectrum prefer to see a very kid-unfriendly movie! Suppose travel costs are not an issue here: all 300 fans will attend a movie at the nearest firm, and if two or more firms are equidistant, then those firms will split the customers equally (if there are 2 movies to choose from, they flip a coin). NOTE: Kids are located at odd-numbered locations (1,3,5,7); firms can locate only at even-numbered locations (0,2,4,6,8). a) Suppose F2 has already located at 4/8 and F3 has already located at 6/8. Your job, as manager of F1, is to determine the customer-maximizing "location" on this spectrum. The last row of the…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education