
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
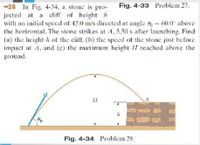
Transcribed Image Text:*28 In Fig. 4-34, a stone is pro-
jected at a cliff of height h
with an initial spccd of 42.0 m/s dirccted at angle 6= 60.0 above
the horizontal. The stone strikes at A, 5.50 s after launching. Find
(a) the hcight h of the cliff. (b) the speed of the stone just before
impact at A, and (c) the maximum height II reached above the
ground.
Fig. 4-33 Problem 27.
Fig. 4-34 Problem 28.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 9- A bowling ball of mass 7.5 kg travelling at 10 m sec-irolls off a horizontal table 1 m high. (Assume the acceleration due to gravity is 10 m sec-2, and the effects of air resistance may be ignored unless otherwise stated.) a Calculate the ball's horizontal velocity just as it strikes the floor. b What is the vertical velocity of the ball as it strikes the floor? c Calculate the velocity of the ball as it reaches the floor. d What time interval has elapsed between the ball leaving the table and striking the floor? e Calculate the horizontal distance travelled by the ball as it falls.arrow_forward10. Wedge Hammer A B 45° -450 mm Fig. 3.20 Neglecting the small amount by which the hammer rises after passing through the vertical through A and assuring that the hammer does not rebound, find the value of R Fig. 3.20 shows a tilt hammer, hinged at 0, with its head A resting on top of the pile B. The hammer, including the arm OA, has a mass of 25 kg. Its centre of gravity G is 400 mm horizontally from O and its radius of gyration about an axis through G parallel to the axis of the pin O is 75 mm. The pile has a mass of 135 kg. The hammer is raised through 45° to the position shown in dotted lines, and released. On striking the pile, there is no rebound. Find the angular velocity of the hammer immediately before impact and the linear velocity of the pile immediately after impact. Neglect any impulsive resistance offered by the earth into which the pile is being driven. [Ans. 5.8 rad/s, 0.343 m/s]arrow_forwardYou have your bicycle upside down while you adjust the chain. The chain is wound around the rear wheels small gear, which has a radius of 4.0 cm. At the pedals, the chain is wound around the large gear, which has a radius of 11.0 cm. The radius of the rear wheel is 35.0 cm. You spin the pedals initially so they finish two revolutions in 1.0 s, starting from rest. Assume constant acceleration. (a) Find the angular acceleration of the rear wheel in rad/s2. (b) Find the magnitude of the total acceleration of a point at the edge of the small gear at the end of 1.5 s (the sum of the radial and tangential accelerations). (c) What is the tangential acceleration for that point during the first second? (d) Calculate the linear acceleration of the chain.arrow_forward
- A BLOCK OF MASS m RESTS ON A FIXED SURFACE AS SHOWN IN THE FIGURE. THE DOUGH IS PUSHED TO THE RIGHT AND THE SPRING IS COMPRESSED A DISTANCE d. THE SPRING IS NOT ATTACHED TO THE BLOCK. IF THE BODY IS RELEASED FROM REST, APPLYING NEWTON'S SECOND LAW DETERMINE: A)THE EXPRESSION OF THE IMPACT VELOCITY OF m WITH M1 AT THE END OF THE DISTANCE TRAVELED S. B)SUPPOSE THAT AFTER THE IMPACT EACH MASS HAD A DISPLACEMENT S1 AND S2 RESPECTIVELY. FIND SPEEDS AFTER IMPACT.arrow_forwardIn the figure, a solid cylinder of radius 12 cm and mass 14 kg starts from rest and rolls without slipping a distance L = 5.0 m down a roof that is inclined at angle 0 = 36°. After leaving the roof, the cylinder hits the ground at distance X = 4.1 m from the house. (a) What is the acceleration of the cylinder while it is rolling dowNn the roof? (b) What is the height H? (c) What are the magnitude and the direction of the velocity before the cylinder hits the ground?arrow_forwardNeed all parts in neat and clean handwritten solution. Do remember before attemptingarrow_forward
- In the situation illustrated in the figure below, a small package is deposited by a conveyor belt at point A onto a ramp at theta = 35 degrees degrees to the horizontal with a velocity of 0.5m / s . The distance between points A and Bis 2 m. a)Calculate the maximum value mu k ^ * of the kinetic friction coefficient between the package and the ramp AB for which the parcel reaches point B. b) If the actual kinetic friction coefficient between the package and AB and BCis mu k =0.5 mu k ^ * calculate the distances on the level surface BC at which the package comes to rest. Note: if you haven't been able to solve part a), take the actual kinetic friction coefficient equal to mu_{k} = 0.28arrow_forwardA Lazy Susan (M=0.5 kg) in the shape of a disk is free to rotate about its center withoutfriction. It is initially motionless when a Texas-sized cockroach (m=10 g) starts runningCCW along the rim. The angular speed of the Lazy Susan is then 1 rad/sec. With whatspeed is the cockroach running (in the rest frame of the table, not the Lazy Susan)? (What more data should be given according to you? If the question seems incomplete to you...)arrow_forwardPlease help solve for v2 at the bottom of the ramp.arrow_forward
- Р.2) A 45 kg rigid body is initially at rest at O on a frozen lake. Is it possible that once it has exploded into the three pieces, A, B, C, with masses ma = 20 kg, 15 kg, and mc = 10 kg, it can occupy the illustrated configuration rA/o = 50j m, rBlo = (30i + 20j) m, and = 70i m, at some later time? %3D MB %3D rcjo L. A j Вarrow_forwardN= 11.03N F= 25 Narrow_forward9. 2) The target is a thin 4.3-kg circular disk of radius r= 273 mm that can rotate freely about the z axis. Initially it is at rest. A 21-g bullet, traveling at v = 630 m/s, strikes the target at A and becomes embedded in it. The dimensions are di = 219 mm and d2 = 90 mm. If the impact time is 0.02 s, determine the average impact force between the bullet and the target. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point, and proper Sl unit. Take g = 9.81 m/s?. 'pearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY