
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
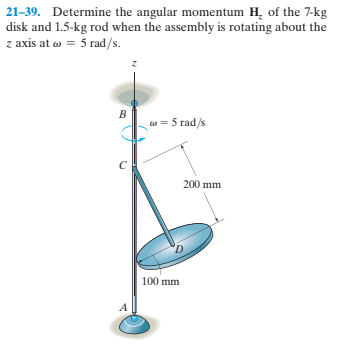
Transcribed Image Text:21-39. Determine the angular momentum H, of the 7-kg
disk and 1.5-kg rod when the assembly is rotating about the
z axis at w = 5 rad/s.
w = 5 rad/s
200 mm
100 mm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The 23-kg uniform thin hollow square plate is pinned at point O, and its side L = 0.3 m. If it is subjected to the constant moment M = 82 N·m and is released from rest from the position as shown, determine its angular velocity W (in rad/s) when it has rotated 45 Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. Take g = 9.81 m/s². M Your Answer: Answerarrow_forwardAt the instant shown, the uniform slender rod with mass m = 31 kg is pin-supported at point O. It is subjected to a counterclockwise moment M = 68 N•m, has a counterclockwise angular velocity of W= 5.3 rad/s, and the dimensions a = 0.10 m and b = 0.65 m. Determine magnitude of the support reaction at point O at this instant. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point, and proper unit. Take g = 9.81 m/s2. a Marrow_forwardThe 10kg rod has a moment of inertia which is computed from Iç =ml². If it is rotating at w = 2, determine its kinetic energy () when it is computed about the mass center G. u-iradearrow_forward
- The 2.5-kgkg rod ACBACB supports the two 4.1-kgkg disks at its ends. If both disks are given a clockwise angular velocity (ωA)1=(ωB)1=4.6rad/s(ωA)1=(ωB)1=4.6rad/s while the rod is held stationary and then released, determine the angular velocity of the rod after both disks have stopped spinning relative to the rod due to frictional resistance at the pins AA and BB. Motion is in the horizontal plane. Neglect friction at pin CC.arrow_forwardThe 10 kg wheel has a radius of gyration about its center O of ko = 300 mm. When the wheel is subjected to the couple moment, it slips as it rolls. Determine the angular acceleration of the wheel and the acceleration of the wheel's center O. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the wheel and the plane is = 0.2. (Figure 1) Figure M 100 N m < 1 of 1 0.4 m Part A Determine the angular acceleration of the wheel. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. α = Submit ■ Part B ao = μÅ X Incorrect; Try Again Value Submit Previous Answers Request Answer Determine the acceleration of the wheel's center O. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. μA Units Value X Incorrect; Try Again Units ? Previous Answers Request Answer ? Units input for part Barrow_forwardAt the instant shown, link CD rotates with an angular velocity of W = 9.0 rad/s. If it is subjected to a couple moment M= 320 N-m, determine the magnitude of the vertical reaction force developed on pin D. The block has a mass of 50 kg and center of mass at G. Neglect the mass of links AB and CD. (Hint, since the mass of link AB or CD is negligible, the external force or moment acting on it sums up to 0.) Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 1 place after the decimal point, and proper unit. Take g = 9.81 m/s². 0.1 m 0.6 m В А 0.4 m' G 0.4 m D C M Your Answer: Answer unitsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY