
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
In the above figure, if the
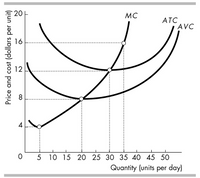
Transcribed Image Text:### Cost Curves in Microeconomics
#### Graph Explanation:
This graph represents the cost structure of a firm in microeconomic theory. It displays the relationships between quantity (units per day) and price/cost (dollars per unit) through various cost curves: Marginal Cost (MC), Average Total Cost (ATC), and Average Variable Cost (AVC).
- **X-Axis (Horizontal):** Represents the quantity of goods produced, measured in units per day. The range extends from 0 to 50 units.
- **Y-Axis (Vertical):** Represents the price and cost, measured in dollars per unit. The scale ranges from 0 to 20 dollars.
#### Curves:
1. **Marginal Cost (MC):**
- The MC curve is upward sloping and intersects both the ATC and AVC curves.
- It initially decreases, reaches a minimum, and then rises sharply, reflecting the law of diminishing returns.
2. **Average Total Cost (ATC):**
- The ATC curve is U-shaped and lies above the AVC curve.
- It starts at a higher cost, decreases to a minimum as quantity increases, and then begins to rise again.
3. **Average Variable Cost (AVC):**
- The AVC curve is also U-shaped and runs parallel to the ATC but lower.
- It shows similar behavior to the ATC curve, indicating how variable costs per unit change with production volume.
#### Key Points of Intersection:
- The MC curve intersects the ATC and AVC curves at their respective minimum points.
- These intersections represent critical points for cost efficiency in production. The point where MC intersects ATC is often the point of most efficient scale.
### Educational Insights:
This graph is essential for understanding how a firm's costs evolve with production volume. Analyzing these curves helps in determining optimal production levels, pricing strategies, and understanding economies of scale.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What does zero economic profits in the long-run mean to the owner of a business operating in a perfect competitive market?arrow_forwardWhy don't firms in a competitive market have excess capacity in the long run?arrow_forwardSuppose the market for peaches is perfectly competitive. The short-run average total cost and marginal cost of growing peaches for an individual grower are illustrated in the figure to the right. Assume that the market price for peaches is $30.00 per box. What is the profit-maximizing quantity for peach growers to produce? boxes. (Enter your response as an integer.) At this level of output, profit will be $. (Enter your response rounded to the nearest dollar.) Peach growers will earn positive economic profit in the short run at any market price above $ per box. (Enter your response rounded to one decimal place.) Price (dollars per box) 40- 36- 32- 28- 24 20 16- 12- 8 4- 10 MC 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Output (boxes of peaches per day) ▬▬ ATC 90 100 Qarrow_forward
- What is the most important decision a perfectly competitive firm must make in order to maximize profit? what quantity to produce what price to charge what quality to produce what quantity of labor is neededarrow_forwardA perfectly competitive firm produces the level of output at which MR=MC on the rising portion of the firm’s marginal cost curve. At that output level, it has the following costs and revenues: TC = $830,000 VC = $525,000 TR = $428,000 Given that the firm produces the level of output at which MR=MC, calculate the amount of profit (loss) this firm earns. is it Profit=TR-TC?arrow_forwardCan you think of a product that meets at least most of the criteria required for a perfectly competitive market? Which criteria does it fail to meet?arrow_forward
- Assuming that the market for cigarettes is in perfect competition, what does allocative and productive efficiency imply in this case? What does it not imply?arrow_forwardMicroeconomicsarrow_forwardExplain how the profit-maximizing rule of setting P = MC leads a perfectly competitive market to be allocatively efficient.arrow_forward
- Consider the perfectly competitive market for steak (a normal good). Starting from long-run equilibrium, show graphically what happens in the short and long run to q. Q. P, and r in the market for steak (in comparison to the starting point) if income increases. Briefly explain.arrow_forwardA perfectly competitive firm is currently maximizing profits. The market for its product is in a long-run equilibrium. Market demand for the product decreases. Briefly explain what happens in the market by describing what will happen to this firm’s production (and most importantly why) as a result of that change. Describe what will happen and why to the firm’s costs and profits as the firm makes its choices. Emphasize why each type of individual cost does or does not change as the firm changes its level of production.arrow_forwardIn the long run, a perfectly competitive firm canarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education