
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
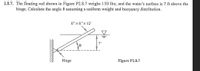
Transcribed Image Text:2.8.7. The floating rod shown in Figure P2.8.7 weighs 150 Ibs, and the water's surface is 7 ft above the
hinge. Calculate the angle 0 assuming a uniform weight and buoyancy distribution.
6"x 6"x 12'
7'
Hinge
Figure P2.8.7
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Hello! Can you please assist me in solving these questions. Thank you in advancearrow_forwardA rectangular plate of width 2 m and height 5 m is suspended in the water so that the top of the plate is 1 m below the water surface, what is the force due to water pressure on one side of the plate? (Hint: Using SI units, pg = 9800 N/m.) (Express numbers in exact form. Use symbolic notation and fractions where needed.) F =arrow_forwardIf the wall in Fig. 4.29 is 4 m long, calculate the total force on the wall due to the oil pressure. Also determine the location of the center of pressure and show the resultant force on the wall.arrow_forward
- help me find a solutionarrow_forwardshow the complete solution. please make sure that your handwritten is readable. thank youarrow_forwardRectangle Gate AB has length L and width b into the paper is hinged at B and has negligible weight. The liquid level, water, h does not reach the top of the gate for an angle theta. Find an equation for the force P, required to keep the gate in equilibrium. Solve for width, b. In the figure. (hint: draw a free-body diagram for the left and right side of the gate separately)arrow_forward
- Consider the tank shown (Figure 2), where the specific weight of the water is yw = 9800 N/m³ and the specific weight of molasses is ym = 1.4x104 N/m³. What is the pressure at the bottom of the tank if h1 = 3.4 m and h2 = 3.7 m. Water h2 Molassesarrow_forwardType your question or/and upload a picture...arrow_forwardSS 3.17 The figure shows a sectional view through a submarine. Calculate the depth of submergence, y. Assume the specific weight of seawater is 10.0 kN/m³. Atmos. pressure 74 mm Hg 60 Conventional baromete 200 mml 840 mm Hg 200 mm- Hg Р3.17arrow_forward
- 2.8.3. A solid brass sphere of 30-cm diameter is used to hold a cylindrical buoy in place (Figure P2.8.3) in seawater (sp. gr. = 1.03). The buoy (sp. gr. = 0.45) has a height of 2 m and is tied to the sphere at one end. What rise in tide, h, will be required to lift the sphere off the bottom? 50 сm h 30 сm sp. gr. = 13.5 Figure P2.8.3arrow_forwardQUESTION 3: An inclined semicircular-shaped (diameter = 7 m) flat plate is entirely submerged in coconut oil (SG = 0.903). The angle between the free surface and the plane of the surface is 47°. Given the hydrostatic P (Pgauge) acting on center of pressure was 73.2 kPa. Assume the both sides of the plate are subjected to Patm. Calculate the: -Line of action F=PA Center of pressure Centroid of area (a) Density of coconut oil. (b) Vertical height from free surface to center of pressure. (c) Inclined distance at centroid from free surface. (d) The resultant hydrostatic force acting on the flat plate.arrow_forwardAn underwater pipeline must be laid 40 meters deep. The density of sea water is 1 025 kg/m³. The pipe has a mass of 40 kg per meter and an outside diameter of 300 mm. The pipe must be anchored every 5 m to the bottom of the sea. (a) What will the vertical force be on each anchor if the 4.3 pipe is empty. (b) What external pressure must the pipe be able to withstand if it is not to be crushed. [1 592 N, 402,2 kPa]arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY