
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
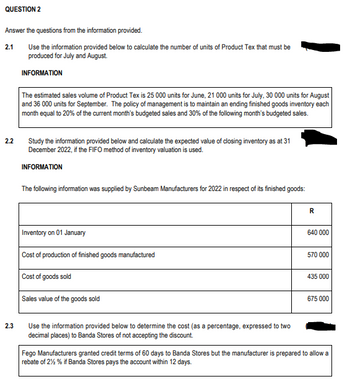
Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION 2
Answer the questions from the information provided.
2.1
Use the information provided below to calculate the number of units of Product Tex that must be
produced for July and August.
INFORMATION
2.2
2.3
The estimated sales volume of Product Tex is 25 000 units for June, 21 000 units for July, 30 000 units for August
and 36 000 units for September. The policy of management is to maintain an ending finished goods inventory each
month equal to 20% of the current month's budgeted sales and 30% of the following month's budgeted sales.
Study the information provided below and calculate the expected value of closing inventory as at 31
December 2022, if the FIFO method of inventory valuation is used.
INFORMATION
The following information was supplied by Sunbeam Manufacturers for 2022 in respect of its finished goods:
Inventory on 01 January
Cost of production of finished goods manufactured
Cost of goods sold
Sales value of the goods sold
Use the information provided below to determine the cost (as a percentage, expressed to two
decimal places) to Banda Stores of not accepting the discount.
R
640 000
570 000
435 000
675 000
Fego Manufacturers granted credit terms of 60 days to Banda Stores but the manufacturer is prepared to allow a
rebate of 2% % if Banda Stores pays the account within 12 days.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
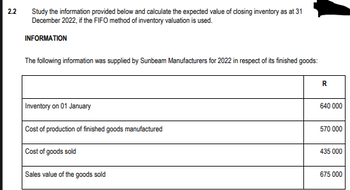
Transcribed Image Text:2.2
Study the information provided below and calculate the expected value of closing inventory as at 31
December 2022, if the FIFO method of inventory valuation is used.
INFORMATION
The following information was supplied by Sunbeam Manufacturers for 2022 in respect of its finished goods:
Inventory on 01 January
Cost of production of finished goods manufactured
Cost of goods sold
Sales value of the goods sold
R
640 000
570 000
435 000
675 000
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question

Transcribed Image Text:2.2
Study the information provided below and calculate the expected value of closing inventory as at 31
December 2022, if the FIFO method of inventory valuation is used.
INFORMATION
The following information was supplied by Sunbeam Manufacturers for 2022 in respect of its finished goods:
Inventory on 01 January
Cost of production of finished goods manufactured
Cost of goods sold
Sales value of the goods sold
R
640 000
570 000
435 000
675 000
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Assume that a company expects to produce 10,300, 11,300, and 13,300 units of finished goods in January, February, and March, respectively. Each unit of finished goods requires 4 pounds of raw material and each pound of raw material costs $1.75. The company always maintains an ending raw materials inventory equal to 25% of next month’s production needs. What is the amount of expected raw materials purchases for February?arrow_forwardCroy Inc. has the following projected sales for the next five months: Month Sales in Units April 3,540 May 3,865 June 4,540 July 4,155 August 3,920 Croy’s finished goods inventory policy is to have 60 percent of the next month’s sales on hand at the end of each month. Direct material costs $2.80 per pound, and each unit requires 2 pounds. Raw materials inventory policy is to have 50 percent of the next month’s production needs on hand at the end of each month. Raw materials on hand at March 31 totaled 3,735 pounds. Required:1. Determine budgeted production for April, May, and June. (Do not round your intermediate calculations and round your final answer to the nearest whole number.) 2. Determine the budgeted cost of materials purchased for April, May, and June. (Use rounded Budgeted Production units in intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 2 decimal places.)arrow_forwardYeah Company expects to sell 1,700 units of finished product in January and 2,050 units in February. The company has 260 units on hand on January 1 and desires to have an ending inventory equal to 40% o the next month's sales. March sales are expected to be 2,120 units. Prepare Yeah's production budget for January and February...arrow_forward
- Osage Incorporated has actual sales for May and June and forecast sales for July, August, September, and October as follows: Actual: May June Forecast: July August 5,300 units 7,800 units September 5,900 units October 5,800 units 6,900 units 6,600 units Required: a. The firm's policy is to have finished goods inventory on hand at the end of the month that is equal to 50% of the next month's sales. It is currently estimated that there will be 2,650 units on hand at the end of June. Calculate the number of units to be produced in each of the months of July, August, and September. b. Each unit of finished product requires 8 pounds of raw materials. The firm's policy is to have raw material inventory on hand at the end of each month that is equal to 80% of the next month's estimated usage. It is currently estimated that 25,000 pounds of raw materials will be on hand at the end of June. Calculate the number of pounds of raw materials to be purchased in each of the months of July and August.…arrow_forwardABCL Corporation predicts the following sales in units for the coming four months: May June July August September Unit sales …… 400 500 520 480 540 Finished goods inventory on April 30: 120 units Raw materials inventory on April 30: 450 pounds Desired ending inventory each month: Finished goods: 30% of next month's sales Raw materials: 25% of next month's production needs Number of pounds of raw material required per finished unit: 4 lbs. Required: How many pounds of raw materials should be purchased in May?arrow_forwardOffenbach & Son has just made its sales forecasts and its marketing department estimates that the company will sell 220,200 units during the coming year. In the past, management has maintained inventories of finished goods at approximately one month's sales. The inventory at the start of the budget period is 14,800 units. Sales occur evenly throughout the year. Required: Estimate the production level required for the coming year to meet these objectives. (Do not round intermediate calculations.) Required production in unitsarrow_forward
- Cahuilla Corporation predicts the following sales in units for the coming four months: April May June July 330 370 398 330 Sales in Units Each month's ending finished goods inventory should be 30% of the next month's sales. March 31 finished goods inventory is 99 units. A finished unit requires 5 pounds of direct material B at a cost of $3.00 per pound. The March 31 Raw Materials Inventory has 290 pounds of B. Each month's ending Raw Materials Inventory should be 20% of the following month's production needs. The budgeted production for May is:arrow_forwardVishnuarrow_forwardFiarrow_forward
- Masters Corporation provided their production budget for the next quarter: Units to be produced Desired Finished Goods Inventory 151,600 148,400 178,400 April 138,800 130,000 30,000 How many units is the company expecting to sell in the month of May? May Please explain what formula you used 150,000 28,400 June 142,000 31,600arrow_forwardWright Lighting Fixtures forecasts its sales in units for the next four months as follows: 20,000 22,000 19,500 18,000 March April May June Wright maintains an ending inventory for each month in the amount of two and one-half times the expected sales in the following month. The ending inventory for February (March's beginning inventory) reflects this policy. Materials cost $7 per unit and are paid for in the month after production. Labor cost is $11 per unit and is paid for in the month incurred. Fixed overhead is $19,000 per month. Dividends of $21,400 are to be paid in May. The firm produced 19,000 units in February. Complete a production schedule and a summary of cash payments for March, April, and May. Remember that production in any one month is equal to sales plus desired ending inventory minus beginning inventory. Note: Input all amounts as positive values except Beginning inventory values under Production Schedule which should be entered with a minus sign. Leave no cells blank…arrow_forwardCousin Eddy provides you with his sales forecast for the next four months: April May 750 June July 790 Sales (Units) 670 The company wants to end each month with ending finished goods Inventory equal to 40% of next month's forecasted sales. Finished goods inventory on April 1 is 268 units. Assume July's budgeted production is 700 units. In addition, each finished unit requires four pounds of raw materials and the company wants to end each month with raw materials inventory equal to 30% of next month's production needs. Beginning raw materials inventory for April was 842 pounds. Assume direct materials cost $5 per pound. Required: For May, how many units must be produced? (Hint: This is your production budget) Submit your answer below 700 with all work submitted via email.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education