
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
In the four piston-cylinder assemblies below, the reactant in the left cylinder is about to undergo a reaction at constant T and P: Which of the other three depictions best represents the products of the reaction?
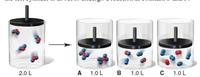
Transcribed Image Text:2.0 L
A
1.0 L
B
1.0 L
1.0L
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A sample of hydrogen gas at 20 °C and 0.570 atm has the pressure on it reduced to 0.100 atm. What is the final temperature of the gas (in °C)? (Assume constant V) (Show Work)arrow_forwardUse the ideal gas law to verify the triple product rule.arrow_forwardA mixture of propane and methane occupied 122 mL at 25⁰C and 1.0 atm. This mixture was totally burned in excess O2 to produce CO2(g) and H2O(g). The mass of the CO2 produced was 0.506 g. What is the mass % composition of the original mixture? Show all work.arrow_forward
- Consider that 2.80 LL of N2N2, at 25 ∘C∘C and 1.83 atmatm , is mixed with 2.60 LL of O2O2, at 25 ∘C∘C and 0.181 atmatm , and the mixture is allowed to react. N2(g)+O2(g)→2NO(g) How much NONO, in grams, is produced?arrow_forwardTrue or false. Why?arrow_forwardaring Suppose that 2.45 g of gaseous nitrogen, N2, is placed in a 2.15 L container The pressure is measured to be 475.0 mmHg What is the Celsius temperature of the gas? [Hint: Your first step should be solving the ideal gas equation for T.] ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ?arrow_forward
- Calculate to three significant digits the density of carbon monoxide gas at exactly −20°C and exactly 1atm . You can assume carbon monoxide gas behaves as an ideal gas under these conditions.arrow_forwardWhat would happen to the average kinetic energy of the molecules of a gas sample if the temperature of the sample decreased from 100°C to 50 C? OR would double OR would decrease would beceome half its value t would increasearrow_forwardAmmonia is among the top ten synthesized compounds. Its many uses include the manufacture of ammonium nitrate and other fertilizers. Ammonia decomposes at high temperatures. In an experiment to explore this behavior, 2.00 moles of gaseous NH3 are sealed in a rigid 1-liter vessel. The vessel is heated at 800 K and some of the NH3 decomposes in the following reaction:2NH3(g)<-->N2(g)+3H2(g) The system eventually reaches equilibrium and is found to contain 1.74 mole of NH3. What is the value of KC for the decomposition reaction at 800 K? What is the value of KP for the decomposition reaction at 800 K?arrow_forward
- 7. When detern ing the mass of a liquid, ras in a hurry and did not allow enough time for the temperature of the flask to reach the temperature of the boiling water bath. The student recorded the temperature of the gas as 100.0°C when it was only 80.0°C, Is the molar mass calculated by the student higher or lower than the accepted molar mass, or does this error have no effect on the calculated result? Briefly explain your answer # 2/HB Office DEPOTS b) If the student assumed the volume of the flask was 125 mL (as marked by the side of the flask) rather than measuring the volume experimentally, would the unknown's calculated molar mass be too high, too low, or unaffected? Explain. # 2/HB 4arrow_forwardA 335 mL sample of oxygen gas at 25 °C is heated to 50 °C. What is the final volume of the gas (in mL)? (Assume constant P) (Show Work)arrow_forwardXenon and helium are both ideal, monatomic gases, but they have very different molar masses (Mxenon = 33*Mhelium). If you have 1 mole of each gas and the gases are at the same temperature, which one of the following statements is true? They both have the same internal energy, but xenon has a lower root-mean-square speed than helium. They both have the same internal energy and root-mean-square speed. They both have the same root-mean-square speed, but xenon has a greater internal energy than helium. They both have the same internal energy, but helium has a lower root-mean-square speed than xenon. They both have the same root-mean-square speed, but helium has a greater internal energy than xenon.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY