
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781305501607
Author: Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher: CENGAGE L
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Solve this and show your work
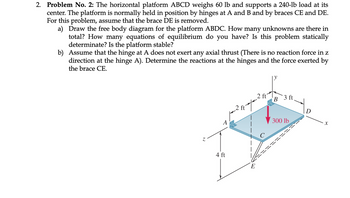
Transcribed Image Text:2. Problem No. 2: The horizontal platform ABCD weighs 60 lb and supports a 240-lb load at its
center. The platform is normally held in position by hinges at A and B and by braces CE and DE.
For this problem, assume that the brace DE is removed.
a) Draw the free body diagram for the platform ABDC. How many unknowns are there in
total? How many equations of equilibrium do you have? Is this problem statically
determinate? Is the platform stable?
b) Assume that the hinge at A does not exert any axial thrust (There is no reaction force in z
direction at the hinge A). Determine the reactions at the hinges and the force exerted by
the brace CE.
N
2 ft
B
3 ft.
4 ft
E
300 lb
X
=======
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The weight of the uniform bar AB is W. The stiffness of the ideal spring attached to B is k, and the spring is unstretched when =80. If W=kL, the bar has three equilibrium positions in the range 0, only one of which is stable. Determine the angle at the stable equilibrium position.arrow_forwardThe center of gravity of the nonhomogeneous bar AB is located at G. Find the angle at which the bar will be in equilibrium if it is free to slide on the frictionless cylindrical surface.arrow_forwardThe mechanism of negligible weight supports the weight W. Find the value of for equilibrium. Is the equilibrium position stable or unstable?arrow_forward
- Find the smallest value of P for which the crate in the Prob. 4.34 will be in equilibrium in the position shown. (Hint: A rope can only support a tensile force.)arrow_forwardThe figure shows a three-pin arch. Determine the horizontal component of the pin reaction at A caused by the applied force P.arrow_forwardThe uniform bar AB of weight W and length L is pinned to a sliding collar at A and to the sliding rod BD at B. The spring wound around rod BD has a stiffness k and is undeformed when rod AB is in the position =0. Determine the expression for the angle (other than =90 ) at equilibrium and investigate the stability of equilibrium for this position.arrow_forward
- Draw the FBDs for the beam ABC and the segments AB and BC. Note that the two segments are joined by a pin at B. Count the total number of unknowns and the total number of independent equilibrium equations.arrow_forwardThe uniform bar of weight W is held in equilibrium by the couple C0. Find C0 in terms of W, L, and .arrow_forwardThe bent rod of negligible weight is supported by the ball-and-socket joint at B and the cables attached to points A and C. Find the forces in the cables and the magnitude of the reaction at B. Dimensions Figure P.5.39arrow_forward
- Find the magnitude of the pin reaction at B caused by the weight W=80lb. Neglect the weights of the members.arrow_forwardThe linkage is made of two homogenous bars of weights shown in the figure. Determine the horizontal force P required to hold the linkage in the position shown.arrow_forwardDraw the FBDs for the entire structure and the member BDE. Count the total number of unknowns and the total number of independent equilibrium equations. Note that the cable that supports the 1200-lb weight runs over a smooth peg at D.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L