
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
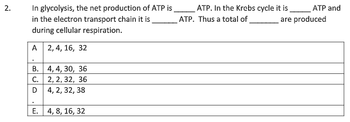
Transcribed Image Text:2.
In glycolysis, the net production of ATP is
in the electron transport chain it is
during cellular respiration.
A 2, 4, 16, 32
B.
4, 4, 30, 36
C.
2, 2, 32, 36
D
4, 2, 32, 38
E. 4, 8, 16, 32
ATP. In the Krebs cycle it is ATP and
are produced
ATP. Thus a total of
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A chemical or a poison may directly interfere with glycolysis A reacts with NADH and oxidizes it to NAD B reacts with oxygen and depletes its concentration in the cell C binds to pyruvate and inactivates it O increases fermentation E closely mimics the structure of glucose but is not metabolizedarrow_forwardNADH (Select all choices that apply) A. is an oxidized molecule B. is the reduced form of NAD+ C. is produced in photosynthesis non-cyclic reactions D. is responsible for allowing more ATP production than FADH2 E. plays a role in glycolysis, transition, Krebs cycle and the ETSarrow_forward8. Indicate the number of moles each of the molecules below formed from running three moles of glucose through glycolysis and Krebs cycle Moles produced from two moles of glucose running through Glycolysis Moles produced from two moles of glucose being oxidized in the PDC/Krebs Cycle Molecule Produced ATP GTP NADH + H* FADH2 CO2 D Focus United States) W DE DELL F11 F12 F8 F9 F10 F6 FZ (8)arrow_forward
- 1. What stages of energy transformation occur after glycolysis in the presence of oxygen? Pyruvate oxidation and fermentation O Pyruvate oxidation, citric acid cycle, and fermentation Pyruvate oxidation, citric acid cycle, and electron transport/ATP synthesis All of the above 2. Which statement is most accurate? * Oxygen is more electronegative than carbon Carbon is more electronegative than oxygen Oxygen and carbon are equally electronegative All of the above 3. Reduction is the of electrons (or hydrogens, since they are so generous with their electrons). Oxidation is the ___________ of electrons (or hydrogens) gain; loss loss: gain gain; gain loss; lossarrow_forward1. Overall, what do glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and electron transport do? (Know starting materials and products.) Explain very briefly how energy stored in glucose is converted into energy stored in ATP. Where are oxygen, carbon dioxide, glucose, water, and ATP involved, and how do they relate to each other? Where is the most number of ATP produced? 2. Account for the 6 Carbons in glucose. In other words where does the 6 carbons in glucose end up 3. When is fermentation used instead of cellular respiration? How does this apply to humans? Know the industrial uses of fermentation 4. What is ATP synthase do? Where is it located? 5. How are oxygen and carbon dioxide related to the function of the mitochondria? Why do we REALLY need to breathe? (Hint: where does CO2 come from? Where is O2 used?) 6. Know how cyanide stops cellular respirationarrow_forward5. Place the steps of Cellular respiration in order. A. Activation of the ATP Synthase B. ATP is invested C. Glucose oxidation completed and its carbon atoms released in carbon dioxide D. Glucose is split E. Pyruvate oxidized into Acetyl CoA F. Reduction of oxygen into water A. DBECFA B. BDECFA C. ABCDEF D. CEFBAD E. BDFEACarrow_forward
- Cellular respiration releases the energy stored in the (Level 1) bonds in carbon dioxide molecules bonds in glucose molecules atoms of oxygen atoms of carbon 26,420 MacBook Air 80 888 DII F3 F4 FS F7 F8 F2 2# $ & 3 4 5 9. 7 8 W E T. Y 一 D F G H J K C V M nd Barrow_forwardNADH pills can be purchased over the counter and are often taken by sufferers of chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS). How might these pills benefit a CFS patient? They would decrease the rate of alcoholic fermentation. They would decrease the rate of glycolysis. They would increase the number of electrons provided to the electron transport chain. They would increase energy by creating more FADH2.arrow_forward2. Consider a hypothetical organism that produces 12 moles of NADH and 2 moles of FADH2 during the oxidation of glucose. If 4 of the 12 moles of NADH were synthesized during glycolysis, determine the expected ATP output from these coenzymes if the G-3-P shuttle system is used. 36 ATP 32 ATP 34 ATP 42 ATParrow_forward
- 10. Using either the Oxidative Phosphorylation stage of cellular respiration or the Cytochrome complex of photosynthesis, DIAGRAM AND EXPLAIN how electron transport chains function and are used to generate ATP in plants and animals. Make sure to supply sufficient detail to clearly convey your understanding of the process/mechanism.arrow_forward3. Products of the citric acid cycle А. B and BLM 4.2-2 is released as waste. move to the next stage of cellular respiration. A glucose molecule produces C. Energy is released in the form of molecules of molecule of because two molecules of are created from each Copyright 2012 by Nelson Education Ltd.arrow_forward9. Identify the correct order of the four stages of cellular respiration A electron transport chain, glycolysis, Krebs cycle, transition reaction B. Krebs cycle, transition reaction, electron transport chain, glycolysis C. transition reaction, electron transport chain, glycolysis, Krebs cycle D Krebs cycle, glycolysis, electron transport chain, transition reaction E. Glycolysis, transition reaction, Krebs cycle, electron transport chainarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education