
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
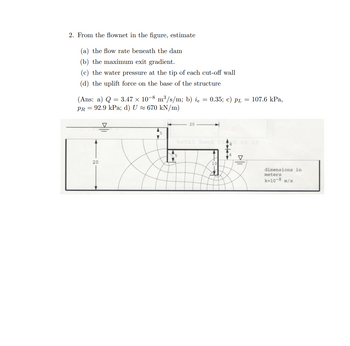
Transcribed Image Text:### Flow Net Analysis for Hydraulic Engineering
2. From the flownet in the figure, estimate:
(a) **The flow rate beneath the dam**
(b) **The maximum exit gradient**
(c) **The water pressure at the tip of each cut-off wall**
(d) **The uplift force on the base of the structure**
**Answers:**
- (a) \( Q = 3.47 \times 10^{-8} \, \text{m}^3/\text{s/m} \)
- (b) \( i_e = 0.35 \)
- (c) \( p_L = 107.6 \, \text{kPa}, \, p_R = 92.9 \, \text{kPa} \)
- (d) \( U \approx 670 \, \text{kN/m} \)
#### Diagram Explanation
The accompanying diagram is a flownet for a dam structure. It represents the flow of water beneath a dam, visualized by a set of equipotential lines and streamlines.
- **Dimensions:**
- The diagram uses a scale where the dimensions are marked in meters.
- The permeability coefficient (\( k \)) is \( 10^{-8} \, \text{m/s} \).
- **Key Features:**
- **Streamlines**: Curved lines representing paths followed by water particles in the flow.
- **Equipotential Lines**: Lines perpendicular to streamlines, indicating points of equal hydraulic head.
- **Flow Conditions:**
- The total head is indicated at a value of 10 meters.
- The cut-off walls are depicted at strategic points to control seepage and impact pressures.
- The diagram shows a change in direction where water infiltrates below the structure and appears to exit downstream.
This diagram and analysis are crucial for understanding the seepage patterns and ensuring the structural integrity against uplift pressures and seepage forces.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An upward flow of oil (mass density 800 kg/m³, dynamic viscosity (0.8 kg/m-s) takes place under laminar conditions in an inclined pipe of 0.1m diameter as shown in the figure. The pressures at sections 1 and 2 are = 200 kN/m². measured as p₁ = 435 kN/m² and P₂ 2- 45° 5m F5 The discharge in the pipe is equal toarrow_forwardThe siphon in Fig. is used to draw water from the large open tank. If the absolute vapor pressure for the water is p = 0.91 kPa, determine the shortest drop length L of the 40 mm diameter tube that will cause cavitation in the tube. Draw the energy and hydraulic grade lines for the tube.arrow_forwarda=4 b=0arrow_forward
- A partially open sluice gate discharges water into a rectangular channel. The tail water depth in the channel is 3m and Froude number is 1/2/2. If a free hydraulic jump is to be formed at downstream of the sluice gate after the vena contracta of the jet coming out from the sluice gate, the sluice gate opening should be (coefficient of contraction Cc = 0.9)arrow_forwardQ: The concrete dam shown in Figure is constructed on a soil with coefficient of permeability k = 0.06 cm/sec and ysat= 19.8 kN/m. Determine: 1- rate of flow (m/day) per meter run of the wall. 2- total head, elevation head, and pressure head at point A. 3- effective stress at point B. 4- hydraulic gradient at point D. 5- exit gradient. 6- depth of water outside the dam which cause instability at point C. 25 m 1.5 m 1= 1.2 m 8 m G.S.L XX WAY A 9 m D. 8 m B Datum AVAEN Rockarrow_forwardFor the 2D duct below, determine the stream function using 4x = 4y = 0.1 m. 3 m 2 m/s ► ► → 5 m 2m 1marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning