
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Answer the following questions
Ea=1.172
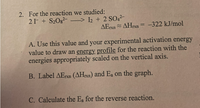
Transcribed Image Text:2. For the reaction we studied:
21- + S20g?-
–> I2 + 2 SO42-
AETX AHrxn = -322 kJ/mol
%3D
A. Use this value and your experimental activation energy
value to draw an energy profile for the reaction with the
energies appropriately scaled on the vertical axis.
B. Label AErxn (AHrxn) and Ea on the graph.
C. Calculate the Ea for the reverse reaction.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
When the reactants are converted to products, some bonds are broken and some are formed. This causes heat change in the reaction.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Gaseous methane (CH4) will react with gaseous oxygen (O₂) to produce gaseous carbon dioxide (CO₂) and gaseous water (H₂O). Suppose 5.77 g of methane is mixed with 41. g of oxygen. Calculate the maximum mass of water that could be produced by the chemical reaction. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. g x10 × Śarrow_forwardumol A chemist must prepare 975. mL of 16.0 µM aqueous silver(II) oxide (AgO) working solution. He'll do this by pouring out some 28.3 aqueous silver(II) oxide stock solution into a graduated cylinder and diluting it with distilled water. Calculate the volume in mL of the silver(II) oxide stock solution that the chemist should pour out. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forwardBlood alcohol content is a measure of alcohol in the blood as a percentage. It is calculated in grams per 100 mL of blood, so a BAC of 0.08 means your blood is 0.08% alcohol by volume. what is the total mass of alcohol (in grams) that is present for the same adult male whose total blood volume is 5.6L?arrow_forward
- A chemist prepares a solution of zinc nitrate ZnNO32 by measuring out 28.g of zinc nitrate into a 400.mL volumetric flask and filling the flask to the mark with water. Calculate the concentration in /molL of the chemist's zinc nitrate solution. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forwardThe speed of light is (2.998e8m/s) How far does light travel in 4.0μs? Set the math up. But don't do any of it. Just leave your answer as a math expression. Also, be sure your answer includes all the correct unit symbols.arrow_forwardA student sets up the following equation to convert a measurement. (The ? stands for a number the student is going to calculate.) Fill in the missing part of this equaarrow_forward
- A chemistry student weighs out 0.117 g of hypobromous acid (HBrO) into a 250. mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water. He plans to titrate the acid with 0.1600 M NaOH solution. Calculate the volume of NaOH solution the student will need to add to reach the equivalence point. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. mL 0 x10 Xarrow_forwardA A chemistry student weighs out 0.130 g of phosphoric acid (H,PO,), a triprotic acid, into a 250. mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water. He plans to titrate the acid with 0.1200 M NaOH solution. Calculate the volume of NaOH solution the student will need to add to reach the final equivalence point. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. mL x10arrow_forwardA student is asked to make up a 16% sodium chloride solution. She makes the solution by weighing an empty beaker (which has a mass of 98.5g). Sodium chloride is added to the beaker. The mass of the beaker and sodium chloride is 114.71 g. Lastly, the student added 84 mL of distilled water to the beaker. Reweighing the beaker she finds that the mass of the beaker, sodium chloride, ad distilled water is 196.14 g. What is the weight percentage of sodium chloride in this solution? Show all work.arrow_forward
- A major component of gasoline is octane (C,H,8). When octane is burned in air, it chemically reacts with oxygen gas (0,) to produce carbon dioxide (CO,) and water (H,O). What mass of carbon dioxide is produced by the reaction of 8.02 g of octane? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. x10 ?arrow_forwardsolution to a reaction flask. Calculate the mass in kilograms of barium acetate the A chemist adds 450.0 mL of a 1.0 mol/L barium acetate (Ba(C,H,O, chemist has added to the flask. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. | kg x10arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY