
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
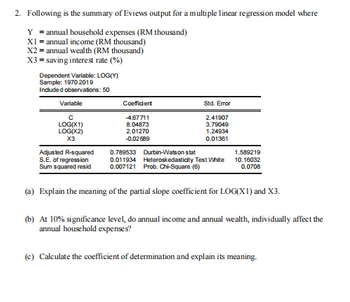
Transcribed Image Text:2. Following is the summary of Eviews output for a multiple linear regression model where
Y = annual household expenses (RM thousand)
X1 = annual income (RM thousand)
X2 = annual wealth (RM thousand)
X3 = saving interest rate (%)
Dependent Variable: LOG(Y)
Sample: 1970 2019
Included observations: 50
Variable
с
LOG(X1)
LOG(X2)
X3
Coefficient
-4.67711
8.04873
2.01270
-0.02689
Std. Error
2.41907
3.79049
1.24934
0.01361
0.789533 Durbin-Watson stat
Adjusted R-squared
S.E. of regression
Sum squared resid
0.011934 Heteroskedasticity Test White
0.007121 Prob. Chi-Square (6)
(a) Explain the meaning of the partial slope coefficient for LOG(X1) and X3.
1.589219
10.16032
0.0708
(b) At 10% significance level, do annual income and annual wealth, individually affect the
annual household expenses?
(c) Calculate the coefficient of determination and explain its meaning.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- When running a ols regression, if one of my 3 control variables are insignificant via T-test should I keep them in the regression/how should I interpret them?arrow_forwardSally Sells Sea Shells by the Sea Shore and collects all sales dataNow she is curious to find out what the elasticity of demand is for her shells Assume they are all the same type and quantity She scatter plots the data and finds there is a linear relationship that looks ripe for a regression estimation of the price response function for her shells The slope of her regression line is 61. Currently, her average daily price is 11.74 and she sells 95 quantity at that priceCalculate the point elasticity of demand for her sea shellsarrow_forward4) identify of intercept (B0), slope of regression line (B1) , and the p value and analysis of their meaningsarrow_forward
- Please briefly explain the results with explanation and clear points. Do not answer this of you want to copy and if you are not confident. Question - List the main results, and explain the intuition behind these results?arrow_forwardSuppose that a 5% rise in the price of apples does not cause the quantity demanded to change. The elasticityof demand for apples would then be: a. 0.b. –1.c. –2.d. infinitely large.arrow_forwardwages = B1 + B2educ + ßzexper + e where wages denotes hourly wages. We estimate the regression in R and obtain the output ## Coefficients: ## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|) ## (Intercept) 2.0 1.0 2 0.0455 * ## educ 0.5 0.5 1 0.3173 ## exper 2.0 0.5 4 6.33e-05 *** ## --- ## Signif. codes: ****' 0. 001 '**' 0.01 **' 0.05 ' 0.1 ' ' 1 Build a 90% confidence interval for B3 using a normal approximation. (Use that if Z ~ N(0, 1) and z1-a satisfies P(Z > z1-a) = a, then zo9 = 1.28, zo95 = 1.64, Z0.975 = 1.96, zo.99 = 2.33, and z0.995 = 2.58). Oa. [2 – 1.64 x (0.5), 2 + 1.64 x (0.5)] O b. [2 – 1.28 × (0.5), 2 + 1.28 x (0.5)] c. [2 – 1.28 x (0.5)², 2 + 1.28 × (0.5)²] O d. [2 – 1.64 × (0.5)², 2 + 1.64 × (0.5)²] O e. [2 – 1.96 × (0.5)², 2 + 1.96 × (0.5)²] O f. [2 – 1.96 × (0.5), 2 + 1.96 × (0.5)]arrow_forward
- q13-arrow_forwardYou estimated a regression with the following output. Source | SS df MS Number of obs = 289 -------------+---------------------------------- F(1, 287) = 41986.64 Model | 664544048 1 664544048 Prob > F = 0.0000 Residual | 4542496.25 287 15827.5131 R-squared = 0.9932 -------------+---------------------------------- Adj R-squared = 0.9932 Total | 669086544 288 2323217.17 Root MSE = 125.81 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Y | Coef. Std. Err. t P>|t| [95% Conf. Interval] -------------+---------------------------------------------------------------- X | 43.81013 .2138056 204.91 0.000 43.38931 44.23096 _cons | 49.31707 16.96222 2.91 0.004 15.93094 82.70319…arrow_forwardIn an OLS regression, which value represents the "best" R2 in terms of explained variance in the dependent variable? A. 2.53 B. 16.22 C. .001 D. 0.53arrow_forward
- Help!arrow_forwardYou estimated a regression with the following output. Source | SS df MS Number of obs = 411 -------------+---------------------------------- F(1, 409) = 4098.54 Model | 22574040.7 1 22574040.7 Prob > F = 0.0000 Residual | 2252702.97 409 5507.83122 R-squared = 0.9093 -------------+---------------------------------- Adj R-squared = 0.9090 Total | 24826743.7 410 60553.0334 Root MSE = 74.215 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Y | Coef. Std. Err. t P>|t| [95% Conf. Interval] -------------+---------------------------------------------------------------- X | 6.727341 .1050822 64.02 0.000 6.520772 6.933909 _cons | -.7552724 9.26027 -0.08 0.935 -18.95894 17.44839…arrow_forwardAn analyst working for your firm provided an estimated log-linear demand function based on the natural logarithm of the quantity sold, price, and the average income of consumers. Results are summarized in the following table: SUMMARY OUTPUT Regression Statistics Multiple R R Square Adjusted R Square Standard Error Observations ANOVA Regression Residual Total Intercept LN Price LN Income df 0.968 0.937 0.933 0.003 30 SS MS F 2 0.003637484 0.001818742 202.48598 0.000242516 8.98206E-06 27 29 0.00388 Coefficients Standard Error 0.57 0.00 0.13 0.51 -0.08 0.15 t Stat 0.90 -19.50 1.13 P-value 0.37 0.00 0.27 Significance F 5.55598E-17 Lower 95% -0.65 -0.09 -0.12 How would a 4 percent increase in income impact the demand for your product? Demand would increase by 60 percent. Demand would increase by 0.6 percent. Demand would decrease by 60 percent. Demand would decrease by 0.6 percent. Upper 95% 1.68 -0.07 0.41arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education