
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
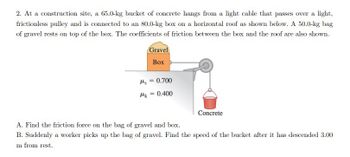
Transcribed Image Text:2. At a construction site, a 65.0-kg bucket of concrete hangs from a light cable that passes over a light,
frictionless pulley and is connected to an 80.0-kg box on a horizontal roof as shown below. A 50.0-kg bag
of gravel rests on top of the box. The coefficients of friction between the box and the roof are also shown.
Gravel
Box
s = 0.700
Mk = 0.400
Concrete
A. Find the friction force on the bag of gravel and box.
B. Suddenly a worker picks up the bag of gravel. Find the speed of the bucket after it has descended 3.00
m from rest.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 18 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 4. In the following figure, a box of m₂= 2.0 kg appears on an inclined plane with a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.15 that makes an angle of 30 degrees. It is connected by a string of negligible mass to a box m₁= 0.5 kg lying on a horizontal friction surface with a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.15. A force of 2.3 N to the right is applied to the box m₁. Determine: a. b. The acceleration of the boxes and the tension in the string. The value of the force applied so that the boxes move at a constant speed. 111 m₂arrow_forwardA sled is on a horizontal surface and a rope with tension T is pulling on it at an angle 0 above the horizontal. The sled had mass M and does not move due to the frictional force. In this case the coefficient of friction is µ̟. In terms of the variables given and g, what is the magnitude of the frictional force in this case? Select one: a. H, Mgsino b. Tcose O c. Tsin0 O d. H, Mgcos0arrow_forward2. A chain consists of identical links, each with a mass of 2.5 kg. You grab the top link and hold the chain at rest so that it hangs vertically. a) Draw a free body diagram of the bottom three links (labeled 1, 2, 3). Label all forces and use double subscript notation to denote which object exerts the force and which object is experiencing the force. b) Find the magnitude of the force exerted on link 1 by link 2, in Newtons. c) Find the magnitude of the force exerted on link 2 by link 3, in Newtons.arrow_forward
- 3. A 6.50 kg block is pressed against a vertical wall by a force (F), as shown in the figure below. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the wall is 0.41 and the directional angle 0 for the force is 46º. Determine the magnitude of the force (F) when the block is about to slide up the wall. N F éarrow_forwardA man pulls a 50.0-kg block of ice with a rope over his shoulder as shown below. Suppose that he applies just enough force to get the block moving and then he continues to apply the same force. If it takes 2.00 seconds for the block to move 3.00 meters and if the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface is ?? =0.100, determine the coefficient of static friction ?? between the block and the surface. You may assume that the acceleration of the block is constant.arrow_forwardMCQ 4. The first of two identical boxes of mass m is sitting on level ground. The second box is sitting on a ramp that makes a 20° angle with the ground. The normal force of the level ground on the first box is NL; the normal force of the ramp on the second box is NR. Which statement is correct? a. NR= NL = mg. b. N₁ mg; NR= mg sin 20°. C. NL = mg; NR = mg cos 20°. d. Nr.= mg; NR= -mg cos 20°. e. NR=-NL = -mg.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON