
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
1. A sanding block is being pushed up a vertical wall by a force F that is being applied at an angle of ? = 33.0° to the vertical as shown in the diagram. The block is moving up the wall at a constant speed. The mass of the block is 0.523 kg and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the wall is 0.937. Calculate the magnitude of the force F. To receive full marks, you must include a diagram showing the physical situation and your choice of coordinate system.
2. A 46.7-kg person, initially at rest, throws a 0.143-kg snowball forward with a horizontal speed of 33.5 m/s. A second person, with a mass of 47.5 kg, catches the snowball. Both people are on skates. The first person is initially at rest, as mentioned, and the second person is initially moving with a speed of 1.45 m/s toward the first person. Disregard air resistance and the friction between the skates and the ice. Take the direction in which the snowball is thrown to be the positive direction. Indicate the directions of the final velocities with the signs of your answers. To receive full marks, you must include a diagram showing the physical situation.
(a) Calculate the velocity of the first person immediately after they throw the snowball.
(b) Calculate the velocity of the second person immediately after they catch the snowball.
(a) thrower (first person) m/s (Give your answer to at least three decimal places.)(b) catcher (second person) m/s (Give your answer to at least three decimal places.)
3. A tire is tied to a rope that is tied to the branch of a tree so that the tire swings in a circular trajectory of radius h1 = 15.31 m. A child takes the tire to the top of a platform that is a height h2 = 12.60 m above the ground, sits in the tire, and swings from rest from the platform. The combined mass of the tire and child is 36 kg. The rope is taut when the child leaves the platform and you may neglect the mass of the rope. At the bottom of the circular trajectory, the child and tire are a height h3 = 0.99 m above the ground. To receive full marks, you must include a diagram showing the physical situation.
(a) Calculate the speed of the child/tire at the bottom of the circular trajectory. m/s
(b) Calculate the maximum tension in the rope as the child/tire swing back and forth. N --
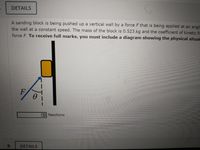
Transcribed Image Text:DETAILS
A sanding block is being pushed up a vertical wall by a force F that is being applied at an angle
the wall at a constant speed. The mass of the block is 0.523 kg and the coefficient of kinetic fr
force F. To receive full marks, you must include a diagram showing the physical situat
F
ENewtons
9.
DETAILS

Transcribed Image Text:18be that is tied to the branch of a tree so that the tire swings in a circular tra
that is a height h, 12.60 m above the ground, sits in the tire, and swings from rest from the
when the child leaves the platform and you may neglect the mass of the rope. At the bottom of
ground. To receive full marks, you must include a diagram showing the physical situatic
(a) Calculate the speed of the child/tire at the bottom of the circular trajectory.
(b) Calculate the maximum tension in the rope as the child/tire swing back and forth.
h
h
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Boxes A and B are connected to each end of a light vertical rope, as shown in the following figure. A constant upward force 80.0 N is applied to box A. Starting from rest, box B descends 11.5 m in 4.50 s. The tension in the rope connecting the two boxes is 32.0 N (Figure 1). Figure F A B 1 of 1 Part A What is the mass of box B? Express your answer with the appropriate units. MB = Submit Part B mA = Submit μA Provide Feedback Value Request Answer What is the mass of box A? Express your answer with the appropriate units. μA Value → Request Answer Units Units ? ?arrow_forwardA sled and rider have a total mass of 60.0 kg. They are on a snowy hill. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the sled and the snow is 0.150. The angle of the hill's slope measured upward from the horizontal is 24.0°. What is the acceleration of the rider?Is the acceleration greater, less than, or equal to your result if a more massive rider uses the same sled on the same hill? Explain.arrow_forwardA 12 kg mass hangs from a rope. A force is applied to the rope that the mass is accelerated upward at 2.6 m/s . What is the tension in the rope? Use g = 9.8 m/s ^ 2arrow_forward
- A 50-N object sits on a 20° rough incline. It is attached to a 10-N object over a pulley. The coefficients of static and kinetic friction are 0.70 and 0.20, respectively. We want to know whether or not the object will slide. With that in mind, fill out the following table, leaving any quantity that is not given as a variable: Force x-component y-component Tension Normal Weight Friction maarrow_forwardWhile moving in, a new homeowner is pushing a box across the floor at a constant velocity. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the floor is 0.393. The pushing force is directed downward at an angle below the horizontal. When is greater than a certain value, it is not possible to move the box, no matter how large the pushing force is. Find that value of 0. Number i Unitsarrow_forwardA block is being pulled by the string as shown below. The string has a tension T and makes an angle with the horizontal. A student claims that the kinetic friction is given by μmg where m is the mass of the block and uk is the coefficient of kinetic friction. Is or isn't this expression correct? Explain your reasoning. Hk m T 0arrow_forward
- Three cables are used to tie the balloon shown in Figure. Determine the magnitude of the vertical force (P) exerted by the balloon at A, knowing that the tension in cable AD is 954 N. y1 = 4.4 m y2 = 2.2 m x1 = 4.2 m x2 = 3 m z = 6 marrow_forwardWhat is T?arrow_forwardA zoologist pulls a block of hay towards an animal enclosure. The zoologist pulls at the angle of 27 degrees above the horizontal with a constant speed of 1 m/s. The mass of the hay is 60 kg and the coefficient of friction between the hay and the concrete is 0.29What is the value of the force F the zoologist is applying? please include a diagram using coordinate system and vectors, implied values, and known values.arrow_forward
- A block and a ball are connected by a string as shown in the figure. The block sits on a level, rough surface. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the surface is μ = 0.841. The ball hangs freely from the string. The mass of the block is 18.82 kg. What is the largest mass of a ball you could hang from the string without causing the block to slide?arrow_forwardA stockroom worker pushes a box with mass 12.9 kg on a horizontal surface with a constant speed of 2.50 m/s. The coefficients of kinetic and static friction between the box and the surface are 0.340 and 0.470, respectively. For general problem-solving tips and strategies for this topic, you may want to view a Video Tutor Solution of Delivering the goods. F₂ = 43.0 N Submit ✓ Correct Part B Previous Answers a = If the worker stops pushing, what will be the acceleration of the box? Express your answer in meters per second squared. Assume that + direction coincides with the direction of velocity. ► View Available Hint(s) Submit VI ΑΣΦ Previous Answers wwww ? X Incorrect; Try Again; 3 attempts remaining Review | Constants m/s²arrow_forwardSubject: physicsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON