
The following information is taken from the accounts of Latta Company. The entries in the T-accounts are summaries of the transactions that affected those accounts during the year.
| Manufacturing |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Debit | Credit | ||
| (a) | 460,000 | (b) | 390,000 |
| Balance | 70,000 |
| Work in Process | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Debit | Credit | ||
| Balance | 15,000 | (c) | 710,000 |
| 260,000 | |||
| 85,000 | |||
| (b) | 390,000 | ||
| Balance | 40,000 |
| Finished Goods | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Debit | Credit | ||
| Balance | 50,000 | (d) | 640,000 |
| (c) | 710,000 | ||
| Balance | 120,000 |
| Cost of Goods Sold | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Debit | Credit | ||
| (d) | 640,000 |
The overhead that had been applied to production during the year is distributed among Work in Process, Finished Goods, and Cost of Goods Sold as of the end of the year as follows:
| Work in Process, ending | $ 19,500 |
|---|---|
| Finished Goods, ending | 58,500 |
| Cost of Goods Sold | 312,000 |
| Overhead applied | $ 390,000 |
For example, of the $40,000 ending balance in work in process, $19,500 was overhead that had been applied during the year.
Required:.
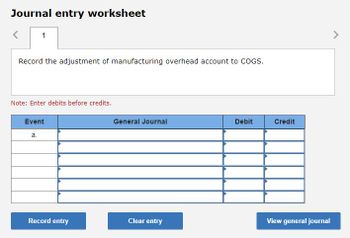
2. Assume that the underapplied or overapplied overhead is closed to Cost of Goods Sold. Prepare the necessary
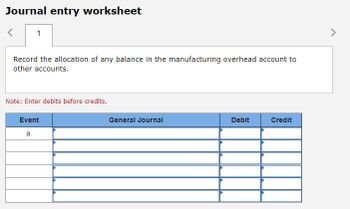
3. Assume that the underapplied or overapplied overhead is closed proportionally to Work in Process, Finished Goods, and Cost of Goods Sold. Prepare the necessary journal entry.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- am. 514.arrow_forwardAelan Products Company, a small manufacturer, has submitted the items below concerning last year's operations. The president's secretary, trying to be helpful, has alphabetized the list. Administrative salaries $4,800 Advertising expense 2,400 Depreciation—factory building 1,600 Depreciation—factory equipment 3,200 Depreciation—office equipment 360 Direct labour cost 43,800 Raw materials inventory, beginning 4,200 Raw materials inventory, ending 6,400 Finished goods inventory, beginning 93,960 Finished goods inventory, ending 88,820 General liability insurance expense 480 Indirect labour cost 23,600 Insurance on factory 2,800 Purchases of raw materials 29,200 Repairs and maintenance of factory 1,800 Sales salaries 4,000 Taxes on factory 900 Travel and entertainment expense 2,820 Work in process inventory, beginning 3,340 Work in process inventory, ending 2,220…arrow_forwardRecord the following journal entries for Brown Company: A (Click the icon to view the transactions.) (Record debits first, then credits. Exclude explanations from any journal entries.) 6. Purchased raw materials on account, $8,000. Date Accounts Debit Credit 7. Used $4,000 in direct materials and 600 in indirect materials in production. Date Accounts Debit Credit 7. 000 bich 700/ Iabor 6.arrow_forward
- Baltimore Manufacturing had a Work in Process balance of $64,000 on January 1, 2018. The year-end balance of Work in Process was $51,000 and the Cost of Goods Manufactured was $500,000. Use this information to determine the total manufacturing costs incurred during the fiscal year 2018.arrow_forwardAll products at Luke Corp. are allocated a portion of corporate overhead costs, which is computed as a percent of product revenue. The percentage rate is based on the level of corporate costs as a percentage of revenues. Data on corporate costs and revenues for the past two years were stated as: Corporate Revenue Corporate Overhead Costs Most recent year $ 112,750,000 $ 10,237,500 Previous year $ 76,200,000 $ 7,921,000 Using the data in the table apply the high low method (based on revenues) to determine the variable corporate overhead costs per sales dollar. Round to the nearest 0.001.arrow_forwardCan you please give answerarrow_forward
- Q. 8. Dula Manufacturing Company has two production departments: Cutting and Assembly. July 1 inventories are Raw Materials $4,200, Work in Process-Cutting $2,900, Work in Process-Assembly S10,600, and Finished Goods $31,000. During July, the following transactions occurred. (a) Purchased $85,200 of raw materials on account. (b) Incurred $60,000 of factory labor. (Credit Wages Payable.) (c) Incurred $60,000 of manufacturing overhead; $34,000 was paid and the remainder is unpaid. (d) Requisitioned materials for Cutting $15,500 and Assembly $9,200. (e) Used factory labor for Cutting $38,000 and Assembly $22,000. (f) Applied overhead at the rate of S16 per machine hour. Machine hours were Cutting 1,870 and Assembly 1,260. (g) Transferred goods costing $87,800 from the Cutting Department to the Assembly Department. (h) Transferred goods costing $120,700 from Assembly to Finished Goods. (i) Sold goods costing $190,000 for $205,000 on account. Instructions Journalize the transactions. (Omit…arrow_forwardAlpesharrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





