
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Can you use the formula in the second picture to answer it, please?

Transcribed Image Text:2. (a) Using table data presented in the text, calculate the focusing power Fmin of the crystalline
lens in the case when eye is focused to view distant objects. (b) Knowing that focusing power of the
cornea is Feornea = 42 D, calculate minimum focusing power of the eye. (c) Find what if the eye
focal length in this case.
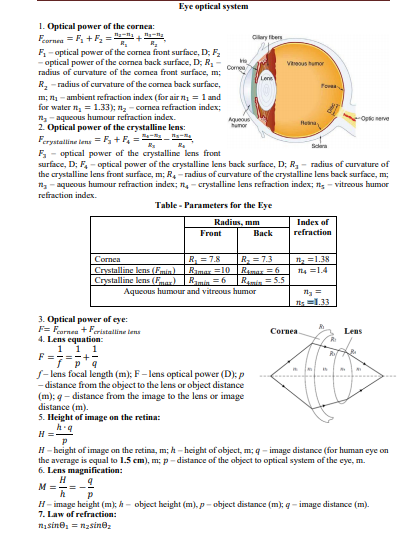
Transcribed Image Text:Eye optical system
1. Optical power of the cornea:
Fornea = F, + F =
F- optical power of the cornea front surface, D; F
- optical power of the cornea back surface, D; R,
radius of curvature of the comea front surface, m;
Clary fibers
R.
Vous humor
Comea
Lene
- radius of curvature of the comea back surface,
R,
Fora
m; n1 - ambient refraction index (for air n = 1 and
for water n, = 1.33); n - cornea refraction index:
n- aqueous humour refraction index.
2. Optical power of the erystalline lens:
Ferystalline tens =F +F, = s-a
E- optical power of the crystalline lens front
surface, D; F, - optical power of the crystalline lens back surface, D; R - radius of curvature of
the crystalline lens front surface, m; R, - radius of curvature of the crystalline lens back surface, m;
n - aqueous humour refraction index; n, - crystalline lens refraction index; n; - vitreous humor
Oplo nerve
Agueous
humor
Rena
Scera
refraction index.
Table - Parameters for the Eye
Radius, mm
Index of
refraction
Front
Back
R = 7.8
Ramar =10
Ramin =6
Aqueous humour and vitreous humor
R, = 7.3
R4maz =6
Ramie =5.5
Cornea
n, =1.38
n4 =1.4
Crystalline lens (Fmin)
Crystalline lens (Fmar)
=1.33
3. Optical power of eye:
F= Farnaa + Feristalline lens
4. Lens equation:
1 1. 1
Cornea
Lens
S- lens focal length (m); F- lens optical power (D); p
- distance from the object to the lens or object distance
(m); g – distance from the image to the lens or image
distance (m).
5. Height of image on the retina:
h.9
Н Е
H - height of image on the retina, m; h - height of object, m; q - image distance (for human eye on
the average is equal to 1.5 cm), m; p - distance of the object to optical system of the eye, m.
6. Lens magnification:
н
H- image height (m); h - object height (m), p - object distance (m); g - image distance (m).
7. Law of refraction:
nisine, = nzsinez
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Need help on finding the values of R_k , R_0 and S . If you can show me how to solve it step by step , thanks in advance .arrow_forwardCan you help with the second one. I have done the math several times and I always end up with 7.44. It's close to 7.44 (within ten per the guidance of the question.) It is not 82 degrees.arrow_forwardStudy Area Student Workbook Document Sharing User Settings An electron moves along the z-axis with v₂ = 2.6 × 107 m/s. As it passes the origin, what are the strength and direction of the magnetic field at the following (x, y, z) positions? Part A (1.0 cm, 0 cm, 0 cm) Express your answers in teslas separated by commas. ► View Available Hint(s) LIVE ΑΣΦ B₂, By, B₂ = Submit Part B (0 cm, 0 cm, 2.0 cm) Express your answers in teslas separated by commas. ► View Available Hint(s) B₂, By, B₂ = Submit IVE ΑΣΦ ? ? T T + 8arrow_forward
- Please answer the 3 subparts A,B,C with the step of solution, because i know the tutor can answer max 3 subparts . Thank u. ( Need In 60-120 minutes )arrow_forwardNeed help finding Y-coordinate I tried 2.21, 2.2, 2.208, and 2.206 and all were wrong.arrow_forwardPlease do it manually not typed and use the (law of Sins) DO NOT USE (COSINES)pleaseee…. show by drawing the angles tooo!!! Do first three questions means 1 ,2 ,3...arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON