
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
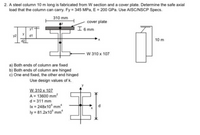
Transcribed Image Text:2. A steel column 10 m long is fabricated from W section and a cover plate. Determine the safe axial
load that the column can carry. Fy = 345 MPa, E = 200 GPa. Use AISC/NSCP Specs.
310 mm
cover plate
I6 mm
y2
10 m
TFF
W 310 x 107
a) Both ends of column are fixed
b) Both ends of column are hinged
c) One end fixed, the other end hinged
Use design values of k.
W 310 x 107
A= 13600 mm?
d = 311 mm
Ix = 248x10° mm
ly = 81.2x10° mm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The beam shown in Figure is a two-span beam with a pin (hinge) in the center of the left span,making the beam statically determinate. There is continuous lateral support. The concentratedloads are service live loads. Determine whether a W12 × 79 of A992 steel is adequate.a. Use LRFD.b. Use ASD.arrow_forward1) Column AB is made of solid 410, cold worked Steel with the following specification Sy=85 KSI, E-29000 KSI Length: 9.5 in. Diameter: 425 in. Ends: Free & Fixed For the above column calculate: a) Type of column failure (show proof) b) The critical load that would cause failure. c) Allowable force with Factor of Safety of 2.5. Answer Unit Value a 13 14 14arrow_forwardHelp me pls i give upvotee33earrow_forward
- A built up section of A992 steel, F, = 345 mPa is %3D made from plates fully welded together. The flanges consist of PL16×380 and PL12×500 for the web. Use the NSCP 2015 specifications. PL16×380 W̟ = 1.5wp A Wu = 3.6wp 10m Which of the following best gives the maximum service dead load, wp? O 40.2 kN/m 26.8 kN/m O 10.8 kN/m O 96.6 kN/m B. PL12x500arrow_forwardA built up compression section is shown in the figure. This forms a non-standard wide flange section. Assume KL - 2.4 m. Use A36 steel with Fy-248 MPa. Use NSCP Specifications. E-200 GPa a) Compute the reduction factor Qs, for unstiffened elements. 276mm STEEL DESIGN - CIVIL ENGINEERING 250mm 12mm 6mmarrow_forwardA plate is used as a tension member, to carry a deadload = 300 KN and live load of 260 KN. Steel used is A36, Fy= 248 MPa, Fu = 400 MPa. If the width of the tension plate is 210 mm, determine: a) The thickness of the plate based on NSCP 2015 ASD, bult used is M20.------ b) The thickness of plate based on NSCP 2015 LRFD. Bolt used is M20.-------- I M20 bolts- 210 mm -Tension Platearrow_forward
- PLEASE ANSWER IT ASAP FOR AN UPVOTE. THANKYOU.arrow_forwardA W14X120 is used as a tension member in atruss. The flanges of the member are connected to a gusset plate by 3/4 inch boltas shown below. Use A36 steel with Fy-36 ksi and Fu=58 ksi Determine the Yielding Capacity of the section based on LRFD (kips) Determine the Tensile Rupture capacity of the section based on LRFD Determine the Demand to Governing Capacity Ratio (based on yielding and rupture only) if the Demand load carried by the section are DL=200 kips LL=400 kips use LRFD Properties and Dimension Ag=35.30 in^2 x = 6.24 in ry= 3.74 in d=14.5 in tf=0.94 in bf=14.7 in tw=0.59 in k=1.54 d=14.5 Y k1=1.5 bf=14.7 tf-0.94 X -tw=0.59 Harrow_forwardIn steel design use nscp 2015 i need a complete solutions ty..arrow_forward
- A W14 x 61 must support a concentrated service live load of 665 KN applied to the top flange. Assume that the load is at a distance of at least half the beam depth from the support and design a bearing plate. Use E= 345 MPa for the beam, E= 250 MPa for the plate and fe'= 21 MPa. Use LRFDarrow_forwardA rectangular tied braced column is reinforced with 6-28mm bars as shown in the figure below. Check the adequacy of the column for the following gravity loads: - - - - - - Service dead load = 1050kN Service live load = 850 kN Service dead load moment = 39 kN-m Service live load moment = 27 kN-m top=bott. = 1.0 40 lu = 5.0m f = 27.6 N/mm², fy = 414 N/mm² axis of bending 500mm Ties 10mm@300c/c } 350mm At eccentricity of 40mm P M +40 + 500mm MU +40- P Top end Bott. endarrow_forwardQ3) The beam shown in Figure below has lateral support at the ends only. The concentrated loads are live loads. Use A992 steel and select a W shape. (Do not check deflections. Use C-1). 23 k 25 k ttstarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning