
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
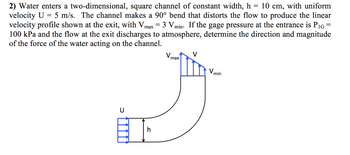
Transcribed Image Text:2) Water enters a two-dimensional, square channel of constant width, h = 10 cm, with uniform
velocity U = 5 m/s. The channel makes a 90° bend that distorts the flow to produce the linear
velocity profile shown at the exit, with Vmax Vmin. If the gage pressure at the entrance is P₁G =
100 kPa and the flow at the exit discharges to atmosphere, determine the direction and magnitude
of the force of the water acting on the channel.
3 V.
V
J
U
ET
Vmax
Vm
min
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A pipe of diameter 11 cm conveying 200 liters/s of water has bend of angle (θ = 90⁰if last digit is zero/even and θ = 0⁰ if last digit is odd) through horizontal plane. Find theresultant force exerted on the bend if the pressure at the inlet and outlet of the bend are 15N/cm2 and 10 N/cm2respectively.arrow_forwardA Borda's mouthpiece 150 mm in diameter discharges water under a head of 3 m. Determine the discharge in L/s if under ideal conditions, the coefficients of a Borda's mouthpiece are Cc = 0.5 and Cv = 1.0.arrow_forward3. Consider the one-dimensional, incompressible flow through the circular channel shown. The velocity at section 1 is given by U=Uo+ U₁ sin(t), where Uo= 20 m/s, U₁ = 2 m/s, and co-0.3 rad/s. The channel dimensions are L- 1 m, R₁-0.4 m, and R₂-0.2 m. Determine the particle acceleration at the channel exit. Plot the results as a function of time over a complete cycle. On the same plot, show the acceleration at the channel exit if the channel is constant area, rather than convergent, and explain the difference between the curves. T R₁ ✓ X1 L X2arrow_forward
- Oil flows through the 100-mm-diameter pipe with a velocity of 8 m/s (Figure 1). The flow occurs in the horizontal plane. Take p = 900 kg/m³. ▼ Part A If the pressure in the pipe at A and B is assumed to be 90 kPa, determine the component of force the flow exerts on the elbow. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ▾ View Available Hint(s) ▾ Hint 1. How to determine the component of force the flow exerts on the elbow Build a free body diagram of the control volume containing oil within the pipe and elbow between cross-sections at A and B. Then using the linear momentum equation determine the component of the force the flow exerts on the elbow. F₂ = Part B HÅ Submit Previous Answers Request Answer Value Fy = X Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining Submit Units If the pressure in the pipe at A and B is assumed to be 90 kPa, determine they component of force the flow exerts on the elbow. Express your answer to three significant figures and…arrow_forward2. Find the velocity field and volumetric flow rate for two stationary plates, imposing pressure p0 on the left endof the channel, and pressure p0 + ∆p (∆p > 0) on the right end of thechannel.arrow_forwardWater flowing in a pipe reaches a point where the cross-sectional area of the pipe is reduced to 1/3 of its previous value. If the speed of the water before the constriction is 1.31 m/s, what is the speed of the water after the constriction?arrow_forward
- Your team is designing a chemical processing plant. You are the liquid handling and transportation specialist, and you need to transport a solvent (μ = 3.1 cP, ρ = 122k kg/m3) from a storage tank to a reaction vessel. Due to other equipment constraints, the fluid velocity must be 0.8 m/sec, and you must use stainless steel piping (ε = 0.00015 mm) with a total length (L) of 12 m. Determine the pipe inner diameter (ID) you will need to achieve a pressure drop of 0.3 kPa. Use the Moody chart.arrow_forwardThe gate shown below has a width, W = 2m, and its shape is described by the equation y = VHx, with H = 1 m. A jet of water with cross sectional area, S = 0.05 m², strikes the top of the gate and is deflected by 60°. What must be the speed of the jet for this situation to be in equilibrium? 60° y = VHx H2O |H =1m ↑ hingearrow_forwardAn incompressible fluid flows steadily through two pipes of diameter 0.15 m and 0.2 m which combine to discharge in a pipe of 0.3 diameter. If the average velocities in the 0.15 m and 0.2 m diameter pipes are 2 m/s and 3 m/s respectively, then find the average velocity in the 0.3 m diameter pipe.arrow_forward
- Question is a fluid mechanicsarrow_forwardAn elbow deflects water upward and discharges it to the atmosphere at a specific rate. Determine the gage pressure at the inlet of the elbow and the anchoring force needed to hold the elbow in place. (gage pressure at the outlet is zero)arrow_forwardWater flows through a constricted pipe at a uniform rate. At one point, the diameter of the pipe is 0.056 m and the pressure is 5.7 x 104N/m2. At another point, 0.8 m higher than the previous point, the diameter is 0.023 m and the pressure is 1 X 104N/m2 . Calculate the velocities at the lower section and the upper section. Also calculate the rate of flow. Density of water = 1000 kg/m3.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY