
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
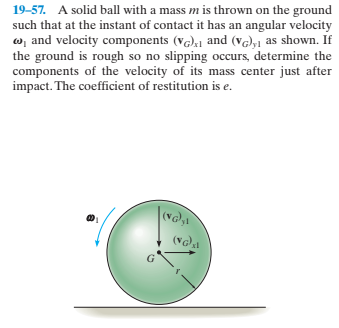
Transcribed Image Text:19-57. A solid ball with a mass m is thrown on the ground
such that at the instant of contact it has an angular velocity
w, and velocity components (vG),1 and (v),1 as shown. If
the ground is rough so no slipping occurs, determine the
components of the velocity of its mass center just after
impact. The coefficient of restitution is e.
(NG,
(VGa
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A motorcycle and rider have a combined mass of 350kg. The vehicle's velocity is 100 km/hr. The rider is to go up a hill incline of 10 meters. The wheels each have a mass of 20 kg and a diameter of 500mm. The wheel design consists of 6 spokes with a mass of 0.5 kg for each spoke. a. Determine the vehicle's velocity at the top of the hill, assuming it was a rolling vehicle with engine being turned off. a. Indicate the vehicle's velocity at each meter through the climb. b. Explain the transfer energy and how this affects the behaviour of the system. At another point in its journey, the motorcycle and rider travel at 80 km/h around a left-hand bend of radius 30m. Calculate: a) The angular velocity of each wheel. b) The moment of inertia of each wheel. c) The angular momentum of the wheel prior to entering the bend. d) The magnitude of the gyroscopic torque produced on the bike as the rider is driving around the bend. What is the effect and why is it important to calculate the gyroscopic…arrow_forwardThe mass center, G, of the 2-lb ball has a velocity of (vd - 5 ft/s when it strikes the end of the smooth 4-lb slender bar, which is at rest. The bar has a length l-Sft. The coefficient of restitution is e-0.8. The goal is to find the angular velocity of the bar after impact. Steo 5: Finally find the angular velocity of the bar after impact in rad/s. Give your answer with 2 decimal placesarrow_forwardEXAMPLE 4 A solid ball with a mass m is thrown on the ground such that at the instant of contact it has an angular velocity and velocity components (VG) and (VG) as shown. If the ground is rough so no slipping occurs, determine the components of the velocity of its mass center just after impact. The coefficient of restitution is e. (va)yt (va)aarrow_forward
- The 0.7 lblb ball is shot from the spring device shown Determine the smallest stiffness k which is required to shoot the ball a maximum distance of 31 in. up the smooth plane after the spring is pushed back 3 in . and the ball is released from rest. The four cords C and plate P keep the spring compressed 2 in. when no load is on the plate.arrow_forwardProblem 96. A child throws a ball from point A with a speed of 50 ft/sec. It strikes the wall at point B and then returns exactly to point A. Determine the necessary angle a if the coefficient of restitution in the wall impact is e = 0.5. -10-arrow_forwardDetermine the velocity of the 58.4-kg cylinder after it has descended a distance of 1.9 m, starting from rest. Gear A has a mass of 10 kg and a radius of gyration of 125 mm about its center of mass. Gear B and drum C have a combined mass of 30 kg and a radius of gyration about their center of mass of 150 mm. 150 mm 200 mm -100 mm Darrow_forward
- ?arrow_forwardBall B is suspended from a cord of length l attached to acart A, which can roll freely on a frictionless, horizontal track.The ball and the cart have the same mass m . If the ballis given an initial horizontal velocity Vo while the cart is atrest, describe the subsequent motion of the system, specifying thevelocities of A and B for the following successive values of theangle θ (assume positive counterclockwise) that the cord willform with the vertical: (a) θ = θmax (b) θ = 0 (c) θ = θminarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY