
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780133594140
Author: James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
1
Transcribed Image Text:192.168.20.0/24
AS2
192.168.10.0/24
17.00.0/
16.00.0/8
18.0.0.0/8
192.168.30.0/24
R2
R1
15.0.0.0/8
AS1
130.10.00/16
10.0.0.0/8
130.20.0.0/16
R4
R3
AS4
11.00.0/
110.30.0.0/16 AS3
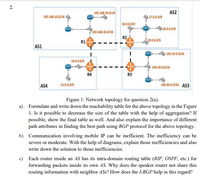
Figure 1: Network topology for question 2(a).
a) Formulate and write down the reachability table for the above topology in the Figure
1. Is it possible to decrease the size of the table with the help of aggregation? If
possible, show the final table as well. And also explain the importance of different
path attributes in finding the best path using BGP protocol for the above topology.
b) Communication involving mobile IP can be inefficient. The inefficiency can be
severe or moderate. With the help of diagrams, explain those inefficiencies and also
write down the solution to those inefficiencies.
c) Each router inside an AS has its intra-domain routing table (RIP, OSPF, etc.) for
forwarding packets inside its own AS. Why does the speaker router not share this
routing information with neighbor ASs? How does the I-BGP help in this regard?
2.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 8 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The Science of Computing Mystery Mania Six men: Bill Fox, Tom Smith, Robert Stevenson, Fred Edison, Larry Davis, and John Harrison were in a library together. Suddenly, the lights went out. When the lights came back on, Bill Fox was found shot. The other detectives have investigated; questioned the suspects, the witnesses, and people who know the suspects; and have collected physical evidence from the crime scene. They have collected 14 clues but have not been able to solve the crime. It's now up to you. Note that no two suspects have the same height, color car, color umbrella, color shirt, or color shoes. The clues: • John Harrison owns a purple car Tom Smith is 5'3" tall • The suspect who was wearing a yellow shirt owns a red car The suspect who is 5'6" tall was wearing a blue shirt • The suspect who owns a red car is 6'3" tall • The suspect who was carrying a yellow umbrella is not the one who owns a green car • The suspect who is 6' tall is not the one who was wearing a black shirt…arrow_forwardIn what year did John von Neumann get his doctoral degree?arrow_forwardIs there any way to tell how John von Neumann's educational background influenced his mathematical work?arrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you
 Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science
Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning
Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education
Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY
Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780133594140
Author:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780124077263
Author:David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781337569330
Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Concepts of Database Management
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781337093422
Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. Last
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Prelude to Programming
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780133750423
Author:VENIT, Stewart
Publisher:Pearson Education

Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781119368830
Author:FITZGERALD
Publisher:WILEY