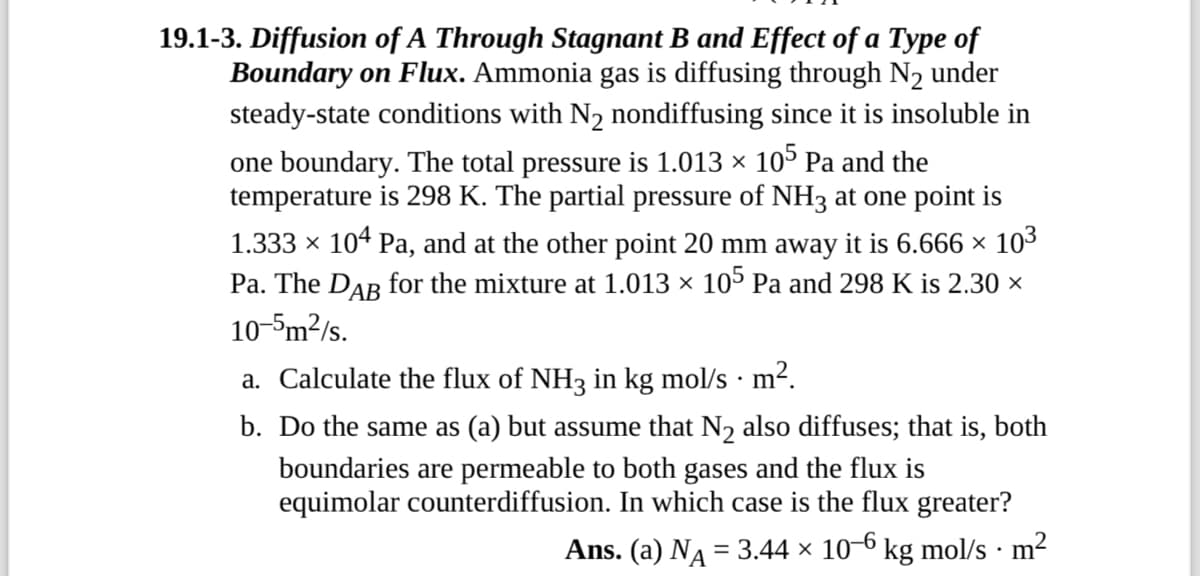
19.1-3. Diffusion of A Through Stagnant B and Effect of a Type of Boundary on Flux. Ammonia gas is diffusing through N2 under steady-state conditions with N₂ nondiffusing since it is insoluble in one boundary. The total pressure is 1.013 × 105 Pa and the temperature is 298 K. The partial pressure of NH3 at one point is 1.333 × 104 Pa, and at the other point 20 mm away it is 6.666 × 10³ Pa. The Dâŋ for the mixture at 1.013 × 105 Pa and 298 K is 2.30 × 10-5m²/s. . a. Calculate the flux of NH3 in kg mol/s · m². b. Do the same as (a) but assume that N2 also diffuses; that is, both boundaries are permeable to both gases and the flux is equimolar counterdiffusion. In which case is the flux greater? Ans. (a) NA = 3.44 × 10-6 kg mol/s · m²
19.1-3. Diffusion of A Through Stagnant B and Effect of a Type of Boundary on Flux. Ammonia gas is diffusing through N2 under steady-state conditions with N₂ nondiffusing since it is insoluble in one boundary. The total pressure is 1.013 × 105 Pa and the temperature is 298 K. The partial pressure of NH3 at one point is 1.333 × 104 Pa, and at the other point 20 mm away it is 6.666 × 10³ Pa. The Dâŋ for the mixture at 1.013 × 105 Pa and 298 K is 2.30 × 10-5m²/s. . a. Calculate the flux of NH3 in kg mol/s · m². b. Do the same as (a) but assume that N2 also diffuses; that is, both boundaries are permeable to both gases and the flux is equimolar counterdiffusion. In which case is the flux greater? Ans. (a) NA = 3.44 × 10-6 kg mol/s · m²
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:19.1-3. Diffusion of A Through Stagnant B and Effect of a Type of
Boundary on Flux. Ammonia gas is diffusing through N2 under
steady-state conditions with N₂ nondiffusing since it is insoluble in
one boundary. The total pressure is 1.013 × 105 Pa and the
temperature is 298 K. The partial pressure of NH3 at one point is
1.333 × 104 Pa, and at the other point 20 mm away it is 6.666 × 10³
Pa. The Dâŋ for the mixture at 1.013 × 105 Pa and 298 K is 2.30 ×
10-5m²/s.
.
a. Calculate the flux of NH3 in kg mol/s · m².
b. Do the same as (a) but assume that N2 also diffuses; that is, both
boundaries are permeable to both gases and the flux is
equimolar counterdiffusion. In which case is the flux greater?
Ans. (a) NA = 3.44 × 10-6 kg mol/s · m²
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 5 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285061238
Author:
Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:
Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780072848236
Author:
Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Companies, The