
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
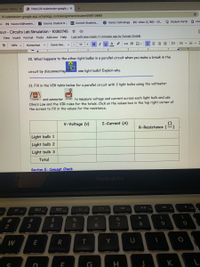
Transcribed Image Text:**Circuits Lab Simulation Exercise**
**20. Question:**
What happens to the other light bulbs in a parallel circuit when you make a break in the circuit by disconnecting one light bulb? Explain why.
**21. Task:**
Fill in the VIR (Voltage, Current, Resistance) table below for a parallel circuit with 3 light bulbs using the voltmeter and ammeter to measure voltage and current across each light bulb and use Ohm’s Law and the VIR rules for the totals. Click on the values box in the top right corner of the screen to fill in the values for the resistance.
**Data Collection Table:**
| Light Bulb | V-Voltage (V) | I-Current (A) | R-Resistance (Ω) |
|---------------|---------------|---------------|------------------|
| Light Bulb 1 | | | |
| Light Bulb 2 | | | |
| Light Bulb 3 | | | |
| **Total** | | | |
**Section E: Concept Check**
**Explanation of Graphs and Diagrams (in absence of diagrams):**
In this activity, you'll be using a simulation tool to observe and measure the characteristics of a parallel circuit. This includes understanding how voltage, current, and resistance behave in parallel circuits.
- **V-Voltage (V):** This column is for recording the voltage across each light bulb. In a parallel circuit, the voltage across each component (light bulb) remains the same.
- **I-Current (A):** This column is for recording the current flowing through each light bulb. In a parallel circuit, the total current is the sum of currents through each branch.
- **R-Resistance (Ω):** This column is for calculating the resistance for each light bulb using Ohm’s Law, R = V/I, where V is voltage and I is current.
Use the provided voltmeter and ammeter tools to measure these values accurately and fill in the table accordingly.

**Figure Description:**
The image includes two separate parallel circuits with light bulbs:
- The top circuit has 2 light bulbs connected in parallel.
- The bottom circuit has 3 light bulbs connected in parallel.
Each light bulb in both circuits emits light rays indicating brightness.
**Question:**
a. Based on the length of the light rays, when a third light bulb is added in parallel the brightness of each bulb _________.
---
In the provided images:
- There are diagrams showing the two parallel circuit setups.
- The top diagram demonstrates 2 light bulbs wired in parallel, each showing long light rays indicating they are bright.
- The bottom diagram shows 3 light bulbs in parallel with slightly shorter light rays for each light bulb compared to the top diagram, suggesting a difference in brightness.
**Conclusions:**
When comparing the brightness of the light bulbs:
- As more bulbs are added in parallel, the brightness of each individual bulb may vary.
- Typically, by adding more bulbs in parallel, the overall brightness can be affected, and each bulb may get slightly dimmer due to the distribution of the constant voltage from the battery.
This comparison helps in understanding the relationship between the number of components in a parallel circuit and their individual performances.
---](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/e59874f9-f705-461a-94a3-07d771601ab4/2344c9d9-3ace-4227-b053-7cd05dd0f1b9/chn53oi_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:---
### Circuits Lab Simulation - 10382745
**Instructions:**
15. Keep the battery voltage the same and build another parallel circuit next to the first parallel circuit using 3 light bulbs.
19. Compare the brightness of 2 light bulbs wired in parallel relative to the brightness of 3 light bulbs wired in parallel.

**Figure Description:**
The image includes two separate parallel circuits with light bulbs:
- The top circuit has 2 light bulbs connected in parallel.
- The bottom circuit has 3 light bulbs connected in parallel.
Each light bulb in both circuits emits light rays indicating brightness.
**Question:**
a. Based on the length of the light rays, when a third light bulb is added in parallel the brightness of each bulb _________.
---
In the provided images:
- There are diagrams showing the two parallel circuit setups.
- The top diagram demonstrates 2 light bulbs wired in parallel, each showing long light rays indicating they are bright.
- The bottom diagram shows 3 light bulbs in parallel with slightly shorter light rays for each light bulb compared to the top diagram, suggesting a difference in brightness.
**Conclusions:**
When comparing the brightness of the light bulbs:
- As more bulbs are added in parallel, the brightness of each individual bulb may vary.
- Typically, by adding more bulbs in parallel, the overall brightness can be affected, and each bulb may get slightly dimmer due to the distribution of the constant voltage from the battery.
This comparison helps in understanding the relationship between the number of components in a parallel circuit and their individual performances.
---
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- a clam-on metter is used to test circuitarrow_forwardA dc ammeter has an internal resistances of 0.1 ohm. A shunt of 1.010 milliohm is connected to the ammeter. What is the multiplier of the set-up?arrow_forwardCalculate the minimum main protection for 6 A/C air conditioners, their main conductors and the minimum protections of each individual air conditioner and their cables (90degrees) and their equipment grounding, their pvc piping, their grounding of the grounding electrode (main supply) for the following valuesarrow_forward
- A series circuit consists of three identical lamps are connected to a battery as shown in Figure below. The switch S, originally open, is closed. What then happens to the brightness of lamp B? A B C S Select one or more: a. It increases b. It does not change c. It decreases d. It drops to zero. + OOOOarrow_forwardVdc0 U=12 V Circuit #1 Ried V LED www Ried_series 0.05 Vdc0 U = 12 V 0,04 Circuit 0.03 0.02 0.01 RED LED GREEN LE Set current to 10 mA LED voltages Given the circuit #1 presented above, answer the following questions: BLUE_LEC Red 0.5 1) Determine the value of the V₁ (voltage forward of the LED) for the LEDS RED, VDRED GREEN, VREEN and BLUE, VOBLUES when the current through the LEDs is 10mA, 2) Is the LED in Circuit #1, connected in the way that will be lighting up or not - Justify your answer Green 3) Calculate the value of the resistance Rled in Circuit #1, to ensure that a RED LED will have a current of 10 mA 1.5 2 25 Voltage across LED (V) 4) Calculate the value of the resistance Rled in Circuit #1, to ensure that a GREEN LED will have a current of 10 mA Blue 5) Calculate the value of the resistance Rled in Circuit #1, to ensure that a Blue LED will have a current of 10 mA 6) Given three LEDs, connected in series as shown in the Circui # 2 (below), calculate the value of the…arrow_forward2. A bank of nickel-cadmium cells is used as the emergency lighting supply for a hospital. There are 100 cells connected in series and each has an A-hr rating of 120 A-hr. The bank has to be replaced, and the manufacturer is no longer supplying nickel-cadmium cells. It is decided to replace the cells with lead-acid cells. How many lead-acid cells will be required if each has an A-hr rating of 60 A-hr, and how should they be connected?arrow_forward
- Which of the following statements is true of an open component in a series circuit? a.. The circuit current will be higher than normal. b. The voltage drop across the component will be lower than normal. c. The voltage drop across the component will be higher than normal. d, The resistance of the component will be lower than normal.arrow_forwardA 0 – 150 voltmeter has a resistance of 2000-ohms per volt. It is desired to change this voltmeter to a 0 – 600 volt instrument by the edition of an external multiplier. What is the resistance, in ohms, of this external multiplier?arrow_forwarda 12 volt source with an internal resistance of 1.2 ohm is connected across a wire wire wound resistor. maximum power will be disipated in the resistor when its resistance is equal to.arrow_forward
- Repeat above (insert image) with the resistors in parallel, insert multitesters (digital or analog) to measure current along each resistor. Comment on the meter readings and set up.arrow_forwardKindly answer all of the questions please, I will rate you with like/upvote. Please answer all of the questions. Thank you so much.arrow_forwardIn step 3, what is the potential difference across D2 after the jumper wire is connectedarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,