
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:w History
Bookmarks
People
Tab
Window
Help
Practice Test x
SAT Practice Test #3| SAT Suit X
O Magnetism Assessment
com/formatives/6057e04c0e661559058a72de
e
O Maps
S Advertisement
8
9.
10
11
12
13
14
15 16
17 18
19 20
Particles B is negative and Particle C is positive
Particle A is travelling equal to or faster than the speed of light
Particles C is negative and Particle B is positive
19
If a charged particle enters an external magnetic field and it moves in a circular orbit, then what must be true?
The particle maintains a constant velocity in the field.
The particle maintains a constant speed in the field.
Positive work is done by the field on the particle.
Negative work is done by the field on the particle.
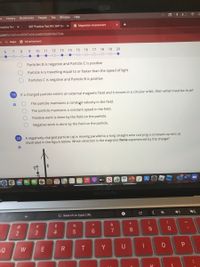
A negatively charged particle (-q) is moving parallel to a long straight wire carrying a constant current as
illustrated in the figure below. Which direction is the magnetic force experienced by the charge?
20
étv
22
MacBook Pro
G Search or type URL
#3
2$
&
4.
7
8.
9.
Q
W
Y U
* 3
OO OO
OOO
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q) If you wanted to shield your electronics from stray magnetic fields, what would you use for the box around your electronics. Explain why.arrow_forward1.) When a particle moves under the influence of a magnetic field, the speed of the particle remains constant. Explain why the magnetic force doesn’t change the speed. Why does this also imply that magnetic fields cannot do work?arrow_forward5arrow_forward
- A charged particle moving through a magnetic field at right angles to the field with a speed of 27.7 m/s experiences a magnetic force of 2.98 10-4 N. Determine the magnetic force on an identical particle when it travels through the same magnetic field with a speed of 5.14 m/s at an angle of 27.2° relative to the magnetic field.Narrow_forward13 A proton moves perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field B at a speed of 2.10 x 10' m/s and experiences an acceleration of 1.90 × 10 m/s- in the positive x-direction when its velocity is in the positive z-direction. Determine the magnitude and direction of the field. magnitude direction ---Select--- Varrow_forward173% NASA and the military have long been interested in so-called “rail guns" to launch projectiles and payloads at very high velocities. A schematic of a rail gun is shown below, where there are two parallel rails separated by a distance d and connected to a powerful battery of voltage V, in a constant magnetic field B = Bok pointing out of the page. The projectile / payload can be modeled as a bar of mass m and resistance R which connects the two rails and completes the circuit. Assume the electrical resistance of the rails is negligible, but take there to be a constant force of kinetic friction with magnitude ƒ between the bar and the rails. (a) What is the current in the circuit when the bar is moving with velocity v? Remember to account for both the battery and the induced EMF. (b) What is the net force on the bar when it is moving with velocity v? (c) Using Newton's second law, F = ma, find a differential equation relating and v. (d) Verify that the solution to your differential…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON