
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
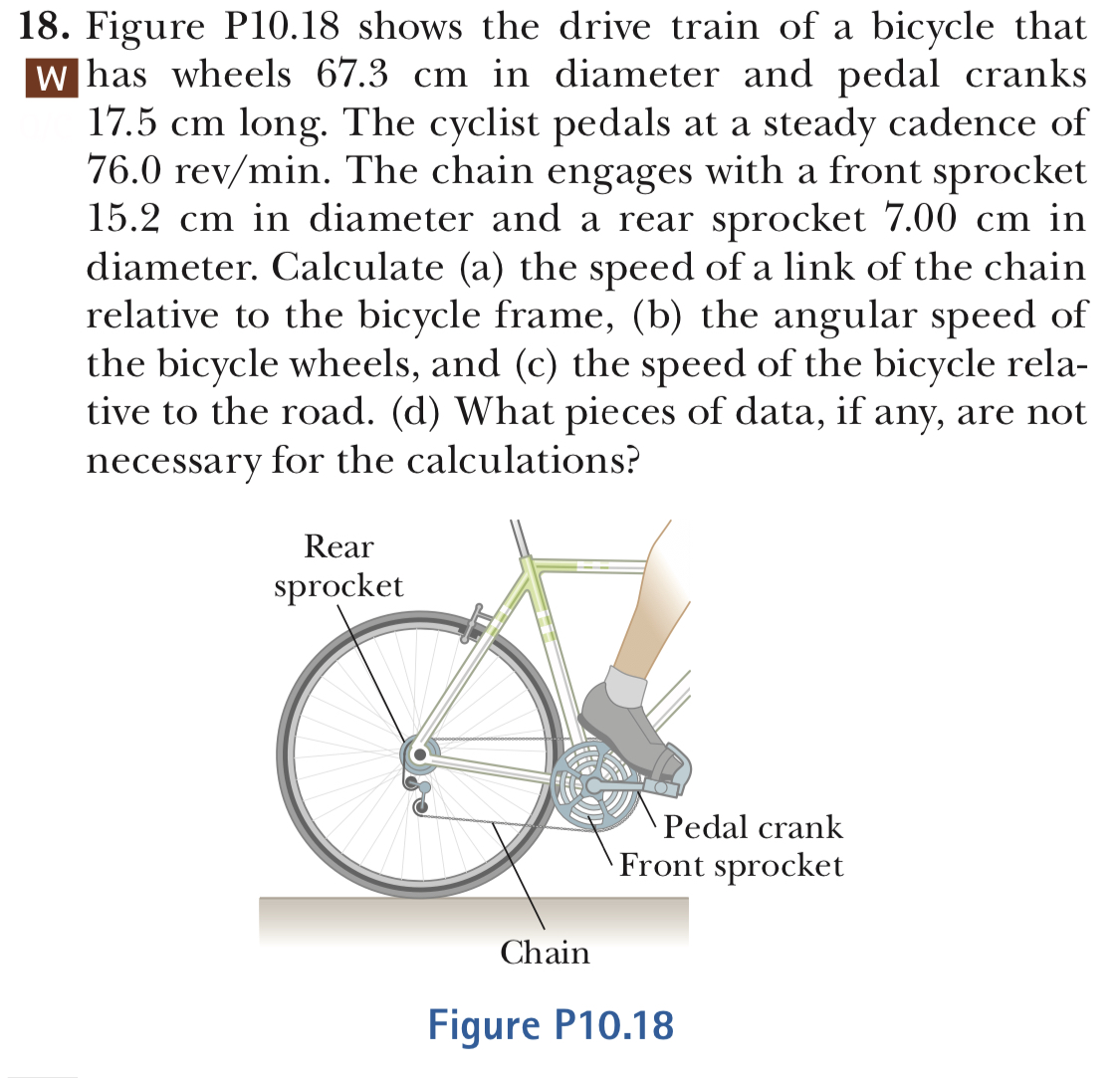
Transcribed Image Text:18. Figure P10.18 shows the drive train of a bicvcle that
has wheels 67.3 cm in diameter and pedal cranks
17.5 cm long. The cyclist pedals at a steady cadence of
76.0 rev/min. The chain engages with a front sprocket
15.2 cm in diameter and a rear sprocket 7.00 cm in
diameter. Calculate (a) the speed of a link of the chain
relative to the bicycle frame, (b) the angular speed of
the bicycle wheels, and (c) the speed of the bicycle rela-
tive to the road. (d) What pieces of data, if any, are not
necessary for the calculations?
Rear
sprocket
Pedal crank
Front sprocket
Chain
Fiqure P10.18
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 7 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The pulley in the figure has radius R = 1.0m and moment of inertia I = 10kg.m2. The block of mass m = 100 kg is displaced down a distance h from its equilibrium position, and is released from rest at t = 0. Determine the period of oscillation of the pulley. Consider that (k = 1000 N / m)arrow_forwardEngineers are designing a system by which a falling mass m imparts kinetic energy to a rotating uniform drum to which it is attached by thin, very light wire wrapped around the rim of the drum (the figure (Figure 1)). There is no appreciable friction in the axle of the drum, and everything starts from rest. This system is being tested on earth, but it is to be used on Mars, where the acceleration due to gravity is 3.71 m/s2. In the earth tests, when m is set to 13.0 kg and allowed to fall through 5.00 m, it gives 300.0 J of kinetic energy to the drum. If the system is operated on Mars, through what distance would the 13.0-kg mass have to fall to give the same amount of kinetic energy to the drum? How fast would the 13.0-kg mass be moving on Mars just as the drum gained 300.0 J of kinetic energy?arrow_forward1. A 97 g ball bobbing up and down on the ocean as the waves roll by has a vertical position that can be described as a function of time by x(t) = cos(10t). What is the force on the ball at a time of 4.6 seconds? Note: The argument of the cosine function is in radians. Hint: Don't forget the sign of the force. F = 6.74 X√ Narrow_forward
- I have been stuck on this question for a while. I broke it down into parts and solved for velocity but I think I am doing something wrong.arrow_forwardTrue or false?arrow_forward10. 3.00 [kg] 1.50 [m] compresses a spring (k 500. [N/m]) by 0.400 [m]. After releasing the shell from rest, it rolls without slipping along the floor and up a sur- face inclined at an angle 0 = 30.0°, as shown in the figure. What is the angular speed of the shell when it 2.00 [m] from the base of the in- A thin spherical shell of mass M = Ax- 0.400m and radius R %| e- 30.0° reaches a distance L %3D cline? (I = }mr²) A. 1.37 [rad/s] B. 1.88 [rad/s] C. 2.01 [rad/s] D. 3.54 [rad/s]arrow_forward
- Can you please explain how to find the angle of theta in this problem? The answer states that it is 88.8 degrees but does not explain how. A propeller blade at rest starts to rotate from t = 0 s to t = 5.0 s with a tangential acceleration of the tip of the blade at 3.00m/s^2. The tip of the blade is 1.5 m from the axis of rotation. At t = 5.0 s, what is the total acceleration of the tip of the blade?arrow_forwardThe figure below shows the drive train of a bicycle that has wheels 67.3 cm in diameter and pedal cranks 17.5 cm long. The cyclist pedals at a steady cadence of 74.0 rev/min. The chain engages with a front sprocket 15.2 cm in diameter and a rear sprocket 8.00 cm in diameter. Rear sprocket Chain Pedal crank Front sprocket (a) Calculate the speed of a link of the chain relative to the bicycle frame. m/s (b) Calculate the angular speed of the bicycle wheels, rad/s (c) Calculate the speed of the bicycle relative to the road. m/s (d) What plece of data, if any, are not necessary for the calculations? O diameter of front sprocket O diameter of wheels O angular rate O length of pedal cranks O diameter of rear sprocket O none of thesearrow_forwardThe smooth hollow tube assembly rotates about a vertical axis with angular velocity ω=θ˙=3.8ω=θ˙=3.8 rad/s and ω˙=θ¨=−2.4ω˙=θ¨=-2.4 rad/s2. A small 0.23-kg slider P moves inside the horizontal tube portion under the control of the string which passes out the bottom of the assembly. If r=0.88r=0.88 m, r˙=−1.9r˙=-1.9 m/s, and r¨=3.8r¨=3.8 m/s2, determine the tension T in the string and the horizontal force Fθ exerted on the slider by the tube. T is positive in tension, and Fθ is positive if in the positive θ direction.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON