17.6 A stainless-steel plate 1.6-cm thick rests on top of a hot plate, which is maintained at 250 C. Air flows over the top surface of the plate to provide a convective heat-transfer coefficient of h = 50 W/m² K. The air temperature is main- tained at 20 C. a. What is the heat flux through the stainless-steel plate, in W/m²? b. What is the temperature at the top surface, T₁, of the stainless- steel plate? C. Based on the analysis above, what can you conclude about the heat-transfer resistance offered by the hydrodynamic boundary layer? bulk air flow 9 loss 9 T∞ = 20 C boundary layer, h = 50 W/m²-K stainless steel ks = 16 W/m-K T₁₁ = ? L = 1.6 cm T₂ = 250 C electrical resistance heater (hot plate)
17.6 A stainless-steel plate 1.6-cm thick rests on top of a hot plate, which is maintained at 250 C. Air flows over the top surface of the plate to provide a convective heat-transfer coefficient of h = 50 W/m² K. The air temperature is main- tained at 20 C. a. What is the heat flux through the stainless-steel plate, in W/m²? b. What is the temperature at the top surface, T₁, of the stainless- steel plate? C. Based on the analysis above, what can you conclude about the heat-transfer resistance offered by the hydrodynamic boundary layer? bulk air flow 9 loss 9 T∞ = 20 C boundary layer, h = 50 W/m²-K stainless steel ks = 16 W/m-K T₁₁ = ? L = 1.6 cm T₂ = 250 C electrical resistance heater (hot plate)
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P
Related questions
Question
heat and
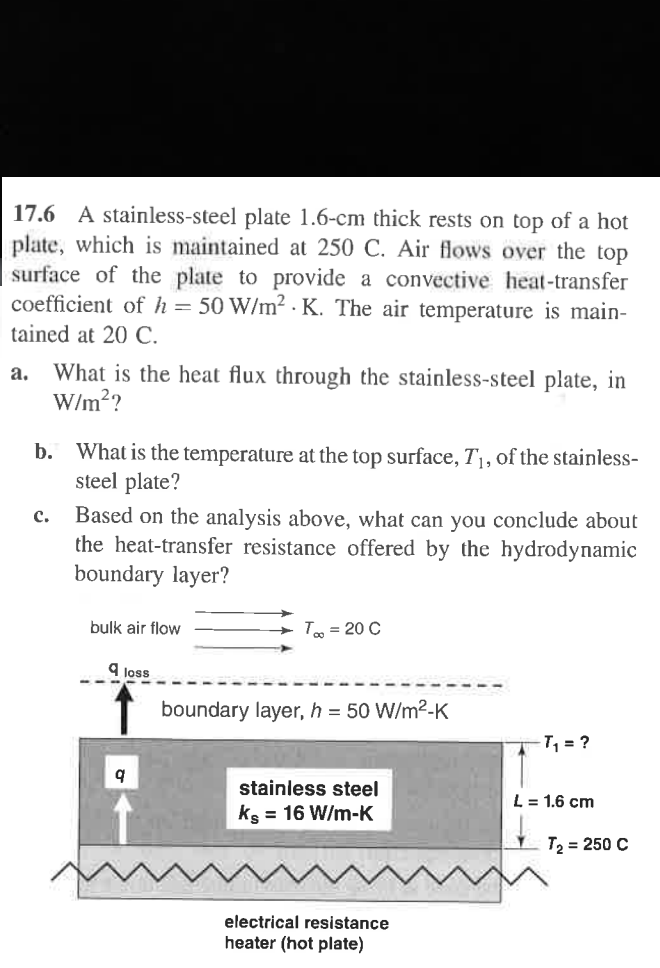
Transcribed Image Text:17.6 A stainless-steel plate 1.6-cm thick rests on top of a hot
plate, which is maintained at 250 C. Air flows over the top
surface of the plate to provide a convective heat-transfer
coefficient of h = 50 W/m² K. The air temperature is main-
tained at 20 C.
a.
What is the heat flux through the stainless-steel plate, in
W/m²?
b. What is the temperature at the top surface, T₁, of the stainless-
steel plate?
C.
Based on the analysis above, what can you conclude about
the heat-transfer resistance offered by the hydrodynamic
boundary layer?
bulk air flow
9 loss
9
T∞ = 20 C
boundary layer, h = 50 W/m²-K
stainless steel
ks = 16 W/m-K
T₁₁ = ?
L = 1.6 cm
T₂ = 250 C
electrical resistance
heater (hot plate)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285061238
Author:
Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:
Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780072848236
Author:
Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Companies, The