
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
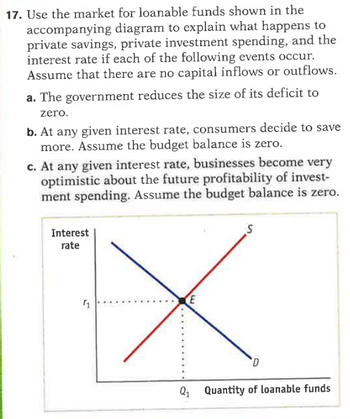
Transcribed Image Text:17. Use the market for loanable funds shown in the
accompanying diagram to explain what happens to
private savings, private investment spending, and the
interest rate if each of the following events occur.
Assume that there are no capital inflows or outflows.
a. The government reduces the size of its deficit to
zero.
b. At any given interest rate, consumers decide to save
more. Assume the budget balance is zero.
c. At any given interest rate, businesses become very
optimistic about the future profitability of invest-
ment spending. Assume the budget balance is zero.
Interest
rate
1
х
S
D
Q₁ Quantity of loanable funds
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The current market rate of interest is 10 percent. At that rate of interest, businesses borrow $300 billion per year for investment and consumers borrow $50 billion per year to finance purchases. The government is currently borrowing $150 billion per year to cover its budget deficit. a. Derive the market demand for loanable funds, and show how investors and consumerswill be affected if the budget deficit increases to $250 billion per year. Draw a graphto show your conclusion. b. Assuming taxpayers do not anticipate an increase in the future market rate of interestdue to the increase in budget deficit, show the impact of the increase in the budget deficit on the market for loanable funds. c. How would your conclusion differ if taxpayers fully anticipate future tax increases to offset the increase in the budget deficit? d. Do you think the Ricardian Equivalence is realistic?arrow_forwardSuppose the government ran a budget surplus in 2018 and a larger surplus in 2019. The loanable funds model would predict that, as a result of the increase in the surplus, A. both the government debt and interest rates increased between 2018 and 2019. B. the government debt decreased and interest rates increased between 2018 and 2019. both the government debt and interest rates decreased between 2018 and 2019. C. D. the government debt increased and interest rates decreased between 2018 and 2019.arrow_forward5. The market for loanable funds and government policy The following graph shows the loanable funds market. For each of the given scenarios, adjust the appropriate curve on the graph to help you complete the questions that follow. Consider each scenario separately by returning the graph to its starting position when moving from one scenario to the next. (Note: You will not be graded on any changes you make to the graph.) INTEREST RATE (Percent) Supply LOANABLE FUNDS (Billions of doll Demand -0- Demand 10 Supplyarrow_forward
- Interest Rate% 12% 10% 8% 6% 4% 2% 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 Supply of Savings Select one: a. The economic dips into a recession and firms see profits fall b. Firms become more optimistic about their expected profits c. An increase in business taxes d. A decrease in household wealth Quantity of loanable funds (billions) Refer to the graph above. Which of the following would cause interest rates to increase? Ti Demand for Borrowingarrow_forward1) Using a graph representing the market for loanable funds, show and explain what happens to interest rates and investment if: a reduction in military spending moves the government’s budget from deficit into surplus. Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forward4. Supply and demand for loanable funds The following graph shows the market for loanable funds in a closed economy. The upward-sloping orange line represents the supply of loanable funds, and the downward-sloping blue line represents the demand for loanable funds. INTEREST RATE (Percent) 10 9 1 0 0 Supply Demand 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 LOANABLE FUNDS (Billions of dollars) ? is the source of the supply of loanable funds. As the interest rate falls, the quantity of loanable funds supplied Suppose the interest rate is 4.5%. Based on the previous graph, quantity of loanable funds supplied is demanded, resulting in a of loanable funds. This would encourage lenders to the quantity of loanable funds supplied and the equilibrium interest rate of % than the quantity of loans the interest rates they charge, thereby the quantity of loanable funds demanded, moving the market towardarrow_forward
- If the interest rates increase this will _____ the quantity of loanable funds demanded, and if the interest rates decrease this will______it. Select one: a. increase; reduce b. increase; increase c. reduce; increase Od. reduce; reducearrow_forward8 Demand, Supply 7 10 4 REAL INTEREST RATE (Percent) 3 2 - 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 QUANTITY OF LOANABLE FUNDS (Billions of dollars) Refer to Figure 33-1. If the real interest rate is 3 percent, the quantity of loanable funds demanded is $50 billion, and the quantity supplied is $30 billion. $20 billion, and the quantity supplied is $60 billion. $50 billion, and the quantity supplied is $60 billion. $30 billion, and the quantity supplied is $50 billion.arrow_forward5. The market for loanable funds and government policy The following graph shows the market for loanable funds. For each of the given scenarios, adjust the appropriate curve on the graph to help you complete the questions that follow. Treat each scenario separately by resetting the graph to its original state before examining the effect of each individual scenario. (Note: You will not be graded on any changes you make to the graph.) INTEREST RATE (Percent) Supply Demand LOANABLE FUNDS (Billions of dollars) Demand Supply (?) Scenario 1: Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAS) allow people to shelter some of their income from taxation. Suppose the maximum annual contribution to such accounts is $5,000 per person. Now suppose there is a decrease in the maximum contribution, from $5,000 to $3,000 per year.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education