
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781285199047
Author: John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
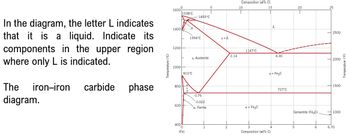
Transcribed Image Text:1600°
1538°C
1493°C
In the diagram, the letter L indicates
that it is a liquid. Indicate its
components in the upper region
where only L is indicated.
The
iron-iron carbide phase
diagram.
Temperature (°C)
1400
8
1394°C
y+L
1200
2.14
y, Austenite
10000
912°C
800a
0.76
0.022
600
400
(Fe)
a, Ferrite
Composition (at% C)
15
1147°C
a + Fe3C
2
3
Composition (wt% C)
L
2500
4.30
2000
y + Fe3C
727°C
1500
Cementite (Fe3C)
1000
4
5
6
6.70
Temperature (°F)
SAVE
AI-Generated Solution
info
AI-generated content may present inaccurate or offensive content that does not represent bartleby’s views.
Unlock instant AI solutions
Tap the button
to generate a solution
to generate a solution
Click the button to generate
a solution
a solution
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Given: Pb2*(aq) + 2e = Pb(s); E° =-0.13 V 2H*(aq) + 2e = H2(g); E° = 0.00 V %3D NO3 (aq) + 4H*(aq) + 3e= NO(g) + 2H,0(1); E° = 0.96 V O2(g) + 4H"(aq) + 4e 2H20(1); E° = 1.23 V PbO2(s) + SO4 (aq) + 4H"(aq) + 2e PBSO,(s) + 2H20(); E° = 1.69 V Under standard-state conditions, which of the following is the best oxidizing agent? O a) Pb2+ () b) NO3 O c) PbO2 O d) H* e) 02arrow_forwardScence Midterm Summ X Material%20Science_Midterm%2 x ewer?url=https://ttu-storage.s3.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/account 1/attachments/390676/Ma ence Midte 02021.pdf Open with Google Docs 5. Iron has a BCC crystal structure, an atomic radius of 0.124 nm, and an atomic weight of 55.85 g/mol. Compute its theoretical density: 6. Below is a unit cell for a hypothetical metal. (a) To which crystal system does this unit cell belong? 40nm 030 nm 0.30 nm (b) What would this crystal structure be called? 1 1 2 7. Sketch a tetragonal unit cell. and witnin that Page Hocations of the point: DELLarrow_forwardMost ceramic materials have low thermal conductivities because:(a) Electron mobility is strongly restricted due to their strong ionic-covalent bonding.(b) False, in general they are excellent thermal conductors (they are used in ovens).(c) Electron mobility is dependent on T and therefore they are poor conductors at high temperatures.(d) Electron mobility is very restricted by secondary bonds.arrow_forward
- PART B Q1 (a) Figure 5 shows the type of point defects that may presence in a metal. Compare the characteristics between the point defects occurred at point 1 and point 3. Figure 5: Possible point defects in a metal material (b) The equilibrium number of vacancies in an aluminium plate at the temperature of 500 °C is 7.57 × 10²3 m³³. The atomic weight and density for aluminium are 26.98 g/mol and 2.62 g/cm³, respectively. Calculate the activation energy for vacancy formation in aluminium. (c) Describe with illustration a point defect that may presence in silicon dioxide crystal structure. Q2 (а) Discuss with suitable example the influence of crystal structure of the solvent iron, Fe lattice to the diffusivity of carbon atom in the formation of a steel alloy. (b) Discuss the possible diffusion that take places in the making of electronic integrated circuit wafer with help of suitable diagram.arrow_forwardThe maximum solid solubility of carbon in ferrite occurs at 0.022 wt% C and 727 ° C, the eutectoid composition is 0.76 wt% C, the maximum solid solubility of carbon in austenite occurs at 2.14 wt% C and 1147 ° C, and the cementite composition is 6.7 wt% C. For 2122 g of a 3.2134 wt% C steel at 726 ° C, what will be the mass of carbon present as part of a compound?(a) 67.9 g(b) 74.2 g(c) 58.7 g(d) 83.5 garrow_forwardThe mixed oxide ceramic Tl2Ca2Ba2Cu3O10+x has zero electrical resistance at 125 K. Calculate the average oxidation number of the copper in this compound if x = 0.50 and thallium is in the 13 oxidation state.arrow_forward
- The equilibrium density of vacancies ns is given by Nexp(-Es/kT) , where N is the density of semiconductor atoms and Es is the energy of formation. Calculate ns in silicon at 27° C, 900 ° C, and 1200° C. Assume Es = 2.3 eV.arrow_forwardMost ceramic materials have low thermal conductivities because(a) Electron mobility is strongly restricted due to their strong ionic-covalent bonding.(b) False, in general they are excellent thermal conductors (they are used in ovens).(c) Electron mobility is dependent on T and therefore they are poor conductors at high temperatures.(d) Electron mobility is highly restricted by secondary bonds.arrow_forwardPlease do not give solution in image format thanku Minerals are grouped by their chemical composition. The major groups or families of mineralsinclude the Silicates, Oxides, Sulfates, Sulfides, Carbonates, Native elements, and the Halides.Match the following chemical formulas from a variety of minerals to the mineral family to which theybelong based on their chemical formula.Fe203PbSCaCO3(Mg,Fe)2SiO4AuCaSO4 H2ONaClOxidesSulfidesCarbonatesSilicatesNative elementsSulfates[Choose ]arrow_forward
- Determine the crystal structure for the following: (a) a metal with a0 = 4.9489 Å, r = 1.75 Å and one atom per lattice point; and (b) a metal with a0 = 0.42906 nm, r = 0.1858 nm and one atom per lattice point.arrow_forwardMetallurgical and materials engineers are often called upon to design alloys with high strength, but with some ductility and toughness; typically, ductility is sacrificed when an alloy is reinforced. Various hardening techniques are available to an engineer, and often the selection of the alloy depends on the material's ability to be adapted to the mechanical characteristics required for a specific application. There are several methods to increase the hardening of metals, each suited to different applications and strength requirements. Some of these methods include heat treatment, such as annealing and quenching, which alter the crystalline structure of the metal to make it harder. Additionally, cold working, such as cold rolling and forging, can increase the metal's strength by reducing its grain size and increasing its dislocation density. The introduction of alloying elements or the controlled precipitation of particles can also strengthen a metal. Each technique is chosen based on…arrow_forwardThe band gap for the elemental semiconductor silicon is 1.11 eV. That energy corresponds to what wavelength and region of the electromagnetic spectrum? (1eV = 1.602 x 10-19J) Group of answer choices 1117 nm; Infrared 1117 nm; Ultra-violet 1.117 x 10E(-6) nm; Infrared 1.778 x 10E(-19) J; Ultra-violetarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,
Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133958437
Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,