
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
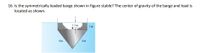
Transcribed Image Text:16. Is the symmetrically loaded barge shown in figure stable? The center of gravity of the barge and load is
located as shown.
1.5 m
2 m
6 m
6 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2.Calculate the earth pressure acting on a concrete structure P Pa Lat Pat Lx1=4 M Ly1=8 M Lz=2 M Px1=14 N/m Px2= 8 N/m Py1=15 N/marrow_forward• Figure shows four differently shaped containers that have the same bottom areas A and depths h. Explain: 1. are the total hydrostatic forces acting on the bottoms of all containers equal? 2. is the total hydrostatic force acting on the bottom of each container equal to the counterforce N on the container from the ground (neglecting the weight of container)? h (a) (b) (d)arrow_forwardA grain silo is in equilibrium under the effect of a variable distributed wheat load and several forces as shown in the Figure. The silo has a gate for releasing the wheat into a rigid u-shape channel at G for dispensing the crop. The channel is connected to the silo by the hinge (or pin) at G and supported externally by the hinge (or pin) H. The silo is also supported by two rigid links (or pendulums) AB and LN. The acting loads are represented by three concentric forces F = 30 kN at K, F2 = 90 kN at D, and F = 40 kN at J, and a couple M = 300 kNm (clockwise) at C. The distributed load effect of the wheat is vertical acting between points C and G of the silo. The distributed load has a magnitude equal to wi = 250 kN/m between points C and E and decreases linearly to w2 = 80 kN/m when it reaches point G due to the releasing effect of the gate. The angles of forces F2 and F, with the horizontal line are 40° and 20°, respectively. F is horizontal. Do the following: 1. Draw the Free Body…arrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning