
Concept explainers
Determine the current, i, at t = 1 s and at t = 4 s for the circuit of Figure P 2.9-1.
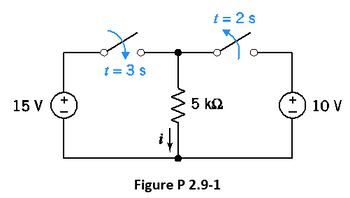
Introduction
Current
"Current" in an electrical circuit refers to the flow of electric charge through a conductor, such as a wire. It is a measure of the amount of electric charge passing a particular point in a circuit per unit of time and is usually measured in Amperes (A).
Transient analysis
The aim of the transient analysis is to understand how the circuit behaves under different conditions, such as changes in load, fault conditions, and switching events. By understanding the circuit's transient response, engineers can design circuits that are more stable and reliable.
Given Data
The circuit is given by
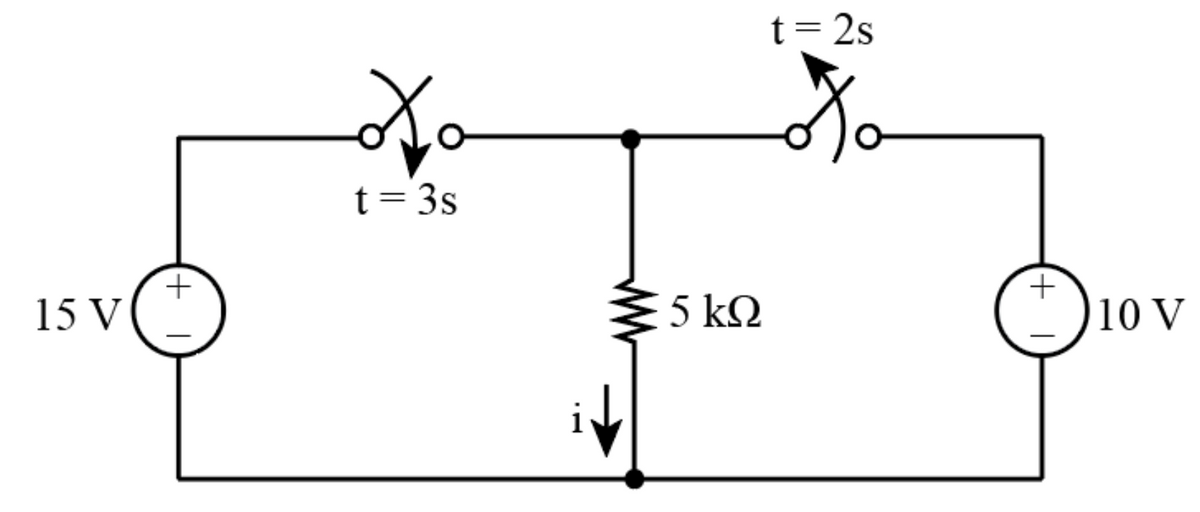
To determine
The value of the current at and .
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

- Help me answer, I want to check my solution To get the contribution of the 75V source to iR, we first kill the 50mA source. What is the resulting equivalent resistance in series with the 75K resistor (in Kohms) To get the contribution of the 75V source to iR, we first kill the 50mA source. What is the resulting value of iR (in mA)? What is the nodal equation for Vx? What is the Thevanin voltage in (Volts) and Thevanin resistance in (Kohms)?arrow_forwardGive an independent set of linear that can ve solved for the current shown. Use the Junction Rulearrow_forwardHow do I solve this using Kirchoff's Voltage Law?arrow_forward
- Need asap pls. Thanks.arrow_forwardConsider the circuit shown below. R1 = 100 N R2 = 100 N C1 10 mF V = 12 V R3 3 100 N C, = 4.7 mF %3D %3D a. After the switch has been closed for a very long time, what are the voltages across the capacitors C1 and C2? Hint for (a) Voltage across C1 is V, and voltage across C2 is V. b. After the switch has been closed for a very long time, what is the energy stored in each capacitor? Hint for (b) Energy stored on C, is J, and energy stored on C, is J.arrow_forward"To solve a circuit" means to use the values of potentials and resistances to find all currents passing through, and voltage drops across all elements in the circuit. Create a general procedure to solve any circuit DC circuit with any number of resistors. You may use the Structure Physics Problem-Solving Method as a model.arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





