
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
A certain orthodontist uses a wire brace to align a patient's crooked tooth as in the figure below. The tension in the wire is adjusted to have a magnitude of 28.0 N. Find the magnitude of the net force exerted by the wire on the crooked tooth.
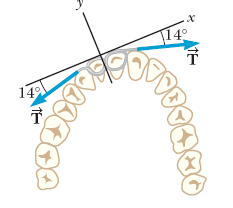
Transcribed Image Text:14°
T
149
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You can hold a book against the wall, preventing it from sliding down, if you press your hand against it. Suppose the coefficient of static friction between the book and the wall is 0.450, but there is no friction between your hand and the book. The mass of your book is 3.75 kg. What minimum force (P) do you need to apply to keep the book from slipping down the wall? Give your answer in units of Newtons. Hint: apply Newton's 2nd law to the book, and set the acceleration equal to zero, since it is not moving! Parrow_forwardA certain orthodontist uses a wire brace to align a patient's crooked tooth as in the figure below. The tension in the wire is adjusted to have a magnitude of 12.5 N. Find the magnitude of the net force exerted by the wire on the crooked tooth.arrow_forwardThree students, Adam, Bailey and Carlos, are tugging on a multi-colored hoop (as in the figure). Despite the three forces, the tire does not move. Adam pulls with a force FA of magnitude 210 N. and Carlos pulls with a force Fc of magnitude 175 N. Angle AB = 145 degrees. Note that the direction of Fc is not given. What is the magnitude of Bailey's force? FB = N BAB Adam Bailey Carlosarrow_forward
- PAMP4 ** F20 T2 T1 sign In the figure. the sign suspended by very light and uniform wires is at rest. The tensions in two wires are labeled. What is the value for the angle 0? Please use the values T. = 371Nand T .EAarrow_forwardTwo forces, F₁ and F2, act at a point. The magnitude of F₁ is 8.50 N, and its direction is an angle 65.0° above the negative direction of x-axis in the second quadrant. The magnitude of F2 is 5.00 N, and its direction is an angle 52.1° below the negative direction of x-axis in the third quadrant. What is the x-component of the resultant force? What is the y-component of the resultant force? What is the magnitude of the resultant force?arrow_forwardThe figure below shows a bird feeder that weighs 167.9 N. The feeder is supported by a vertical string, which is in turn tied to two strings, each of which is attached to a horizontal branch. The left string makes a 60° angle with the branch, while the right string makes a 30° angle. What is the tension in each string (in N)? left string __N right string __N bottom string __Narrow_forward
- The convict escaped either by crawling through the sewage pipes or by hiding out in the back of the delivery truck. But the convict did not escape by crawling through the sewage pipes. Therefore, the convict escaped by hiding out in the back of the delivery truck. Given that:s = The convict escaped through the sewage pipesd = The convict escaped by hiding out in the back of the delivery 1.) What is the symbolic form of the argument? 2.) Is the argument valid? Yes or No.arrow_forwardA bag of cement weighing 525 N hangs in equilibrium from three wires as suggested in the figure below. Two of the wires make angles 0, = 62.0° and 0, = 43.0° with the horizontal. Assuming the system is in equilibrium, find the tensions T,, T,, and T, in the wires. 269.42 T = Consider the net force at the point where the three wires come together. What is the acceleration of this point? N 420.98 Ta = The horizontal component of your T, is not equal to the horizontal component of your T,, so the object would be accelerating horizontally. N T3 525 N T T2 T3 Need Help? Watch It Read Itarrow_forwardThe upper leg muscle (quadriceps) exerts a force of FQ = 1140 N, which is carried by a tendon over the kneecap (the patella) at the angles shown in the figure below. Find the magnitude in newtons and direction in degrees counter-clockwise from an axis directed to the left of the force exerted by the kneecap on the upper leg bone (the femur). magnitude ______ N direction _____ ° counter-clockwise from an axis directed to the leftarrow_forward
- A uniform plank of length 2.00 m and mass 29.5 kg is supported by three ropes, as indicated by the blue vectors in the figure below. Find the tension in each rope when a 685–N person is d = 0.500 m from the left end. magnitude of T1 = magnitude of T2 = magnitude of T3 =arrow_forwardThree cables are used to tie the balloon shown in Figure. Determine the magnitude of the vertical force (P) exerted by the balloon at A, knowing that the tension in cable AD is 954 N. y1 = 4.4 m y2 = 2.2 m x1 = 4.2 m x2 = 3 m z = 6 marrow_forwardA bag of cement weighing 525 N hangs in equilibrium from three wires as suggested in the figure below. Two of the wires make 62.0⁰ and 02 = 43.0° with the horizontal. Assuming the system is in equilibrium, find the tensions T₁, T2, and T3 angles 0₁ 1' in the wires. T₁ = 0 = Consider the net force at the point where the three wires come together. What is the acceleration of this point? N 0.53 X T₂ = The horizontal component of your T₁ is not equal to the horizontal component of your T₂, so the object would be accelerating horizontally. N T3 = 525 N 201 T₁ CEMENT T3 0₂ T₂ Fgarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON