
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
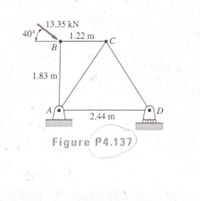
Transcribed Image Text:13.35 kN
40°
1.22 m
B
1.83 m
\D
2,44 m
Figure P4.137

Transcribed Image Text:4.131-4.140 Using the method of joints, calculate the force in each member
of the trusses shown. State whether each member is in tension or compression.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- BM1 ELEV. 1,850.00 meters Compute the elevation of BM2 4.56 7.13 9.50 TP1 T 4.33 6.17 TP2 T 5.80 BM2arrow_forwardHW-2-: Compute the area of cross-section if the formation width is 12 m, side slopes are 1 to 1, average height along the centre line is 5 m, and the transverse slope of the ground is 10 to 1. Ans: A = 157.00 m2.arrow_forwardV 36-A horizontal curve 1T2. having a radius R 530 m, is to join two straights intersecting at point I with an angle A and a forward chaining = 2532.325 m. The distance between the tangency points 11 and T2, on the curve, is T1T2 174.568 m. Using the theodolite and tape at 15 m intervals of through chaining, find the deflection angle for the first sub-chord.arrow_forward
- R = S² 15(0.01e + f) Q1- Derivation of the law of super elevation.arrow_forwardFreeboard is the vertical distance from the water surface to the bottom of the channel а. False b. Truearrow_forward3. An open traverse that runs from A to H has the following deflection angles: B = 1°11'R; C = 3°03'R; D = 7°56'L; E = 6°10'L; F = 1°41'R; G = 9°15'L. If the bearing of AB is N20°30'E, compute the bearings of the remaining sides.arrow_forward
- From point A (elev. = 590.46 m), the angle of elevation of the top of a mountain is 25°. From point B, 298 m nearer the mountain and 35 m lower than point A, the angle of elevation of the same mountain is 35°. Find the elevation of the top of the mountain.arrow_forwardANSWER KEY: D= 51.8319m∆h= 13.5430mElev Sta. A= 70.8530marrow_forwardCalculate for the slope at the free end.arrow_forward
- 5. The center of gravity of a 1.40m diameter open cylinder 2.50m high is 71cm above the bottom. It floats in water at a depth 1.80m. Compute for the metacentric height. a. 0.052 b. 0.011 c. 0.670 d. 0.068 6. From the given in Problem #5, what is the righting moment if it is tilted 12° a. 1.368 b. 1.458 c. 1.136 d. 4.860arrow_forwardConcert to back bearingarrow_forward4. What is the degree of curve of shear AB?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning