Question
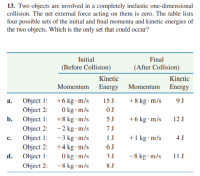
Transcribed Image Text:13. Two objects are involved in a completely inelastic one-dimensional
collision. The net external force acting on them is zero. The table lists
four possible sets of the initial and final momenta and kinetic energies of
the two objects. Which is the only set that could occur?
Initial
Final
(Before Collision)
(After Collision)
Kinctic
Kinetic
Momentum Energy
Momentum
Energy
Object 1:
+6 kg · m/s
15 J
+8 kg · m/s
9 J
a.
Object 2:
0 kg · m/s
OJ
+8 kg · m/s
-2 kg · m/s
Object 1:
Object 2:
5 J
+6 kg · m/s
b.
12 J
7J
+1 kg · m/s
6 J
-8 kg m/s
Object 1:
-3 kg • m/s
1J
4 J
с.
Object 2: +4 kg m/s
d.
Object 1:
0 kg · m/s
3J
11 J
Object 2:
-8 kg m/s
8 J
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Collisions: in a perfectly ELASTIC collision between two perfectly rigid objects:arrow_forwardSuppose F₁ = 2000 N. (Figure 1) You may want to review (Pages 262-266). Figure F, (N) F 0- 0 N. 2 4 6 1 of 1 -t (ms) Part A What impulse does the force shown in the figure exert on a 250 g particle? Express your answer in newton-seconds to two significant figures. WD ΑΣΦ J = Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again Provide Feedback ? N.Sarrow_forwardA 0.020 kg bullet is shot horizontally and collides with a 2.00 kg block of wood. The bullet embeds in the block and the block slides along a horizontal surface for 1.50 m. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface is 0.400, what was the original speed of the bullet? Include a diagram of the situation.arrow_forward
- Two objects are on a collision course. Object #1 has a mass of 4.6 kg and an initial velocity of 7.3 m/s i. Object #2 has a mass of 7.7 kg and an initial velocity of --11.2 m/s i. After colliding, Object #1 has a velocity of -2 m/s i. What is the change in kinetic energy of the system?arrow_forward1.A cart of mass m moves with a speed v on a frictionless airtrack and collides with an identical cart that is stationary. If the two carts stick together after the collision, what is the final kinetic energy of the system?Explain and labled the problem.arrow_forwarda block with a mass of 0.5 kg is released from rest on a frictionless track at a distance 2.5m above the top of the table. it then collides elastically with an object having mass m2=1.0kg that is initially at rest on the table as shown in the figure. the table is h2=2.oo m . a)How far away from the bottom of the table do the objects land ? Hints : determine the velocities just after the collision . how high does object 1 travel back up the track. b) suppose the collision is inelastic , where does combined object land please see attached imagearrow_forward
- A block with mass m and a velocity v10 collides with a block M at rest. At some time later after the collision the two masses have velocities v1 and v2. No other information is given about the surface on which the blocks are sliding. Which of the following is true? The system consists of the two blocks. a) the mechanical energy of the system is conserved, but the momentum of the system is not b) the momentum of the system is conserved, but the mechanical energy of the system is not conserved c) neither the momentum nor the mechanical energy of the system need be conservedarrow_forwardA 2.64-kg steel ball strikes a massive wall at 10.0 m/s at an angle of 0 - 60.0° with the plane of the wall. It bounces off the wall with the same speed and angle (see the figure below). If the ball is In contact with the wall for 0.164 s, what is the average force exerted by the wall on the ball? magnitude direction --Select- varrow_forwardQUESTION 8 Two carts of masses m1 and m2 are moving towards each other with speeds v1 and v2. respectively. The carts collide head-on, elastically. For the values listed below, total kineti energy of the two carts after the collision, in joules, is: m1 = 6.00 kg m2 = 3.51 kg 1 = 2.18 m/s 2 = 7.00 m/sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios