Question
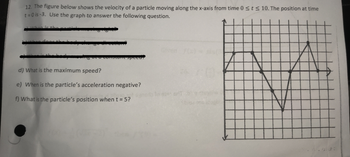
Transcribed Image Text:12. The figure below shows the velocity of a particle moving along the x-axis from time 0 ≤ t ≤ 10. The position at time
t=0 is-3. Use the graph to answer the following question.
peca
d) What is the maximum speed?
e) When is the particle's acceleration negative?
f) What is the particle's position when t = 5?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- B5arrow_forwardYou are given the vzt - graph for an object moving along the x-axis with constant acceleration. Which of the following could you not determine from the information given in this graph alone? A. the object's x-acceleration at any time t B. the object's x-velocity at any time t C. the object's position at any time t D. more than one of the above E. misleading question-you could determine all of these from the v,t- graph alonearrow_forward7. An object's velocity is v = t* – 3t? where t 2 0. a) At what time/times is the object at rest? b) In what time range is the object moving to the left? In what time range is the object moving to the right?arrow_forward
- 3. Irina dives from a 25-meter high platform into a water (see diagram ). 25 m a. Irina's acceleration as she is falling from the platform. What hypothesis(s) must you make in order to state this value as the acceleration? Explain. c. Use kinematic equations to fill in the table below. Time (s) Velocity (m/s) Fallen Distance ( m) Height (m) 25 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0arrow_forward3. Shown below is the acceleration function for a particle over the approximately first two seconds of its motion. Draw an approximate graph of velocity as a function of time assuming v, = 0 m/s. alt) t 20 15 10 5. 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 4. Let vector A point from the origin into the first quadrant of the xy plane and vector B point from the origin into the third quadrant. The vector Ă – B must be in which quadrant?arrow_forwardA particle moves along the x-axis according to r(t) = 4t - 7t² m. a. What is the instantaneous velocity at t 3 s? m/s b. What is the instantaneous speed at t = 3 s? m/s c. What is the average velocity between t = 2 s and t = 3 s? m/sarrow_forward
- 1. The position of a particle moving along the x-axis is given by x(t) = 3.0 – 1.5t m. a. At what time does the particle cross the origin? b. What is the displacement of the particle between t = 3.0 s and t = 5.0 s? 2. Sketch the velocity-versus-time graph from the following position-versus-time graph. Position vs. Time 10 8. 4 2- -2 -4 -6 -8 - -10 - 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2 Time (s) (w) uoņisodarrow_forward3. A ball is thrown upwards at 13.0 m/s toward the ceiling located 6 m above the point where you release the ball. Air resistance is negligible. Objects falling near the earth's surface with no forces acting except gravity have a downwards acceleration of magnitude g. For this problem use g = 10 m/s². Write any equation you use in symbolic form before substituting in numbers. Make a labeled picture with symbols and all relevant values. Put a coordinate system on the a. picture by indicating the location of the origin and position direction. b. Find the time taken to reach the ceiling. Find the velocity just before the ball touches the ceiling. C.arrow_forwardSuppose an object moves along a line at 10 m/s for 0sts2 s and at 16 m/s for 2arrow_forward2-arrow_forwardi need help with Only the last 3 parts ( C D and E)arrow_forwardI Review I Constants A particle moving along the x-axis has its velocity described by the function v. 2t? m/s, where t is in s. Its initial position is xo = 2.4 m at to = 0 s . Part A You may want to review (Pages 55 - 56) . Part B Part C At 2.2 s , what is the particle's acceleration? Express your answer with the appropriate units. HA ? Value Units a = Submit Request Answerarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios