
Biochemistry
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781305577206
Author: Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Please atleast answer this question
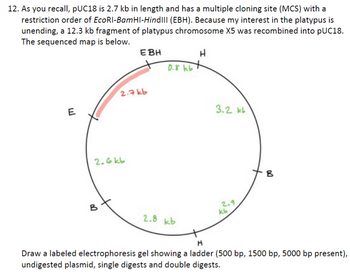
Transcribed Image Text:12. As you recall, pUC18 is 2.7 kb in length and has a multiple cloning site (MCS) with a
restriction order of EcoRI-BamHI-HindIll (EBH). Because my interest in the platypus is
unending, a 12.3 kb fragment of platypus chromosome X5 was recombined into pUC18.
The sequenced map is below.
H
E
2.6kb
B
EBH
2.7 kb
0.8 kb
2.8 kb
3.2 kb
2.9
kb
B
H
Draw a labeled electrophoresis gel showing a ladder (500 bp, 1500 bp, 5000 bp present),
undigested plasmid, single digests and double digests.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please in detail, what the picture attached representsarrow_forwardHeteroduplex DNA Formation in Recombination From the information in Figures 28.17 and 28.18, diagram the recombinational event leading to the formation of a heteroduplex DNA region within a bacteriophage chromosome.arrow_forwardHomologous Recombination, Heteroduplex DNA, and Mismatch Repair Homologous recombination in E. coli leads to the formation of regions of heteroduplex DNA. By definition, such regions contain mismatched bases. Why doesn’t the mismatch repair system of E. coli eliminate these mismatches?arrow_forward
- 5' 3' ORF for gene X +1 You find a mutation elsewhere in the genome (not within the sequence above) that you decide to call Mutation #2. When Mutation #1 in gene X (from the above question) is combined with Mutation #2 in the same organism, you get the phenotype in the blots below. This second mutation is most likely in what specific factor? Wild Type Northern Gene X O ribosome O sigma factor O DNA polymerase RNA polymerase Double mutant Wild Type Western Gene X direction of transcription Double mutant 3' 5'arrow_forwardplease help thank you a lotarrow_forwardBelow is a portion of an exon from a gene that encodes protein X in the genome of the plant Arabidopsis. Wildtype DNA3’ TTC AAT GCT CCG AAT ACC 5’ template strand5’ AAG TTA CGA GGC TTA TGG 3’ non-template strand A new strain (Strain B) of Arabidopsis is identified with the same region of the gene coding for protein X: 3’ TTC AAT GCT CCC AAT ACC 5’ template strand5’ AAG TTA CGA GGG TTA TGG 3’ non-template strand Compare the two DNA sequences and look for any differences. Based on what you find a. There is no mutation in Strain B compared to Strain A. b. After the point of the mutation, all the amino acids encoded by the Strain B template will be different than the Strain A protein X. c. Protein X made from the Strain B template will be much shorter than protein X made from the Strain A template d. Protein X from Strain B will have one amino acid difference that would not affect protein function. e. There is a mutation but there will not be any difference in the…arrow_forward
- plz choose incorrect option . Q. Telomere is a typical heterochromatic region in eukaryotic genome. Choose an incorrect description about gene silencing in telomere. ① Methylation on H3K9 is an initiating event for heterochromatin formation in telomere ② Mutation of Rap1 will disrupt the heterochromatic formation in telomere ③ Region of heterochromatin can spread along the chromosome until inhibiting mechanisms stop it ④ Sir complex is the key factor that condenses nucleosome in telomerearrow_forwardThe completely synthetic yeast chromosome Syn IIIcontains a loxP site in the 3′ UTR of every gene thatis potentially nonessential to yeast survival. As youwill recall from Chapter 6, loxP sites are targets ofsite-specific recombination. The researchers who constructed Syn III included these loxP sites as a way to“scramble” the chromosome, meaning that parts ofthe chromosome could easily be deleted or rearranged.The goal of these investigations is to drive the evolution of Syn III so as to define a minimal genome thatcan support the life of this organism. Outline the experiment the researchers would do to scramble Syn IIIin order to define a minimal genome.arrow_forward2c) If the whole potoroo genome is 4.2 x 10' bp, and the highlyrepetitive DNA in the potoroo genome is composed entirely ofcopies of the sequence 5'AAGACT' and its complement, howmany copies of this sequence are present in the potoroogenome?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning