
Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781285199030
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
Transcribed Image Text:11:21 Mon May 3
Done <
AA
A session.masteringchemistry.com
<Problem Set #9 (Ch 19) Adaptive Follow-Up
For Practice 19.7 - Enhanced - with Feedback
Item 6
Cu²+(aq) + 2e¯→Cu(s)
0.34
Mn²+(aq) + 2e→Mn(s)
-1.18
2H+ (aq) + 20¯→H2(g)
0.00
Alš+ (aq) + 3e¯→Al(s)
-1.66
Fe+ (aq) + 3€¯→F€(s)
Pb?+ (aq) + 20→P6(s)
Mg²+ (aq) + 2e-→Mg(s)
Na* (aq) +e¯→Na(s)
Ca²+ (aq) + 2e¯→Ca(s)
Ba2+ (aq) + 2e→Ba(s)
-0.036
-2.37
-0.13
-2.71
Sn²+ (aq) + 2e¯→Sn(s)
-0.14
-2.76
Ni²+ (aq) + 20→N¡(s)
Co2+ (aq) + 2e-→Co(s)
-0.23
-2.90
K* (aq) +E¯→K(s)
Lit (aq) + e→Li(s)
-0.28
-2.92
Cd2+ (aq) + 2e¯→Cd(s)
-0.40
-3.04
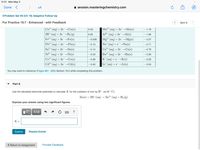
You may want to reference (Pages 861 - 865) Section 19.5 while completing this problem.
Part A
Use the tabulated electrode potentials to calculate K for the oxidation of zinc by H+ (at 25 °C):
Zn(s) + 2H+(aq) → Zn?+(aq) + H2 (g)
Express your answer using two significant figures.
?
K =
Submit
Request Answer
< Return to Assignment
Provide Feedback
Transcribed Image Text:11:21 Mon May 3
Done <
AA
A session.masteringchemistry.com
<Problem Set #9 (Ch 19) Adaptive Follow-Up
For Practice 19.7 - Enhanced - with Feedback
Item 6
I nevievWI COnSldns
Trenouic Tabie
Standard reduction half-cell potentials at 25° C
Half-reaction
E° (V)
Half-reaction
E° (V)
Au³+ (aq) + 3e¯→Au(s)
Fe2+ (aq) + 20¯→F€(s)
1.50
-0.45
Cr³+ (aq) + e-→Cr²+ (aq)
Crtt (aq) + Зе —Cr(s)
Ag+(aq) + e¯→→Ag(s)
0.80
-0.50
Fe+ (aq) + 3e→Fe²+(aq)
0.77
-0.73
Cu+ (aq) +e¯→Cu(s)
Zn2+ (aq) + 2e¬Zn(s)
0.52
-0.76
Mn²+ (aq) + 2e→Mn(s)
Cu²+ (aq) + 2e¯→Cu(s)
2H+ (aq) + 20¯→H2(g)
0.34
-1.18
0.00
Al³+ (aq) + 3e¯→Al(s)
-1.66
Fe+ (aq) + 30→FE(s)
Mg2+ (aq) + 2e→Mg(s)
Na+ (aq) +e¯→Na(s)
Ca2+ (aq) + 2e-→Ca(s)
Ba2+ (aq) + 2e→Ba(s)
-0.036
-2.37
Pb2+ (aq) + 2e¯–→Pb(s)
-0.13
-2.71
Sn2+ (aq) + 2e¯→Sn(s)
Ni²+ (aq) + 2e-→Ni(s)
-0.14
-2.76
-0.23
-2.90
Co2+ (aq) + 2e-→Co(s)
к" (аq) + e — К(s)
Lit (aq) +E¯→L¡(s)
-0.28
-2.92
Cd2+ (aq) + 2e-→Cd(s)
-0.40
-3.04
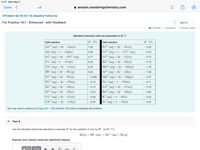
You may want to reference (Pages 861 - 865) Section 19.5 while completing this problem.
Part A
Use the tabulated electrode potentials to calculate K for the oxidation of zinc by H+ (at 25 °C):
Zn(s) + 2H†(aq) → Zn²+ (aq) + H2 (g)
Express your answer using two significant figures.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Convert 45 mi/h to m/s, showing how the units cancel appropriately.arrow_forwardLe Chateliers principle. 7 / + 3 Beg) = 2 A#= +60,000 Inc [B] Dec [D] Inc [C] €² 2 C + D (2) до Inc. I Дес Рarrow_forwardTab Caps M Inbox (1,600)-fantil@udeledu X Mail- Francesca A Tantillo-Out X x ← C app.101edu.co < DA 。。 A 88°F ME Mostly sunny Fn Z 2 W S X 3 Alt E Silane, SiH, is a colorless, pyrophoric, toxic gas that is used to deposit elemental silicon for semiconductor and photovoltaic applications. D SiH. has 8 total valence electrons. Draw the Lewis structure for SiH, that minimizes the formal charges on all atoms. $ 4 EXP DOP #12: Geometry-CHM150xAktw Chemistry C R F Pll S % 5 T Question 18.d of 23 V G Click to draw a new structure 6 Y + B * H & 7 PrtScn 8 N Home UL U M ( 9 K K End na O POUP $11 0 L P Alt A PgDn A D 90% B 0 Update Submit 6:19 PM D X 7 Del Backss (arrow_forward
- Tab Minbox (1,600)-fantilOudeledu X Mail- Francesca A Tantillo-Out xEXP #12: Geometry-CHM150-2x Aktiv Chemistry ← → C < Esc app.101edu.co Mostly sunny O ! D 7 A Silane, SiH., is a colorless, pyrophoric, toxic gas that is used to deposit elemental silicon for semiconductor and photovoltaic applications. Given the electron configuration of Si is [Ne]3s 3p2, how many valence electrons does Si have? Z 2 W S X # 3 E D $ 4 C OL R F % 5 FS T Question 18.b of 23 V G ^ 6 Y B & 7 H PrtScn U N 8 J Home ( 9 M K X End O 1 4 7 +/- PgUp 0 2 5 8 1. P 3 - 6 9 0 Pgon $12 0 APD + Update Submit C x 100 5:21 PM 7/6/2022 X 10 Del Backspacearrow_forwardAnswer all pleasearrow_forwardRsimi, Nour 2023VVA Chemistry.7b.FA1 An unknown solid substance is heated according to the temperature versus time graph below. Temperature (°C) 70 40 30 20 288 8 2 0 0 5 15 Time (min) 20 00 4 of 5 1 2 3 4 5 25 While the substance is a liquid, at what temperature do the molecules of the substance have the greatest average kinetic energy? 2 % 3 4 5 16 7 8 insertarrow_forward
- 8. For Ausys to always be negative, what must be TRUE? A. q=w B. q> -w C. W> -q O D. -W>q Which ALSEO Darrow_forwardChlorite is reduced by bromide in acidic solution according to the following balanced equation: C10₂ (aq) + 4Br- (aq) + 4H+ (aq) → Cl(aq) + 2Br2 (aq) + 2H₂O (1) A[Br₂] If At A[C10₂] At during the same time interval? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. = 4.1x10-6 M/s, what is the value of A[C10₂] At Part B = O Rate = μA Value Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining Units What is the average rate of consumption of Br during the same time interval? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. μАA Value Units ? ?arrow_forwardSubstance AG°F (kJ/mol) FeO(s) -255.2 H2(g) Fe(s) H20(1) Pb(s) -237.2 02(g) H2SO4(aq) PbSO4(s) -744.5 -813.0arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781285199030Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781285199030Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781285199023Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781285199023Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199030
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199023
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133109655
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning


Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning