
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Approximate Vapor–Liquid–Liquid Equilibrium.
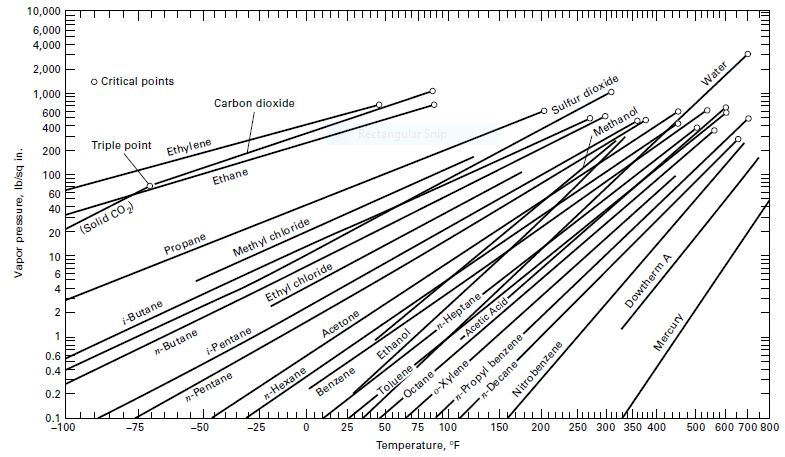
A mixture of 1,000 kmol of 75 mol% water and 25 mol% n-octane is cooled under equilibrium conditions at a constant pressure of 133.3 kPa from a temperature of 136oC to a temperature of 25oC.Determine: (a) the initial phase condition, and (b) the temperature, phase amounts, and compositions when each phase change occurs.Assume that water and n-octane are immiscible liquids. The vaporpressure of octane is included in Figure 2.3.
Transcribed Image Text:10,000
6,000
4,000
2,000
1,000
o Critical points
600
400
Carbon dioxide
200
Triple point
100
Ethylene
60
40
Ethane
20
Sulfur dioxide
(Solid CO,)
Water
10
Methanol
Propane
4
Methyl chloride
i-Butane
Ethyl chloride
0.6
0.4
n-Butane
i-Pentane
0.2
n-Heptane
Acetic Acid
Acetone
0.1
-100
n-Pentane
Ethanol
-75
п-Нехапе
Toluene
-Oc tane-
и
n-Propyl benzene
n-De cane
Benzene
-50
-25
o-Xylene-
25
50
75
Temperature, "E
100
150
luulinbinluulwuul
200
250 300 350 400
500 600 700 800
ШAL
Vapor pressure, Ib/sq in.
2.
Nitrobenzene
Dowtherm A
Mercury
ППTTT
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please answer sub-part d. Thank you so much.arrow_forwardTwo liquids A and B mix to form an ideal solution. Consider A to be the solvent (majority component) and B to be the solute (minority component). What is the relationship between the Gibbs energy and chemical potential for a pure phase? How does the Gibbs energy of A(solution) COmpare to Gibbs energy of Apure liquid)? How does the Gibbs energy of B(solution) compare to Gibbs energy of B(pure liquid)? d. When B is added to pure A, what happens to the Gibbs energy of A? а. b. C. e. Why does the Gibbs energy of the solvent of an ideal solution (in this case, A) decrease upon the addition of a solute (in this case, B)? Provide mathematical and conceptual explanations.arrow_forward5.20. Multistage stripper. A stripper at 50 psia with three equilibrium stages strips 1,000 kmol/h of liquid at 300°F with the following molar composition: 0.03% Cı, 0.22% C2, 1.82% C3, 4.47% nC4, 8.59% nC, 34.87% nCio. The stripping agent is 1,000 kmol/h of superheated steam at 300 F and 50 psia, Use the Kremser equation to estimate the com positions and flow rates of the stripped liquid and exiting rich gas Assume a K-value for Cio of 0.20 and that no steam is absorbed. Calculate the dew-point temperature of the exiting gas at 50 psia. If it is above 300°F, what can be done?arrow_forward
- 2. At a temperature of 400°C, the specific enthalpy of a water sample is 3100 KJ/kg. What is the phase of the water? a. Solid b. Solid-liquid mixture c. Subcooled liquid d. Saturated liquid e. Saturated mixture f. Saturated vapor g. Superheated vapor For the water in problem 2, determine the following: a. If saturated mixture calculate the quality, x = b. Determine the pressurearrow_forwardA Stirling cycle is a thermodynamic cycle similar to the Carnot cycle and is defined by the following processes. -> 2: Isothermal expansion -> 3: isochoric cooling -> 4: isothermal heating -> 1: isochoric heating Solve the graph for a Stirling cycle with the given information in which 50g of Ar (treated as an ideal gas) is isothermally expanded from 4L to 16L at a temperature of 700K. The sample is then undergoes isochoric cooling to 298K. The sample is then isothermally compressed to 3L and finally undergoes isochoric heating back to 700K.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The