
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The rib-joint pliers are used to grip the smooth pipe C. If the force of 100 N is applied to the handles, determine the state of stress at points A and B on the cross section of the jaw at section a–a. Indicate the results on an
element at each point.
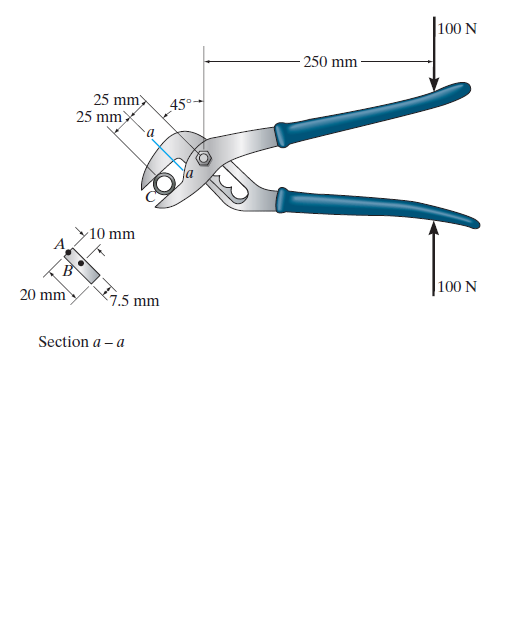
Transcribed Image Text:100 N
250 mm
25 mm>
25 mmx
45°
10 mm
20 mm
100 N
7.5 mm
Section a – a
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The wheel on a trolley is held in place on the leg using a 5-mm-radius pin. If the wheel is subjected to a normal force of 10 kN, determine the average shear stress in the pin. Neglect the friction force and assume the pin only supports the vertical 10-kN loadarrow_forwardThe solid bar has a diameter of 50 mm. The two forces and the torque Tx are acting at the origin of the x-y-z coordinate system which is coincident with the centroid of the cross-section of the bar; the 1800 N force is acting in the y-z plane and torque Tx is acting about the x-axis. Determine the state of stress at points A and B, and show the respective stress components acting on differential elements located at these two points. 200 mm/ y 200 mm 1200 N Tx = 40 N.m %3D 1800 Narrow_forward40 mm The yoke-and-rod connection is subjected to a tensile force of 5 kN. Determine the average normal stress in each rod and the average shear stress in the pin A 5 k between the members. 30 mm A 25 mm 5 kNarrow_forward
- 7-67. If the allowable shear stress for each of the 10-mm-diameter steel pins at A, B, and Cis Tllo - 90 MPa, and the allowable normal stress for the 13-mm-diameter rod is oalon - 150 MPa, determine the largest intensity w of the uniform distributed load that can be suspended from the beam. 1.2 m 0.3marrow_forward1.5 ft 5 ft 400 lb 300 lb 2 in. 2.5 in.- B Probs. 8–42/43 *8-44. Determine the normal stress developed at points A and B. Neglect the weight of the block.arrow_forwardThe 3/4-in.-diameter shaft is subjected to the loading shown. Determine the stress components at point A. Sketch the results on a volume element located at this point. The journal bearing at C can exert only force components Cyand Cz on the shaft, and the thrust bearing at D can exert force components Dx, Dy, and Dz on the shaft.arrow_forward
- Determine the maximum ram force P that can be applied to the clamp at D if the allowable normal stress for the material is sallow = 180 MPa.arrow_forwardThe sign is supported by a hollow structural tube of 15 in. outer diameter and 0.5 in. wall thickness. Given the weight and the design 3ft wind loading both acting at the center of the sign, determine the state of stress at points a and 6. Write cach state of stress in the form of a tensor, olserving the r-y-z coordinate system shown, and sketeh the stresses acting on a differential element at each point. s kips 3 kips 3 ft 3ftarrow_forward13-50. The C-frame is used in a riveting machine. If the force at the ram on the clamp at Dis P -8 kN, sketch the stress distribution acting over the section a-a. -200 mm- 10 mm 60 mm -10 mmarrow_forward
- The screw of the clamp exerts a compressive force of 500 lb on the woodblocks. Sketch the stress distribution along section a–a of the clamp. The cross section is rectangular, 0.75 in. by 0.50 in.arrow_forwardNeed helparrow_forwardDetermine the shortest distance d to the edge of the plate at which the force P can be applied so that it produces no compressive stresses in the plate at section a–a. The plate has a thickness of 10 mm and P acts along the centerline of this thickness.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY