
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
A 160 mm pipe branches into a 100 mm pipe and a 50 mm pipe, as shown in the figure. In both pipes, as indicated, they are made of hydraulic copper 30 m long, the fluid that circulates is water at 10°C.
Determine what the resistance coefficient K of the valve should be to obtain equal flow rates of 400 L*7min in each branch
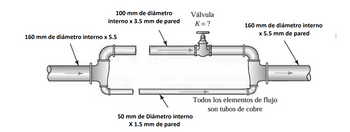
Transcribed Image Text:100 mm de diámetro
interno x 3.5 mm de pared
Válvula
K=?
160 mm de diámetro interno
x 5.5 mm de pared
160 mm de diámetro interno x 5.5
50 mm de Diámetro interno
X 1.5 mm de pared
Todos los elementos de flujo
son tubos de cobre
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 2. A nozzle 3 m long has a diameter of 1.3 m at the upstream end and reduces linearly to 0.45 m diameter at the exit. A constant flow rate of 0.12 m /sec is maintained through the nozzle. Find the acceleration at the midpoint of the nozzle. Hint: velocity at any point is equal to the flow rate divided by the area of the pipe at that point. [Ans. a=0.02579 m/s/s] 3. Water accelerates in an upward sloping pipe at a rate of 1.5 m/s?. The pipe slope is set at 40 degrees and has a length of 6 m. If the pressure is 63 kPa at section 1, what will be the pressure at section 2? [Ans. P2=16165.52 Pa] 1arrow_forwardFor the open tank, with piezometers attached on the side, containing two different immiscible liquids, as shown in Figure 1, find the total pressure at the bottom of the tank. (answer in kPa)arrow_forwardWater at 20°C is pumped at a rate of 15 L/s into a reservoir as shown in the Figure below. Between the pump and the reservoir is 150 m of 100 mm diameter PVC pipe, and the water surface elevation in the reservoir is 8 m above the centerline of the inflow pipe. The roughness height of the PVC pipe can be assumed to be negligibly small. Estimate the gauge pressure (kPa) on the downstream side of the pump. 15 L/s 133 120 111.7 131.5 Pump P - 150 m. 100 mm Reservoir 8marrow_forward
- PLEASE USE EQUATIONS ATTACHED 9.95. The mean velocity of water in a 150 mm horizontal pipe is 0.9 m/s. Calculate the loss of head through an abrupt con- traction to 50 mm diameter. If the pressure in the 150 mm pipe is 345 kPa, what is the pressure in the 50 mm pipe, neglecting pipe friction? K₁ from Table 2 for abrrupt contraction find Using work- energy equation Az A₂/A₁ C K₂ 21102392 A1 2.A? 81000.0 1J0321 to 19 1200 to find the pressure. 14 or. Mive stolwlog si/s919 mE.0 P but mop, +V² F 2 P₂ + Cup 2.10 erived one wolf 829) NINY 2.0 = 9 . TABLE 2 Contraction, C., and Loss, Kr, Coefficients for Abrupt Contractions 0 0.617 0.50 0.1 0.624 0.46 0.2 0.632 0.41 0.3 0.643 0.36 0.4 0.659 0.30 V₂² + Z₂ +h₁0/₂ 2 milyot has 9919 0.5 0.681 0.24 0.6 0.712 0.18 0.7 0.755 0.12 0.8 0.813 0.06 0.9 0.892 0.02 1.0 1.00 0arrow_forwardA cylindrical tank of water is 20 m in diameter and 3.5 m tall. There is a 1.0 cm diameter hole at the bottom from which water is leaking. A feeder pipe at the top of the tank, 4.0 m above the ground delivers water at a rate of 0.02 m/min. Ir the tank is initially half full, tal what is the water flow rate in m^3/sec from the top feeder pipe? (bi what is the pressure at the bottom of the tank? (Hint: Bernoul's principle) () what is the water speed at the bottom? (d) what is the leaking flow rate at the bottom? fe) at what rate is the volume of water changing? (Assume the tank is open to air at the top)arrow_forwarda=4 b=0 C=1arrow_forward
- A 25-mm-diameter pipe 35m long is used to convey oil. The oil has a density of 880kg/m³ and a kinematic viscosity of 0.25×10*m³/s. The discharge in the pipe is Q=24x10*m³/min. Given that the pipe is placed horizontally and there are no any minor losses. Determine the pressure drop between the entrance and exit of pipe.arrow_forwardthe marked answers are correct. Expalin the stepsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning